Large-scale, quantitative protein assays on a high-throughput DNA sequencing chip
Posted on: 26 June 2018
Preprint posted on 14 June 2018
Article now published in Molecular Cell at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.019
From sequence to function: Current Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology adapted to carry out functional screening on a huge variety of proteins.
Selected by Samantha SeahCategories: molecular biology
Background
Illumina high-throughput sequencing technologies have been widely utilised to tackle many biological problems. For example, RNA-Seq enables the study of gene expression changes, Hi-C considers chromatin architecture and ChIP-seq examines binding of DNA-binding proteins. In Illumina sequencing, DNA fragments are added to sequencing flow cells, where they bind to flow cell oligonucleotides and via bridge amplification, produce clusters of identical DNA molecules. The subsequent addition and excitation of fluorescently-labelled reversible terminators enables the identification of each added base, as each base has a unique emission. The emission profiles present at each cluster over subsequent rounds of synthesis enable the elucidation of DNA sequences, in a process known as sequencing-by-synthesis.
In contrast to the success in linking DNA sequence variation to function, there has been less success linking protein sequence to function. A recent preprint by the Greenleaf lab outlines a technology (Prot-MAP: Protein display on a Massively-Paralleled Array) that combines sequencing-by-synthesis with protein function assays to enable quantitative protein function assays with a massively high throughput.
Key Findings
To generate protein arrays, the authors first created a library of DNA constructs encoding their polypeptides of interest, which are then clustered and sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq, with the cluster positions recorded (Figure 1A). The authors then carried out in vitro transcription and translation with stalling of both the E. coli RNA Polymerase and ribosome, such that both the transcript and peptide remain associated with the DNA template. They then use fluorescence-based assays to study protein function. As the position of the clusters remain the same from the initial Illumina MiSeq to the final functional assays, DNA sequence, which determines protein sequence, can be directly correlated with protein function.
To test the technology with protein binding assays, the authors utilised the well-characterised FLAG peptide/M2 antibody system. Previous studies have identified DYKxxDxx to be the consensus sequence of the M2 epitope. From this, the authors engineered a library of 13,154 sequences that included single, double, triple-combination of mutant positions, with each position substituted to 6 different amino acids. After DNA sequencing and peptide generation, the M2 antibody was introduced, before the introduction of a fluorescent secondary antibody and imaging, similarly to an ELISA. To determine the binding affinity of the M2 antibody to the peptides, the above process was repeated for increasing concentrations of M2 antibody, enabling the elucidation of the limit of detection (LoD) for each peptide, i.e. the lowest antibody concentration at which binding is detected.
Upon studying the mutant affinity landscapes, the authors note that they largely recapitulate the expected consensus sequence (DYKxxDxx), and even find a “superFLAG” sequence that has a LoD 7.9x lower (meaning higher binding affinity) than that of the wild-type FLAG. They also find additional constraint at position 4: antibody binding only occurs when D or L are present at this position, and reduced binding upon substitution of D by L. Further study of the triple mutants including D4L indicate that some mutations at other positions, including D5E and D7K, partially rescue D4L, and that some of these mutation combinations even exhibit cooperativity.
For enzymatic catalysis assays, the authors also tested their technology on the SNAP-tag protein modification, which can be fused to proteins and subsequently tagged with a ligand, such as a fluorescent dye. They tested 7 residues that have been previously associated with modulating function, and made single, double and triple-mutants combinations across all 20 possible amino acid substitutions, testing over 150,000 variants in total. They find that the mutational constraints vary between different residues. Some residues are strictly constrained (such as Y114), while others are much more tolerant to mutations (for example, A121 and L153). By studying double mutants more closely, the authors found pairs of mutations that exhibited positive cooperativity, and noted that most strong positively-cooperative pairs are in close proximity in the protein (Cα-Cα distances of less than 13 Å). They also found that histidine was extremely capable of participating in cooperative interactions, and hypothesised that this was due to the variability in the charge and hydrogen bonding state of histidine in different contexts.
