Diverse mechanisms for epigenetic imprinting in mammals
Posted on: 18 June 2021 , updated on: 21 June 2021
Preprint posted on 30 April 2021
Genomic imprinting in mammals: the extraembryonic lineage expands its epigenetic-based toolbox to regulate imprinting
Selected by Sergio MencheroCategories: genetics
We, as mammals, have two copies of all autosomal genes and in most cases, those genes are expressed from both copies (alleles). Each of these copies is inherited from each of our parents. In very few cases, some genes are expressed from only one of the copies, in a conditioned termed mono-allelic expression. For mono-allelically expressed genes, these genes are already marked with a silencing imprint in one of the copies when the newly formed zygote inherits the genetic material. As a consequence, they will be only expressed from the other, non-silenced, allele. The phenomenon of inherited allelic silencing is known as genetic imprinting.
Genomic imprinting is established and maintained thanks to different epigenetic mechanisms. DNA methylation was the first epigenetic modification identified to be able to pass from the germ cells to the embryos. More recently, the transmission of histone modifications (specifically H3K27me3) from the oocyte to the embryo was described as a non-canonical imprinting mechanism (Inoue et al. 2017). Non-canonical imprinting seems to be a mechanism particularly enriched in the regulation of placental-associated genes (Chen et al. 2019; Hanna et al. 2019).
In this preprint, the authors investigate allele-specific expression in E6.5 mouse embryos both in the epiblast (the embryonic lineage) and in the extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE, the extraembryonic lineage that will form the placenta). After the identification of all the imprinted genes in both lineages, the authors perturbed several epigenetic pathways to understand which of them affect the allele-specific expression of imprinted genes. This systematic approach allowed them to conclude that while the imprinted genes in the epiblast are mainly regulated by DNA methylation, a wider diversity of epigenetic mechanisms regulate genomic imprinting in placenta progenitor cells.
Key findings
- Mapping imprinted genes in E6.5 mouse embryos. The authors performed RNA-seq of epiblast and ExE in E6.5 mouse embryos harvested from highly polymorphic mouse strains (in reciprocal crosses). They found 22 imprinted autosomal genes in the epiblast and 41 in the ExE (19 of them were shared between lineages). They also analysed the behaviour of X-linked genes in females in more detail given that X-chromosome inactivation is imprinted in the ExE. Most of the X-linked genes (~86%) were maternally expressed as expected, but they also found some genes that escaped X-inactivation. Some of them did it independently of the mouse strain, while others behaved in a strain-specific manner.
- Disruption of key epigenetic pathways in zygotes. The authors performed Cas9-based genetic editing to disrupt the following genes:
- Dnmt1: affecting DNA methylation
- Ehmt1/Ehmt2: affecting H3K9 methylation
- Rnf2: affecting PRC1 (H2AK119ub)
- Eed: affecting PRC2 (H3K27me3)
The authors then performed RNA sequencing in epiblast and ExE samples of mutant E6.5 embryos to examine allelic-specific expression of the previously identified imprinted genes.
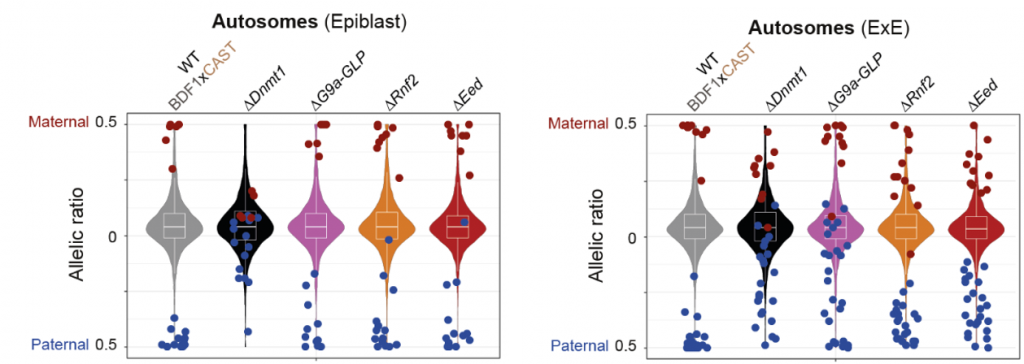
- Imprinted genes in the extraembryonic lineage are regulated by a wider set of epigenetic mechanisms. Most autosomal imprinted genes gained bi-allelic expression in the epiblast after disruption of Dnmt1 (14 out of 19) (Fig 1). Something similar happened in the ExE when they analysed Dnmt1 mutant embryos (20 out of 37 gained bi-allelic expression). However, other genes gained bi-allelic expression when disrupting other epigenetic pathways specifically in the ExE. Ehmt1/Ehmt2 regulate a set of paternally imprinted genes while Rnf2 and Eed regulate some maternally imprinted genes (Fig 1). It is remarkable that from the 24 paternally imprinted genes in the ExE, 12 of them are dependent on Ehmt1/Ehmt2 and these had been identified as non-canonical imprinted genes.
