Single Cell Gene Expression Analysis Reveals Human Stem Cell-Derived Graft Composition in a Cell Therapy Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Posted on: 27 September 2019
Preprint posted on 5 August 2019
What's in my graft? Single-cell RNAseq comparison of fetal midbrain and stem cell-derived dopamine neuron progenitors transplanted into Parkinson's disease model rats shows many similarities and several COLorful differences!
Selected by Jessica XieCategories: neuroscience
Background
A multitude of reasons make Parkinson’s disease (PD) an ideal candidate disease for the development of cell replacement therapy. PD is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative diseases, and no disease-modifying treatments are currently available. The motor problems that characterize this disease are caused by the loss of a single, well-defined cell-type located in a single region: dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the mesencephalon (midbrain). Furthermore, the immune-privileged nature of the central nervous system reduces the issue of allograft tissue immunogenicity that may be problematic for the transplantation of other tissue/cell types.
The proof is in the pudding. For the past 30+ years, transplantation of fetal ventral mesencephalic (VM) cells has been greatly successful, with long-term graft survival of up to decades, as well as improved clinical outcomes for many patients (Li et al., 2016; Barker et al., 2013).
Alas, the use of fetal tissue for this purpose is impractical. Tissue supply problems meant that only 20 out of over 90 planned surgeries for the landmark TRANSEURO clinical trial actually took place (Barker et al., 2017); the ethical and logistical barriers preventing this need little further elaboration.
Recent advancements in in vitro differentiation techniques have provided an appealing alternative, commencing with the initial landmark discovery that VM dopaminergic neurons differentiated from human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived floor plate progenitors can rescue behavioral deficits in animal PD models (Kriks et al., 2011). Dopaminergic neurons and progenitors have also been produced through direct reprogramming, and from other cell-types such as astrocytes and fibroblasts (Arenas et al., 2015).
Nonetheless, most PD cell replacement therapy research has focused on optimizing the hPSC-derived directed differentiation of VM progenitors, for example by correlating the gene expression profile of in vitro hESC-derived VM progenitors with graft outcome following in vivo transplantation (Kirkeby et al., 2017). This previous work, which highlighted the need for FGF8b-induced caudalization and identified better molecular markers of the caudal VM, was another seminal collaboration between the Parmar and Perlmann labs.
However, one important question had yet to be thoroughly investigated: how does the molecular identity of transplanted hPSC-derived grafts compare to that of fetal grafts?
Key findings
The authors transplanted fetal VM or in vitro hESC-differentiated VM progenitors into rat striatum, then characterized mature grafted cells 6 months later by single-cell RNA-sequencing.
Several of the study’s findings were to be expected:
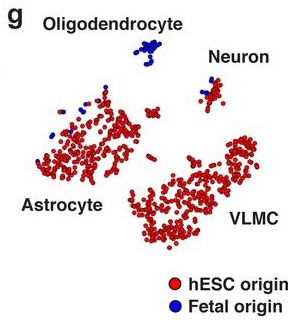
- Both fetal and hESC-derived VM mature grafts yielded cells identifiable as neurons and astrocytes [Fig. 2G].
- The proportion of proliferative cells decreased dramatically following engraftment and maturation, from about a quarter of fetal VM and a third of hESC-derived VM prior to transplantation to just over 1% post-transplantation [Ext. Fig. 3].
Some were a little surprising:
- Only fetal VM cells generated oligodendrocytes; no hESC-derived VM cells were identified in the cluster marked by high expression of OLIG1, OLIG2, NKX2.2, and SOX10 [Fig. 2C].
- Less than 10% of cells in both fetal and hESC-derived VM grafts segregated into the “neuron” cluster that expressed GAP43, TH, and NR4A2. As subsequent immunohistochemical analysis found the proportion of NeuN+ grafted cells to be about 70% (a figure more in accordance with previous work), the authors attribute this underrepresentation to the technical difficulty of dissociating and isolating mature neurons.
And one came completely unexpected:
- hESC-derived VM grafts contained a perivascular/fibroblast-like population whose gene expression profile most closely resembled that of vascular leptomeningeal cells (VLMC).
