Antlions are sensitive to subnanometer amplitude vibrations carried by sand substrates
Posted on: 9 October 2018
Preprint posted on 1 October 2018
Article now published in Journal of Comparative Physiology A at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00359-020-01437-3
Antlion larvae hiding in their sand pits detect sand vibrations just a fraction of a nanometer in size. These vibrations inform the antlion of an approaching ant, and they respond by throwing sand to prevent prey from escaping their sand pits.
Selected by James FosterCategories: animal behavior and cognition
The Story
Most arthropods use some form of sensory hair to detect vibrations, and some species, among them scorpions and spiders, have been shown to use surface vibrations to detect approaching prey. Antlion larvae build conical pits in granular earth and bury themselves at the bottom, waiting for smaller insects to fall in—towards their waiting jaws. Antlion larvae are covered in sensory bristles that allow them to detect the vibrations of walking ants up to 20 cm away.
The Study
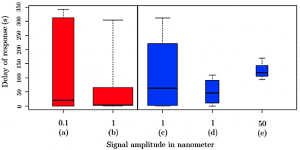
The surface vibrations produced by a walking ant are extremely small and remain in the sub-nanometer range while the ant is outside of the antlion’s pit. In this study the vibration patterns of a walking ant were recorded and ‘played back’ to antlion larvae at intensities ranging from 1/10 of a nanometer to 50 nanometers, using a piezoelectric transducer. Antlions have previously been shown to respond to nearby ants by throwing sand, after a delay that can amount to several minutes while the larva waits for its prey to get closer. This sand is thought to trigger and enhance tiny avalanches that hinder escape attempts. In this study, the authors show that not only can antlion larvae detect and respond to vibrations smaller than a nanometer, these sub-nanometer vibrations prime the larva to respond faster and more often to nanometer-scale vibrations—presumably because this pattern is indicative of an ant walking-towards and then falling-into their pit.
Questions
Might the rare and delayed responses to 50 nm stimuli suggest they are interpreted as larger, less appropriate prey?
Are these distinctive vibration patterns learnt or do the antlions have an inherent bias towards ‘ant-walking’ vibrations?
(photo credit: Vincent Lorent)

doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.5119
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the animal behavior and cognition category:
Cannibalism as a mechanism to offset reproductive costs in three-spined sticklebacks
Tina Nguyen
Morphological variations in external genitalia do not explain the interspecific reproductive isolation in Nasonia species complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae)
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
Trade-offs between surviving and thriving: A careful balance of physiological limitations and reproductive effort under thermal stress
Tshepiso Majelantle
preLists in the animal behavior and cognition category:
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Bats
A list of preprints dealing with the ecology, evolution and behavior of bats
| List by | Baheerathan Murugavel |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)