Dynamics of PAR proteins explain the oscillation and ratcheting mechanisms in dorsal closure
Posted on: 18 July 2018
Preprint posted on 15 June 2018
Article now published in Biophysical Journal at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2018.10.014
Oscillations lead to commitment and union: modelling of PAR proteins and myosin recapitulates different dynamic features of dorsal closure in Drosophila
Selected by Yara E. Sánchez Corrales, Arnaud MonnardBackground
During Drosophila embryonic development, dorsal closure, i.e. the closure of an epidermal layer on amnioserosa cells, represents the last in a series of major morphogenetic changes (Jacinto et al. 2002). This morphogenetic event can be divided into three different stages depending on the dynamics of area reduction: early phase, slow phase, and fast phase (Figure 1C-D). During the early phase, the area of cells oscillates, but the tissue maintains its size. Subsequently, in the slow phase, the cells show oscillating apical constriction that gradually reduces the tissue area. Finally, in the fast phase, both the tissue and cells show persistent and rapid decreases in area.
Using exclusively mathematical modelling, Durney et al. replicate the dynamics of dorsal closure. Their model is able to account for autonomous cell oscillations and the transition through phases based on the dynamics of the PAR proteins and actomyosin.
Key findings
To model dorsal closure, the authors represented the amnioserosa tissue by a 2D vertex model in which a biochemical network is embedded and modelled as a set of differential equations (Figure 1A-B). The model is able to recover important aspects of dorsal closure from the dynamics of the PAR complex during the different phases:
Early phase: autonomous cell oscillations dominated by Myosin dynamics. Two types of negative feedback (Bazooka on aPKC and aPKC on actomyosin) are used in the model; these two types of feedback are used to demonstrate a cell-autonomous mechanism for the oscillation, with regulator “Ra” (an unknown but accounted regulator) playing a central role in the feedback mechanism.
Slow phase: ratcheting mechanism of cell area reduction. The model explains the actomyosin ratcheting by a finite availability of aPKC.
Fast phase: steady decrease in cell area without oscillations. In the model, the transition from the slow to the fast phase is triggered by the restriction of the availability of aPKC. The drop of aPKC relieves the negative feedback acting on Ra, thus promoting the assembly of Myosin and allowing the transition into the fast phase. The fast phase corresponds to the end of Myosin oscillations and instead a steady rise of Myosin translating into persistent contraction at a cellular and tissue level.
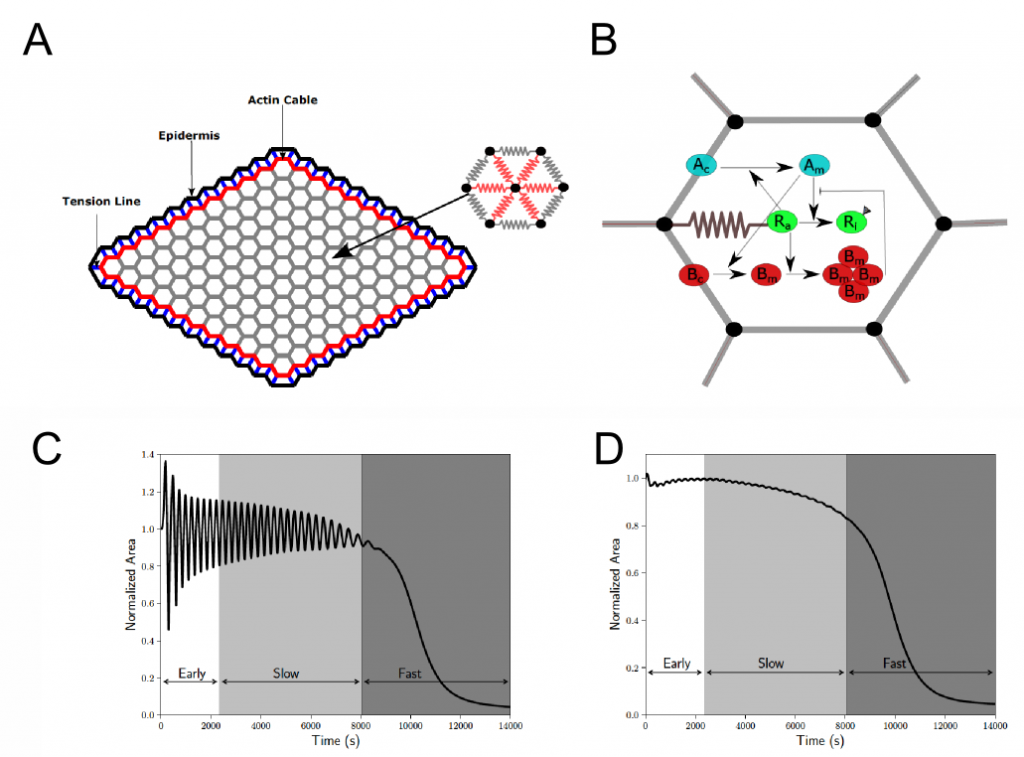
Figure 1. A) The amnioscerosa tissue is modelled as a grid of hexagonal cells. Each cell has 6 edges (grey) and 6 spokes (red) that respond elastically. The spokes also carry the active myosin force. B) Schematic summary of the biochemical network simulated in each cell (cyan: aPKC; green: a hypothetical Myosin regulator; red: Par3/Bazooka). C) Cell area dynamics of a single cell through different phases (early, slow and fast) of dorsal closure and D) tissue area dynamics. Panels A and B corresponds to Figure 1 of the preprint and panels C and D correspond to Figure 2 of the preprint.
What we like about this preprint and open questions
We found it very interesting that the authors were able to summarize in a predictive model the different dynamic features of dorsal closure (autonomous oscillations, ratcheting, and persistent contraction) using a set of differential equations based on a biochemical network.
The authors propose the existence of a factor “Ra” that links the kinetics of the Par proteins and the mechanics of actomyosin contraction. What might be the nature of this regulator? The authors proposed Rho kinase (Rok) as a candidate. Rok may indeed be a good candidate because it has been shown that phosphorylation by aPKC can remove it from the membrane (Ishiuchi and Takeichi, 2011) and Rok is able to phosphorylate Baz (Simões et al., 2010). However, to our knowledge, there are no reports on Rok recruiting aPKC from the cortex to the apico-medial domain.
Question: Which Myosin II regulator could recruit aPKC from the cortex to the apico-medial domain?
The model predicts that the available pool of aPKC is a crucial factor in regulating dorsal closure, thus changes in its levels will potentially lead to a change in the dynamics of the oscillations. An interesting experiment would be to modify the available levels of aPKC to experimentally validate this prediction. This could be achieved by overexpressing, knocking down (RNAi) and sequestering (trapping) of aPKC.
Question: According with the model, what effect could the changes in aPKC have in dorsal closure dynamics?
References
- Jacinto A, Woolner S, Martin P. Dev. Cell, 3 (2002), pp. 9-19. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00208-3
- Ishiuchi T, Takeichi M. Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 19;13(7):860-6. doi: 10.1038/ncb2274.
- Simões Sde M, Blankenship JT, Weitz O, Farrell DL, Tamada M, Fernandez-Gonzalez R, Zallen JA..Dev Cell. 2010 Sep 14;19(3):377-88. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.08.011.











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)