Differential mosquito attraction to humans is associated with skin-derived carboxylic acid levels
Posted on: 15 January 2022 , updated on: 19 December 2022
Preprint posted on 5 January 2022
Article now published in Cell at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.034
The answer to a buzzing question: Why are some people more attractive to mosquitoes than others?
Selected by Kristina KuhbandnerCategories: animal behavior and cognition, neuroscience
Updated 25 October 2022 with a postLight by Kristina Kuhbandner
This preprint by De Obaldia and colleagues from the Vosshall lab was published in Cell (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.034) on 18 October 2022. Congratulations to all contributors!
The published version of the article did not undergo any substantial changes compared to the preprint posted on bioRxiv in January 2022. One obvious change is that the paragraphs and the associated figures (Figures 2 and 3 in the preprint) about the effect of Onco and Ir8a receptor mutations – both do not impair the ability of mosquitoes to differentiate individual humans – were summed up to make the results more concise. Furthermore, a section dealing with the “Limitations of the study” was added to the discussion. Here, the authors first point out that their findings do not demonstrate a direct causality between skin carboxylic acids and the attractiveness of individuals to mosquitoes. This would require evidence for necessity and sufficiency of these compounds which, at the moment, is extremely difficult to prove. Then, they emphasize that this study only focuses on compounds containing carboxylic acid groups; therefore, other chemical substances in human skin odor might play a role as well. Lastly, they mention that it remains unclear whether carboxylic acids or more volatile derivatives thereof are also involved in differential mosquito attraction to humans across long distances. The open questions raised in this preLight were not mentioned in this paragraph.
Overall, the implemented changes make the article even more concise, and I am excited to see how this work will contribute to the identification of mosquito magnets and the development of new intervention strategies to prevent the spread of pathogens caused by mosquitoes in the future.
Background
Mosquito bites are not only unpleasant, but can pose severe health risks from viral infections including Zika or dengue fever. It is well known that some humans are more often the target of these insects than others (1). But what distinguishes these “mosquito magnets” from less preferred persons? To date, it is assumed that the differences are caused by variation in individual skin odors produced by humans, which are often linked to their unique skin microbiota (2). Interestingly, besides a heritable component, individuals can also become more attractive, for example following malaria parasite infection or beer consumption (3, 4). However, the specific chemical mechanism contributing to “mosquito attractiveness” is not known yet.
In their study, De Obaldia and colleagues clear up the myth of “sweet blood” by determining the differences in skin odor components between highly and weakly attractive humans. Furthermore, they shed light on the mosquitoes’ sensory pathways involved in the attraction to preferred individuals.
Main findings
- Mosquitoes strongly prefer some individuals over others
Initially, De Obaldia et al., compared the “attractiveness” of different individuals to female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. They assessed mosquito preferences between the forearm skin odor collected on nylon sleeves of eight human probands using an adapted two-choice olfactometer (Fig. 1). By applying an attraction score system, they ranked the subjects from most to least attractive, with the most attractive subject being 100 times more attractive than the least attractive subjects. Of note, these preferences were stable over several months indicating that differences in skin odor remain consistent for long time periods.
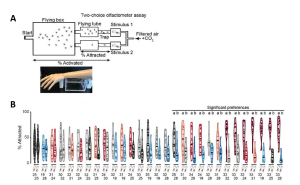
Figure 1 (A) Top: Illustration of the two-choice olfactometer setting: a mixture of air and CO2 was blown over each stimulus to carry volatile odors to mosquitoes downwind. Mosquitoes flew upwind and those that reached one of the two traps in front of a stimulus were scored as “attracted”. Bottom: Picture of a model forearm on top of the stimulus box in the two-choice olfactometer. (B) Pairwise comparison of attractiveness of human-worn nylons to wildtype mosquitoes. Numbers on the x-axis indicate the subjects tested in the two-choice olfactometer assay (adapted from Fig. 1 De Obaldia et al., 2022, made available under a CC-BY 4.0 International license).