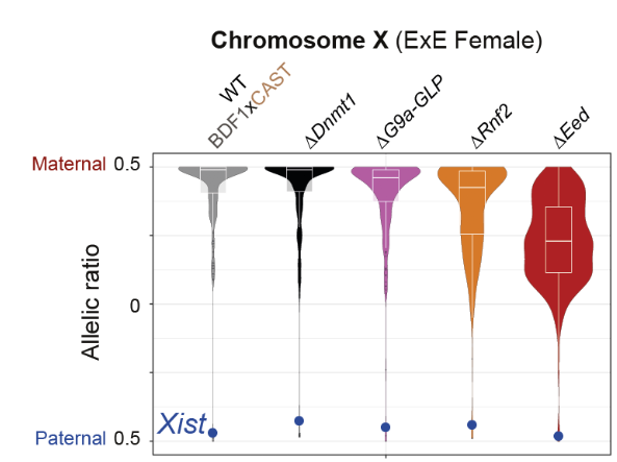
- Polycomb regulates imprinted X-linked genes in the extraembryonic lineage. The authors then pay attention to the regulation of the X-chromosome in the ExE of female embryos. Out of 180 maternally expressed X-linked genes in the ExE, around 65% lost their allele-specific expression when one of the Polycomb complexes was disturbed (particularly PRC2). Interestingly, Xist, the master regulator of X-inactivation which is expressed from the paternal allele, did not lose its allele-specific expression in any of the mutants. Finally, the authors found that the X-linked genes that are not affected by PRC associated disruptions are localised in specific clusters along the X chromosome.
Why I chose this preprint
I find very interesting and intriguing how some genes need to be expressed in an allele-specific manner. And even more intriguing the fact that to achieve that, the epigenetic marks that act as imprints need to survive to a whole genome epigenetic reprogramming during the early stages of development in mammals.
The emergence of a placenta and the phenomenon of genetic imprinting are features that characterise mammals. Thus, I quite liked that the authors separate the embryonic and the extraembryonic lineage to investigate how genomic imprinted is regulated. It seems clear that we cannot assume a similar behaviour in different tissues, and the placenta behaves in a very interesting manner.
This work adds a new framework to the genetic imprinting field, which has been enriched in the last few years with the findings of non-canonical imprinting and still leaves many open questions to be addressed in future studies.
Questions to the authors
- It is very interesting how many identified non-canonical imprinted genes were de-regulated in Ehmt1/Ehmt2 mutant embryos. I had understood that H3K9me3 marks were usually more associated with DNA methylation than H3K27me3 marks. Since it has been shown that many non-canonical imprinted genes that are first independent of DNA-methylation are then regulated by DNA-methylation (Chen et al. 2019), do you think this regulation by Ehmt1/Ehmt2 is a transient state between H3K27me3 and DNA methylation? Or could it be co-regulating together with H3K27me3?
- In general, histone-based silencing mechanisms are considered more reversible than DNA methylation. Do you think the regulation of imprinted genes during placenta development could need more reversible mechanisms that could explain why it depends on a higher number of epigenetic pathways and not just DNA methylation? Or could it have just evolved differently in this tissue?
- It is noticeable that one of the genes whose expression is not affected by any of the perturbations you assessed is Xist. Would you speculate some type of cooperation between pathways that could make its regulation more robust?
References
Chen et al (2019). Allelic H3K27me3 to allelic DNA methylation switch maintains noncanonical imprinting in extraembryonic cells. Sci. Adv. 5, eaay7246.
Hanna et al (2019). Endogenous retroviral insertions drive non-canonical imprinting in extra-embryonic tissues. Genome Biol. 20, 225.
Inoue et al (2017). Maternal H3K27me3 controls DNA methylation-independent imprinting. Nature 547, 419–424.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.29610
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the genetics category:
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
VANGL2 shapes the mouse heart tube from adjacent epithelia and without planar polarity
Anubhav Prakash
preLists in the genetics category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)