Yersinia pestis genomes reveal plague in Britain 4,000 years ago
Posted on: 7 February 2022
Preprint posted on 26 January 2022
Tracing the plague route: Ancient DNA analysis reveals the presence of Yersinia pestis genome in individuals from Britain 4000 years ago
Selected by Niveda UdaykumarCategories: evolutionary biology, microbiology
Background
Ancient DNA analysis of extinct lineages has identified Yersinia pestis as the causal agent of the historical plague that spread through Asia and Central Europe five thousand to three thousand years before the present (BP). Yersinia pestis is a zoonotic bacterium that is transmitted through an infected flea vector, causing either bubonic or septicaemic plague1-3. One extinct lineage of this bacteria, Late Neolithic, and Bronze Age (LNBA) are believed to have spread to Central Europe through human populations migrating from Eurasian steppes. These bacteria lack the virulence factor ymt which enables survival and transmission in the midgut of the fleas, meaning it is most likely to have spread person-to-person via the respiratory route. This lineage of the plague is believed to have wiped out several European societies of the Late Neolithic Age1. Though there is evidence of plague observed in Bell Beaker archaeological complexes in present-day Germany, it is still unclear as to how the outbreak spread through Bronze Age Europe.3
In this preprint, Swali et.al., show the spread of LNBA plague to the north-western periphery of Europe by sequencing Yersinia pestis genomes from two individuals retrieved from an unusual mass burial site in Somerset, UK, approximately dating back to 4000 years cal BP (calibrated years before present), suggesting the spread of the plague to the Beaker complexes via Britain.
Key Findings
Dentine samples were taken from 16 individuals retrieved from a mass burial site in Somerset (Charterhouse Warren), England. Single-stranded DNA libraries were prepared from the powdered extracts of the dentine samples. This was followed by screening for DNA from the pathogen Yersinia pestis in the retrieved ancient DNA samples. Of the screened individuals, two samples, C10091 and C10098, showed a high number of sequences matches to the pathogen Yersinia pestis compared to the outgroup Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Further, radiocarbon dating of the dentine samples revealed that these two individuals were children between the ages of 10-15, had Beaker culture characteristics (an archaeological complex that links individuals from continental Europe with Britain), and existed at least 4100-3800 cal BP. Following carbon-dating, the libraries were subjected to hybridization by an in-solution target enrichment using RNA of Yersinia pestis as baits. The hybridization of the baits showed an average 1.5-2-fold average coverage of the Yersinia pestis genome in the individuals C10091 and C100098.
Phylogenetic analysis of 25 modern and ancient Yersinia pestis strains shows that the Charterhouse Warren Yersinia pestis genome falls in the cluster of strains from the Bronze Age period. Further, the genomes of C10091 and C10098 lacked a 32.4kb region and the presence of a unique 36kb region found in strains of Germany (post6), confirming the similarity of these genomes to the younger representatives of the LNBA lineages (Fig 1A and B).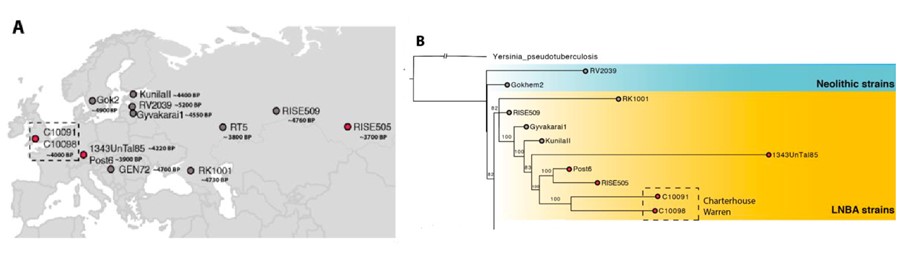
Fig 1-A: Geographical location of the individuals of the Charterhouse Warren site in Somerset, England. 1-B: Phylogenetic tree of Yersinia pestis lineage identified in the genomes of the individuals C10091 and C10098(Adapted from Fig 1, Swali et.al., 2022).
Functional analysis showed that the C10091 and C10098 genomes had all virulence factors except the ymt gene. Genes such as UreD, pde-2, and flhD associated with flea toxicity, downregulation of biofilm formation, and immune evasion were functional in the Charterhouse Warren genomes as well, suggesting that the deaths were not likely due to a plague outbreak.
Why did I choose to highlight this preprint?
I found the preprint to be an interesting read where the authors used modern approaches to deduce the cause/spread of an event of historical significance.
Questions to authors
- On what basis is an archaeological site chosen for analyses such as the one in this study?
- What are the challenges faced by you in carrying out such studies?
- How relevant/necessary do you think it is to carry out studies with combinations of historical and biological techniques/perspectives?
References
- Rasmussen, S. et al. Early divergent strains of Yersinia pestis in Eurasia 5,000 years ago. Cell 163, 571–582 (2015).
- Rascovan, N. et al. Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia pestis during the Neolithic Decline. Cell 176, 295–305.e10 (2019).
- Andrades Valtueña, A. et al. The Stone Age Plague and Its Persistence in Eurasia. Biol. 27, 3683–3691.e8 (2017).
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.31382
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the evolutionary biology category:
Morphological variations in external genitalia do not explain the interspecific reproductive isolation in Nasonia species complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae)
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Dissecting Gene Regulatory Networks Governing Human Cortical Cell Fate
Manuel Lessi
Also in the microbiology category:
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
Citrobacter rodentium infection activates colonic lamina propria group 2 innate lymphoid cells
André Luiz Amorim Costa, Marcus Oliveira
preLists in the evolutionary biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment', organised at EMBL Heidelberg, Germany (May 2023).
| List by | Girish Kale |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
Also in the microbiology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)