- Highly attractive humans have elevated levels of carboxylic acids
In the following, differences in the chemical composition of the skin odor between highly and weakly attractive individuals were assessed by gas chromatography/quadrupole time of flight-mass spectrometry (GC/QTOF-MS). This analysis revealed that highly attractive individuals produce increased levels of carboxylic acids. This class of organic acids typically contains a carboxyl group (C(=O)OH) attached to an R-group and includes among others fatty acids, amino acids and keto acids.
- Mosquitoes are equipped with a highly redundant and efficient sensory system
Mosquitoes detect olfactory cues with the help of odorant (ORs) and ionotropic receptors (IRs), which are both odor-gated ion channels. While ORs are mainly involved in sensing esters, alcohols and ketones, IRs bind carboxylic acids and amines (5). Mosquitoes lacking the OR co-receptor Orco were impaired in their ability to detect specific odors, but could still distinguished highly and weakly attractive individuals. Strikingly, mutating either of the IR co-receptors Ir8a, Ir25a, and Ir76b strongly affected the mosquitoes’ overall attraction to human scent but also maintained the ability to differentiate highly and weakly attractive people. This suggests the evolution of highly redundant sensory pathways which allow mosquitoes to detect attractive individuals even in the presence of severe genetic disruption of the olfactory system.
Why I chose this preprint
All of us might already have asked ourselves the question why some people are more attractive to mosquitoes than others. Although olfactory cues in human skin odor seem to play a major role, not much is known about the specific chemical mechanism. In their study De Obaldia et al. identify carboxylic acids as a class of compounds that are very likely to contribute to the “attractiveness” of an individual. Furthermore, their investigation of the sensory pathways involved allows us to perceive the redundancy and high effectivity of the mosquitoes’ olfactory system, which have evolved in a fascinating evolutionary process. Ultimately, this knowledge can help to develop more effective strategies to protect “mosquito magnets” from mosquito bites and prevent the spread of diseases caused by these insects.
Questions
- As pointed out, due to limited sample size, human subjects were not further divided into subgroups regarding demographic factors such as sex and age, or other factors like dietary habits. Nevertheless, did you notice any striking features distinguishing highly from weakly attractive individuals, for example were there obvious gender or age differences?
- Given that microbiota play a key role in the production of skin odor, are you planning to map the skin microbiome of highly and weakly attractive individuals to identify strains associated with increased carboxylic acid production?
References
- Qiu, Y. T., et al. “Interindividual variation in the attractiveness of human odours to the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae ss.” Medical and veterinary entomology3 (2006): 280-287.
- Verhulst, Niels O., et al. “Composition of human skin microbiota affects attractiveness to malaria mosquitoes.” PloS one12 (2011): e28991.
- De Moraes, Consuelo M., et al. “Malaria-induced changes in host odors enhance mosquito attraction.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences30 (2014): 11079-11084.
- Lefèvre, Thierry, et al. “Beer consumption increases human attractiveness to malaria mosquitoes.” PloS one3 (2010): e9546.
- Benton, Richard, et al. “Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila.” Cell 136.1 (2009): 149-162.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.31274
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the animal behavior and cognition category:
Cannibalism as a mechanism to offset reproductive costs in three-spined sticklebacks
Tina Nguyen
Morphological variations in external genitalia do not explain the interspecific reproductive isolation in Nasonia species complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae)
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
Trade-offs between surviving and thriving: A careful balance of physiological limitations and reproductive effort under thermal stress
Tshepiso Majelantle
Also in the neuroscience category:
Electrophysiological correlates of conscious experiences during sleep: Lucid dreams, sleep paralysis, out-of-body experiences, and false awakenings
uMontreal Neuro preLighters et al.
PPARδ activation in microglia drives a transcriptional response that primes phagocytic function while countering inflammatory activation
Isabel Paine
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
preLists in the animal behavior and cognition category:
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Bats
A list of preprints dealing with the ecology, evolution and behavior of bats
| List by | Baheerathan Murugavel |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Also in the neuroscience category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (1 votes)
(1 votes)