Bacteriophage resistance alters antibiotic mediated intestinal expansion of enterococci
Posted on: 30 January 2019 , updated on: 31 January 2019
Preprint posted on 26 January 2019
Article now published in Infection and Immunity at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00085-19
Resistance is futile: Phage therapy used with antibiotics to combat enterococci in a dysbiotic microbiota
Selected by Yasmin LauCategories: microbiology, molecular biology
Background
The use of viral phages is a customary method for the treatment of bacterial infections, such as those responsible for systemic infections and bio-film formations. This technique utilises a membrane protein on the phage cell surface which binds to bacterial receptors; this subsequently allows for the “hijacking” of bacterial system as a means to produce progeny (1). In the case of the bacteria E. faecalis, a species of enterococci attributed to vancomycin resistance, only the PIP(EF) (Phage infection protein of E. faecalis) has been identified as a target receptor for phage treatment to date. The expansion of the repertoire of target phage receptors for E. faecalis, as well as many other bacteria species, forms the cusp of overcoming the ever-emerging dilemma of antibiotic resistance. In this preprint, through a library of phages, the authors demonstrate that the development of phage resistance through mutations in polysaccharide biosynthesis genes compromises insensitivity towards antibiotics targeting the cell wall.
Key Findings
The mutation of the epa (enterococcal polysaccharide antigen) gene in phage resistance and adsorption
The first key finding is the promotion of phage resistance through the mutation of the enterococcal polysaccharide antigen gene. A collection of 19 different phages were used to treat phage-resistant mutant strains of E. faecalis which showed a broad range of host range variability. 5 of these, in which 2 displayed narrow host ranges and 3 with broad host ranges, were further examined with transmission electron microscopy to observe any differences in structural features, as seen in Figure 1. Following genome sequencing of phage-resistant mutants selected with specific phages, it was found that for all mutants, even with differing selection, contained mutations in the epa gene. This gene encodes for a cell surface polysaccharide containing rhamnose (2).
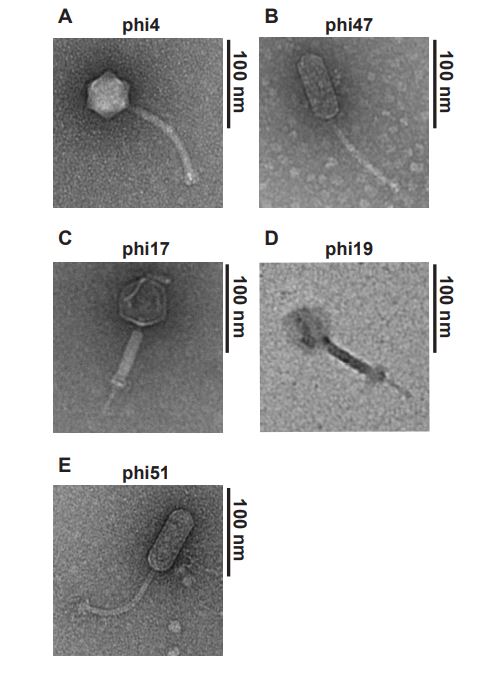
Figure 1: Transmission electron microscopy reveals diverse structural features of phages that display different host range variabilities.
Furthermore, the specific variable genes of epa, epaS and epaAC, were found to confer resistance against most phages in the library upon confirmation through observing growth phenotypes of mutants with deleted isogenic epaS and epaAC. The growth assays of these were compared to those of the isolated mutants (through phage selection) in the previous host range variability assay, in which the deletion strains and the isolates both showed highly similar phenotypes.
It was further iterated that structural changes in the cell wall is essential for unsuccessful phage adsorption, and thus infection, upon observation of the treatment of epaS and epaAC deletion strains compared to wild-type strains. Here, phage adsorption was found to be much higher in wild-type strains than those in both genotyped and resistance-isolated mutants.