The authors confirmed—using multiple antibodies—that the protein COL1A1, which uniquely marks the VLMC cluster, is present in the graft [Fig. 2H].
They further verify the expression of COL1A1 in:
- grafts derived from other hESC and iPSC lines [Fig. 3A–D],
- grafts from cryopreserved hESC-derived VM progenitors [Fig. 3E] (of practical therapeutic relevance)
- in vitro cultures from several differentiation protocols, including 3D organoids [3G–J].
Importance of this work
While single cell RNAseq is undeniably becoming increasingly ubiquitous—even, as some may claim, overdone—it’s entirely justified here as an unbiased high-throughput approach to tackling this critical yet unaddressed question of cell identity, and indeed led to the identification of a surprising cell-type. This was followed up with extensive validation utilizing multiple antibodies, stem cell lines, and directed differentiation protocols, and will thus no doubt require further investigation: corroboration by other labs, as well as additional characterization. It will be critical to understand the implications of this finding for PD cell replacement therapy—perhaps, as the authors suggest, these VLMC-like cells may improve graft survival, maturation, and function.
Not to overlook the other findings though, in particular the promising features of hESC-derived VM progenitors: their transcriptomic resemblance to fetal VM following maturation, lack of proliferation, and lack of serotonergic neurons. The absence of oligodendrocytes in hESC-derived grafts also bears further study!
Questions
- Aside from showing capability to achieve functional rescue, how might one go about investigating the significance (if any) of the lack of oligodendrocytes in hESC-derived VM progenitors? (Point taken that it’s impossible to prove a negative!)
- Have you/the authors looked into staining for other VLMC molecular markers (other than COL1A1)? Showing colocalization of multiple defining markers might help to more conclusively establish this very striking finding!
- There are several single-cell RNAseq papers on in vitro PSC-derived neuronal (admittedly predominantly cortical) differentiation, but to the best of my knowledge, none have really made especial note of this fibroblast-like population. Might this somehow be a midbrain-or dopaminergic neuron-specific phenomenon—or might the authors have another explanation?
- I’m exceedingly curious about the developmental origin of this VLMC population, particularly its in vivo localization around blood vessels. Any speculations to share? Future plans for RNAseq at earlier timepoints, or pseudotime trajectory?
References
- Arenas, E., Denham, M., & Villaescusa, J. C. (2015). How to make a midbrain dopaminergic neuron. Development, 142(11), 1918–1936. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.097394
- Barker, R. A., Barrett, J., Mason, S. L., & Björklund, A. (2013). Fetal dopaminergic transplantation trials and the future of neural grafting in Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet Neurology, 12(1), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70295-8
- Barker, R. A., Parmar, M., Studer, L., & Takahashi, J. (2017). Human Trials of Stem Cell-Derived Dopamine Neurons for Parkinson’s Disease: Dawn of a New Era. Cell Stem Cell, 21(5), 569–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2017.09.014
- Kirkeby, A., Nolbrant, S., Tiklova, K., Heuer, A., Kee, N., Cardoso, T., … Parmar, M. (2017). Predictive Markers Guide Differentiation to Improve Graft Outcome in Clinical Translation of hESC-Based Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell, 20(1), 135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.09.004
- Kriks, S., Shim, J.-W., Piao, J., Ganat, Y. M., Wakeman, D. R., Xie, Z., … Studer, L. (2011). Dopamine neurons derived from human ES cells efficiently engraft in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature, 480(7378), 547–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10648
- Li, W., Englund, E., Widner, H., Mattsson, B., van Westen, D., Lätt, J., … Li, J.-Y. (2016). Extensive graft-derived dopaminergic innervation is maintained 24 years after transplantation in the degenerating parkinsonian brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(23), 6544–6549. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1605245113
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.14023
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the neuroscience category:
Imaging cellular activity simultaneously across all organs of a vertebrate reveals body-wide circuits
Muhammed Sinan Malik
Post-translational Tuning of Human Cortical Progenitor Neuronal Output
Jawdat Sandakly
Maturation of the glymphatic system confers innate resistance of the brain to Zika virus infection
Jimeng Li
preLists in the neuroscience category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)