Embryo geometry drives formation of robust signaling gradients through receptor localization
Preprint posted on 11 December 2018 https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/12/11/491290
Article now published in Nature Communications at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12533-7
Polarity, geometry and patterning: an in vivo role for BMP receptor basolateral polarization and tissue geometry in robust embryonic patterning.
Selected by Diana PinheiroCategories: developmental biology
Background: Morphogens are long-range signaling molecules able to act in a concentration-dependent manner to induce cellular responses and elicit pattern formation during embryonic development and organ morphogenesis (reviewed in Sagner and Briscoe, 2017). BMPs , well-known morphogens, regulate several aspects of mouse post-implantation development, including germ cell differentiation and anterior-posterior patterning. In the early mouse embryo, BMP signaling requires BMP4 secretion by the extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE) into the pre-amniotic cavity, thereby inducing epiblast cells to differentiate into mesoderm (reviewed in Rivera-Pérez and Hadjantonakis, 2015). Previous work in human embryonic stem cell colonies (hESCs) implicated BMP receptor re-localization along the apical-basal axis as a critical mechanism regulating cellular responses to morphogen signaling and gastruloid self-organization (Etoc et al., 2016). Nonetheless, whether a similar mechanism occurs in vivo and whether it contributes to embryonic development and/or organ morphogenesis has remained largely unexplored.
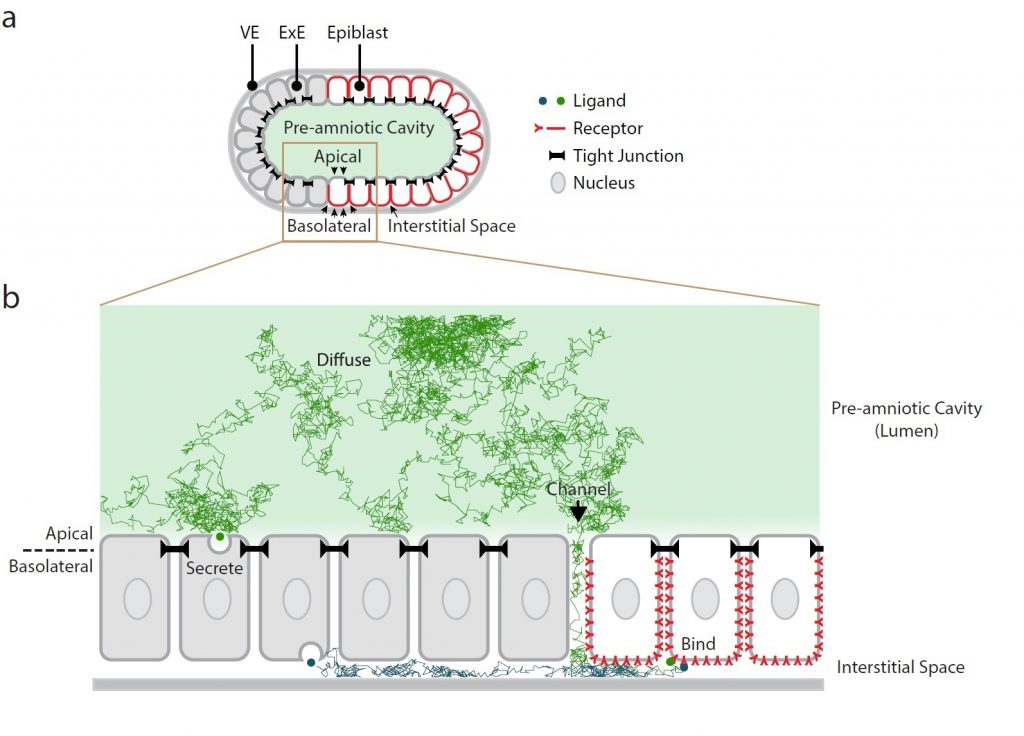
Key findings: Zhang and colleagues addressed this fundamental question in the early mouse embryo using a combination of mathematical modeling, embryological perturbation and microfluidics. The authors provide convincing evidence that BMP gradient establishment in the early mouse embryo requires basolateral localization of its receptors. This is corroborated by surface immunostaining of BMP receptors within the mouse epiblast, analysis of the proximal-distal gradient of phosphorylated SMAD1/5 (pSMAD1/5, BMP signaling downstream effectors), as well as by a perturbation assay showing that homogeneous distribution of BMP receptors along the apical-basal axis is sufficient to induce ectopic signaling in distal and anterior epiblast cells (which normally do not exhibit active BMP signaling). The authors propose that restricted accumulation of BMP receptors in epiblast cells limits their accessibility to BMP4 ligands to regions close to the epiblast edge. In this model, embryo geometry is therefore critical, as BMP4 ligands, secreted into the pre-amniotic cavity must diffuse through a channel between the ExE and proximal epiblast edge to reach the narrow interstitial space and bind the basolateral-localized BMP receptors in epiblast cells. Restricted ligand diffusion and preferential localization of BMP receptors within the epiblast therefore cooperate to generate a robust BMP signaling gradient from the proximal epiblast edge inwards, able to buffer strong fluctuations in BMP4 levels. In line with this, in BMP-soaked embryos, where dissected epiblast/visceral endoderm cups are exposed to uniformly high BMP4 ligand concentration, the pSMAD1/5 gradient is displaced only by a few cell widths as compared to wild type embryos. Overall, these findings support the importance of apical-basal receptor localization and geometrical constraints in shaping BMP signaling during embryogenesis.