Mutations in epa variable genes cause modifications in cell surface and increase cell wall susceptibility towards antibiotics
Next, the genotyped epaS and epaAC delete mutants were compared to a wild-type strain upon treatment with the antibiotics vancomycin and daptomycin. As seen in Figure 2, epaS mutants showed higher susceptibility towards both antibiotics significantly compared to wild-type at varying concentrations. This behaviour is also seen in epaAC mutants albeit showing less sensitivity compared to the former. This emphasises that both epaS and epaAC genes are key players in the biosynthesis of cell wall components to maintain integrity against antibiotic treatment.
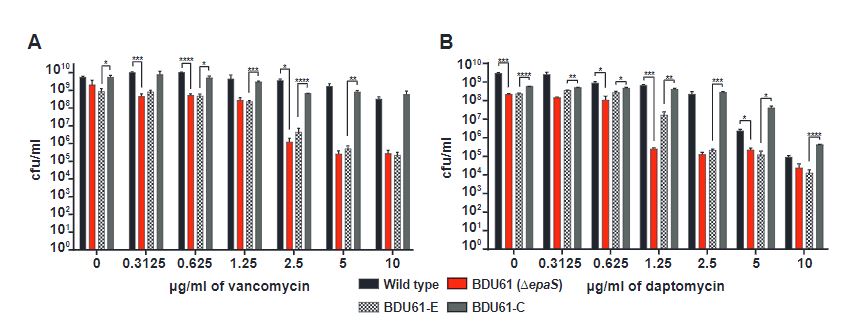
Figure 2: EpaS and epaAC mutants show increased susceptibility towards vancomycin and daptomycin compared to wild-type.
The epaS gene is required for the inheritance of E. faecalis from mothers to new born mice
Using mother mice infected with both wild-type and EpaS mutant E. faecalis, the extent of transmission of the bacteria from mother to new born mice was tested. Levels of the bacteria were measured in the faeces of both mother and new born, and significantly less EpaS mutants were found after 3 weeks post-birth (Figure 3). This implicates that in addition to antibiotic resistance, the epaS variable gene also plays an important role in colonisation ability.
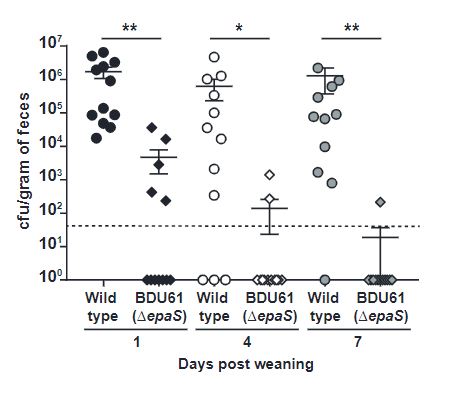
Figure 3: The EpaS gene is important for the transmission and colonisation of E. faecalis from mother to new born mice.
Why I like this preprint
This preprint provides a promising and elegant potential solution to antibiotic resistance. The way in which targeting a specific bio-synthetic pathway by exploiting mutations in a gene cluster such as the EpaS and EpaAC in the epa gene, could disarm the resistance towards cell wall antibiotics is interesting. In addition to cell-wall components and structural integrity, the identification of mutations of genes encoding for other biosynthetic pathways could also be useful in re-sensitising bacteria towards antibiotics which target those specific pathways. This approach discloses many possibilities, considering the plethora of phage cocktails, as well as species of bacteria, that could be investigated further.
Questions
1. In addition to the epa gene cluster, have there been other genes implicated whose mutation(s) also confer increased sensitivity towards antibiotics with increase phage resistance?
2. Considering the main stages of phage infection of bacteria, could it be possible for the subsequent stages of infection (host-receptor engagement and DNA replication) to also be compromised, and therefore targeted by certain antibiotics?
References
1. Lin, D., Koskella, B. and Lin, H. (2017). Phage therapy: An alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8(3), p.162.
2. Xu, Y., Murray, B. and Weinstock, G. (1998). A Cluster of Genes Involved in Polysaccharide Biosynthesis from Enterococcus faecalis OG1RF. Infection and Immunity, 66(9), pp.4313–4323.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.8023
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the microbiology category:
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
Citrobacter rodentium infection activates colonic lamina propria group 2 innate lymphoid cells
André Luiz Amorim Costa, Marcus Oliveira
Also in the molecular biology category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
preLists in the microbiology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the molecular biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)