Automated continuous evolution of proteins in vivo
Posted on: 27 April 2020
Preprint posted on 22 February 2020
Article now published in ACS Synthetic Biology at http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00135
Evolution in a test tube: orthogonal replication plus automated feedback control allows for continuous evolution in live cells.
Selected by Pavithran RavindranCategories: bioengineering, synthetic biology
Background
Engineering of enzymes and other biological materials has been a central problem for bioengineering for over a dozen years. The advent of directed evolution has allowed for engineers to screen through an unprecedented number of variants and better understand the sequence to function relationship of these molecules1. However, screens to find which variants are capable of a desired outcome and multiple rounds of ex vivo mutagenesis limit such efforts. An evolution on the current methods would allow one to simultaneously vary a protein of interest in vivo and then screen for functionality. In this work, the authors decide to tackle exactly this problem and have invented a method they call ACE: automated continuous evolution.
Key Findings
In this preprint, the authors set out to develop a method to evolve proteins in live cells using the advantages of feedback control. In a beautiful collaboration, two groups that independently made advances on this problem came together to invent a technology that absorbs the best features of their respective systems. The Liu group recently created OrthoRep, which is a system for targeted, in vivo mutagenesis of a gene of interest2. Essentially, they use a error-prone, orthogonal DNA polymerase-plasmid pair to mutate genes of interest in yeast achieving a 100,000 fold increase in mutation rate to drive accelerated evolution. The Khalil group developed eVOLVER which is a continuous culture platform that allows one to control multiple parameters and apply selective pressures using feedback control and real-time monitoring of growth speeds3. Because this system is completely automated, the system does not need to rely on a priori selection schedules or algorithmic selection routines that can drive the culture to an oscillatory growth regime or overshoots leading to culture extinction. In the ACE system, the authors set up eVOLVER to have two media inputs: (1) ‘no selection’ base media and (2) ‘full selection’ media that had maximum amount of drug or no nutrient. The system then would read out the OD of the culture and appropriately mix the two input medias to apply a constant pressure to drive the growth of the culture to a specific OD using a closed loop proportional-integral-derivative controller (Fig 1).
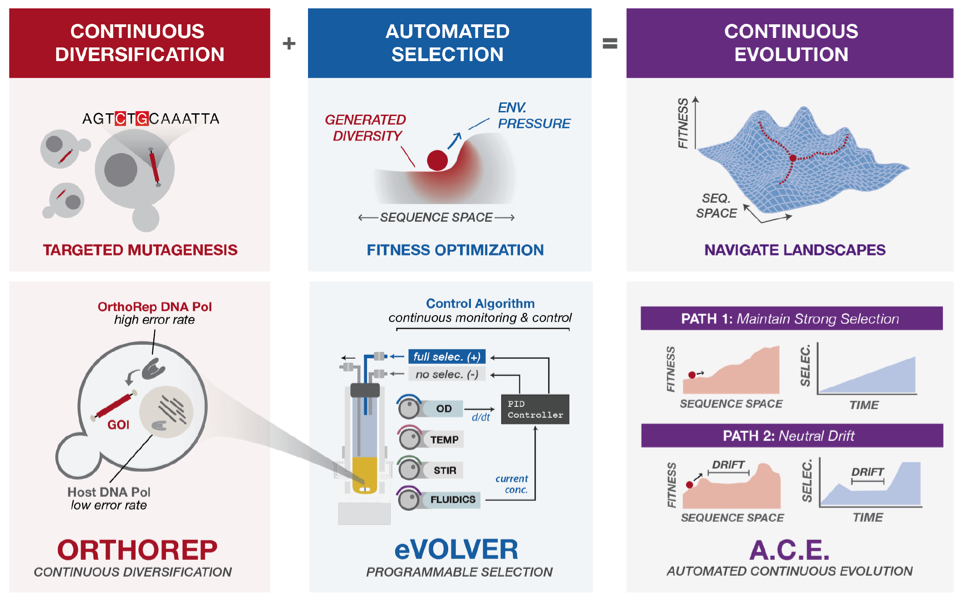
As a first test, the authors wanted to evolve Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase (PfDHFR) to get drug resistance to pyrimethamine. To accomplish this, the authors encoded PfDHFR on OrthoRep in yeast that needed this protein for survival. They then found put these cells in eVOLVER that kept the growth of the cells at a target growth rate, thus maintaining constant strong selection pressure by the drug, causing rapid mutations to build up on the PfDHFR protein. After ~550 hours of ACE, five of the six replicates adapted to the highest possible concentration of the drug and the PfDHFR variants had converged upon known resistance mutations due to the high mutation rate of OrthoRep. The authors then chose to evolve a thermophilic Thermotoga maritime HisA enzyme to function in yeast at moderate temperatures. TmHisA is an enzyme important for histidine biosynthesis but does not complement the loss of the yeast ortholog HIS6, likely due to the thermophilic nature of the original host organism. To evolve this thermophilic protein into a mesophilic one they encoded TmHisA on OrthoRep in yeast that lack HIS6. With 600 hours of ACE, four independent replicates were able to grow in media completely lacking histidine meaning OrthoRep had once again mutated the TmHisA in a manner that allowed for the protein to function at a mesophillic condition. They found that the replicates had between 6 and 15 mutations to allow this protein to function under these conditions. This shows that ACE is durable enough to handle much more complex fitness landscapes and effectively navigate this to evolve proteins with interesting properties.