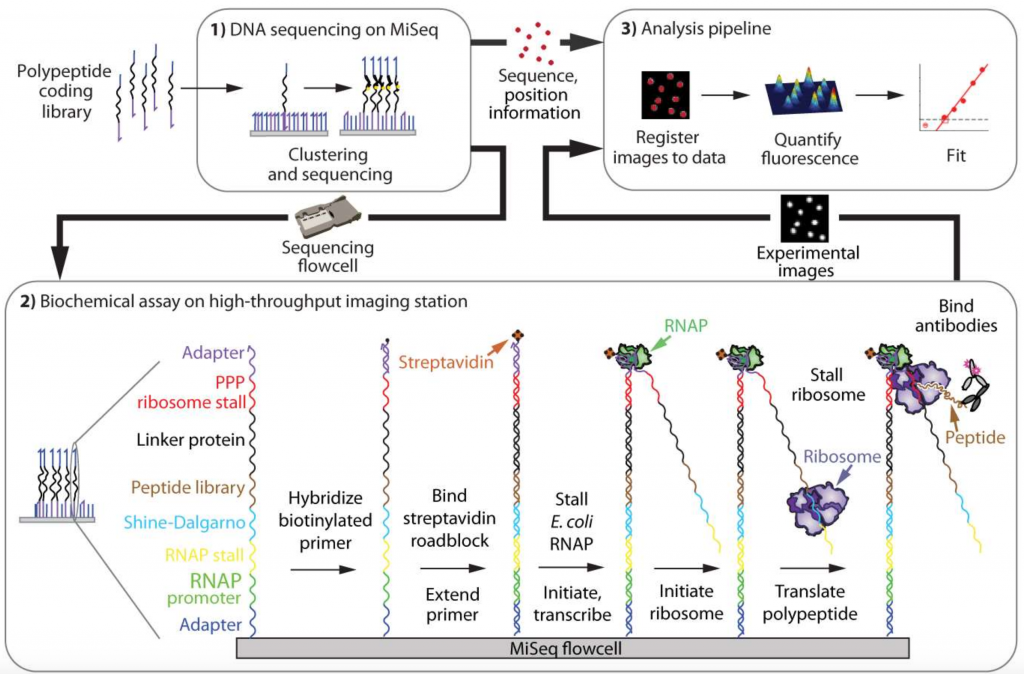
Figure 1A of the preprint: Workflow for enabling the establishment of a high-throughput protein array.
What I like about this work
I think that this is a brilliant modification to current Illumina sequencing technology to enable it to be used for high-throughput functional protein assays. The microfluidic chips and sequencing technology required are commercially available and the imaging software is simply adapted from current Illumina sequencing. By including a series of simple, yet elegant changes that enable the DNA fragment to be transcribed and translated, with the RNA and protein remaining attached to the DNA fragment, the authors have made it possible to study an additional dimension (protein function) while maintaining a high throughput.
Kudos to the authors for simply co-opting the positional information that enables the linking of nucleotides into a complete DNA sequence, to link DNA sequence to protein function.
Outlook
A key limitation of the technology is the size of DNA molecules that can be clustered. This in turn severely restricts the size of the protein that can be studied, and may result in the technology being used largely only to study peptide fragments or protein domains. I wonder if the authors see this as the key limitation of this technology, or if they see a way to somehow overcome this.
Further reading
She, R., et al., Comprehensive and quantitative mapping of RNA–protein interactions across a transcribed eukaryotic genome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2017. 114(14): p. 3619-3624.
Jung, C., et al., Massively Parallel Biophysical Analysis of CRISPR-Cas Complexes on Next Generation Sequencing Chips. Cell, 2017. 170(1): p. 35-47. e13.
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the molecular biology category:
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
preLists in the molecular biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)