Maternal pluripotency factors prime the zygotic genome to respond to intercellular signals
Posted on: 25 July 2018
Preprint posted on 23 April 2018
The pioneers of pluripotency: Sox3/Pou5f3 unlock the chromatin for Xenopus ZGA
Selected by Claire Simon & Sophie MorganiBackground
How does a limited signaling toolkit encode the multitude of diverse outcomes required for development? Cells respond in a variety of ways to the same signal depending on which DNA regions are accessible to signaling mediators. Here, the authors show that the maternal transcription factors Pou5f3 and Sox3 remodel the chromatin landscape during zygotic genome activation (ZGA) in Xenopus. Sox and Pou factors are also implicated in zebrafish and mouse ZGA, emphasizing their conserved critical role in reprogramming and pluripotency.
What we like about this pre-print
We like the logical systematic approach taken in this work. By cross comparing binding site enrichment at genes activated during ZGA and proteomics data on oocytes, Gentsch and colleagues identify a shortlist of candidate regulators of this process that they can functionally test.
They find that the maternally provided transcription factors Pou5f3 and Sox3 facilitate the expression of a subset of genes at ZGA. Sox/PouV act as ‘pioneer factors’, binding to closed chromatin and are required for enhancer priming; increased chromatin accessibility, chromatin remodeling and enhancer-promoter interactions. Sox/PouV primed enhancers are competent for transcriptional activation of target genes in response to signaling cues at gastrulation. However, the pioneering activity of Sox/PouV is context specific, presumably dependent on the presence of differentially expressed binding partners expressed at various developmental stages and tissues.
Open questions
What makes a transcription factor a “pioneer” and what regulates its specificity?
How do pioneer factors interact with one another and is this context dependent?
While the opening of silenced chromatin by defined pioneer factor cocktails may improve reprogramming or transdifferentiation, are parallel methods needed to shut down the active somatic cell genes and avoid ‘confused’ cell types?
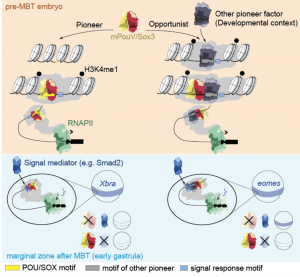
Model of pioneer-initiated chromatin remodelling 282 to facilitate the transcriptional response to signals during ZGA (Taken from Gentsch et al., 2018).
Further reading
- Iwafuchi-Doi, M. and K.S. Zaret, Pioneer transcription factors in cell reprogramming. Genes & Development, 2014. 28(24): p. 2679-2692.
- Zaret, K.S. and J.S. Carroll, Pioneer transcription factors: establishing competence for gene expression. Genes & Development, 2011. 25(21): p. 2227-2241.
Read preprint











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)