Why I chose this preprint
Directed evolution is an amazing tool that allows researchers to evolve proteins for specific novel properties. Sadly, the method for such a method typically involves multiple rounds of PCR to mutate the sequence of the protein, cloning to put the DNA into an expression vector, transformation into host organism of interest and finally screening. This leads to a time-intensive methodology that is limited. Here, the authors have developed a method to have completely hand-off evolution of proteins. An added benefit is that the enzymes are simultaneously screened for the ‘best’ variants in vivo for function. It will be very interesting to see how the authors and others are able to take this system to novel proteins for evolution and screen for more complex fitness landscapes and phenotypes.
Questions for the authors
- ACE looks like an amazing system for the evolution of proteins in yeast. How does this system compare to/is this different from other continuous evolution systems like PACE4?
- In this manuscript you have shown how well this system works for the evolution of proteins in yeast. With the interest in “smart-drugs”, what do you think the limitations are to moving this sort of system to mammalian cells?
References
- Arnold, F. H. Directed Evolution : Bringing New Chemistry to Life. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 57, 4143–4148 (2018).
- Ravikumar, A. et al. Scalable , Continuous Evolution of Genes at Mutation Rates above Genomic Error Thresholds Resource Scalable , Continuous Evolution of Genes at Mutation Rates above Genomic Error Thresholds. Cell 175, 1946–1957.e13 (2018).
- Wong, B. G., Mancuso, C. P., Kiriakov, S., Bashor, C. J. & Khalil, A. S. Precise , automated control of conditions for high- throughput growth of yeast and bacteria with eVOLVER. 36, (2018).
- Esvelt, K. M., Carlson, J. C. & Liu, D. R. A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules. Nature 472, 499–503 (2011).
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.19562
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioengineering category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages modify development of human kidney organoids
Theodora Stougiannou
Matrix viscoelasticity regulates dendritic cell migration and immune priming
Roberto Amadio
Also in the synthetic biology category:
Enzymatic bromination of native peptides for late-stage structural diversification via Suzuki-Miyaura coupling
Zhang-He Goh
Enhancer cooperativity can compensate for loss of activity over large genomic distances
Milan Antonovic
Discovery and Validation of Context-Dependent Synthetic Mammalian Promoters
Jessica L. Teo
preLists in the bioengineering category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Advances in microscopy
This preList highlights exciting unpublished preprint articles describing advances in microscopy with a focus on light-sheet microscopy.
| List by | Stephan Daetwyler |
Also in the synthetic biology category:
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Advances in Drug Delivery
Advances in formulation technology or targeted delivery methods that describe or develop the distribution of small molecules or large macromolecules to specific parts of the body.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |











 (1 votes)
(1 votes)