Highlights: This study nicely builds upon recent observations in hESC colonies, so-called gastruloids due to their ability to recapitulate the embryonic arrangement of mammalian germ layers upon BMP4 stimulation (Etoc et al., 2016). This preprint now reports that also in vivo, in the early mouse embryo, BMP receptors localize preferentially to the basolateral membranes of epiblast cells. The authors propose that this preferential localization is sufficient to restrict receptor access to BMP4 ligands diffusing through the interstitial space between the epiblast and the underlying endoderm. Embryo geometry therefore plays a critical role in restricting ligand diffusion in vivo, as it regulates the time and distance a ligand can travel before encountering their cognate receptors. As a result, a BMP signaling gradient is established from the proximal edge of the mouse epiblast inwards. The main advantages of this system are: (a) its ability to generate patterning despite uniform ligand distribution and, (b) its potential to buffer large-scale variations in ligand concentration, since restricted diffusion ultimately limits dispersion of BMP4 ligands within the epiblast. Altogether, this elegant work sheds light on the interplay between BMP receptor polarization and tissue geometry during morphogen signaling and embryonic patterning.
Future directions: A critical aspect of the authors’ model is that embryo compartmentalization essentially acts as a diffusion barrier for BMP4 ligands. Although this is supported by fluorescein injections into the pre-amniotic cavity of early mouse embryos, it would be interesting to quantitatively probe the mechanisms of BMP4 transport/diffusion in vivo, using for example photobleaching experiments upon injection of fluorescently-tagged BMP4 ligands. Also, does the channel at the epiblast edge scale with embryo size? Could this contribute to buffer variability in patterning of different-sized embryos? Finally, this study highlights the importance of considering not only polarized ligand secretion, but also receptor localization and geometrical constraints when studying how morphogen signaling establishes robust embryonic patterning, still underexplored aspects in the field of Developmental Biology (Manukyan et al., 2017; Shyer et al., 2015).
preLighters Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello have also highlighted this preprint – check out their highlight here.
References:
- Etoc, F., Metzger, J., Ruzo, A., Kirst, C., Yoney, A., Ozair, M. Z., Brivanlou, A. H. and Siggia, E. D. (2016). A Balance between Secreted Inhibitors and Edge Sensing Controls Gastruloid Self-Organization. Dev. Cell 39, 302–315. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27746044
- Manukyan, L., Montandon, S. A., Fofonjka, A., Smirnov, S. and Milinkovitch, M. C. (2017). A living mesoscopic cellular automaton made of skin scales. Nature 544, 173–179. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28406206
- Rivera-Pérez, J. A. and Hadjantonakis, A. K. (2015). The dynamics of morphogenesis in the early mouse embryo. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7, a015867. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24968703
- Sagner, A. and Briscoe, J. (2017). Morphogen interpretation: concentration, time, competence, and signaling dynamics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 6, e271. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28319331
- Shyer, A. E., Huycke, T. R., Lee, C., Mahadevan, L. and Tabin, C. J. (2015). Bending Gradients: How the Intestinal Stem Cell Gets Its Home. Cell 161, 569–580. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25865482
Posted on: 17 January 2019
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.7259
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Alteration of long and short-term hematopoietic stem cell ratio causes myeloid-biased hematopoiesis
Temporal constraints on enhancer usage shape the regulation of limb gene transcription
OGT prevents DNA demethylation and suppresses the expression of transposable elements in heterochromatin by restraining TET activity genome-wide
preLists in the developmental biology category:
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)