Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Posted on: 11 November 2025 , updated on: 13 November 2025
Preprint posted on 27 September 2025
How do endothelial cells differ across tissues? A new single-cell atlas of over 3 million cells shows how microenvironmental signals shape endothelial diversity.
Selected by Charis QiCategories: bioinformatics, genomics, systems biology
Why this preprint is important
Key to this preprint is that it establishes a massive, comprehensive single-cell human endothelial cell (EC) atlas that provides major insights into EC heterogeneity. This atlas is a strong contribution to future single-cell EC research and can be used in many ways. For example, future EC cells can be projected onto this atlas instead of going through the typical scRNA-seq pipeline. An especially innovative feature of this study is the use of topic modeling, a method widely used in natural language processing, to uncover tissue-specific CCC patterns in ECs from biological data.
Background:
Endothelial cells (ECs) line the interior of all blood vessels as well as the lymphatic system in the body. They are crucial in managing the blood vessels and their surrounding tissues [1-4]. While all ECs share the functions of maintaining tissue health, regulating the immune responses, and keeping vessels healthy, their roles can vary depending on vessel type, tissue location, and developmental stage [5].
EC heterogeneity is regulated by two major mechanisms: transcriptional control and microenvironmental regulation [6-7]. Transcription factors such as GATA2 and ETV2 direct early EC formation [8-9]. After EC development, microenvironmental factors such as extracellular matrix components, physical forces, and interactions with neighboring cells shape the EC function to support an organ’s specific functions [10-11]. However, existing studies have only examined the influence of microenvironment on EC behavior in single organs or in mice [12-17]. A comprehensive study comparing EC activity across tissues and vessel types has not yet been conducted.
In this preprint, Zhu and team constructed a human single-cell EC atlas by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets containing over 3 million cells from 15 different tissues. Using this atlas, they found that ECs were more different across vessel types compared to organs. They then implemented a machine learning method to investigate how ECs interact with other cells via cell-cell communication (CCC) and discovered that most communication patterns were tissue-specific. These insights could ultimately help scientists identify new therapeutic targets for diseases related to the endothelium.
Highlights
Human single-cell atlas and computational pipeline uncover EC heterogeneity
To investigate EC heterogeneity, Zhu and colleagues first integrated scRNA-seq datasets from multiple sources to build a comprehensive atlas. They corrected for batch effects, ensuring that cell clustering reflected biological differences rather than technical biases. Principal Component Analysis showed that the ECs in heart and kidney are vastly different than in other tissues regardless of vessel type. Using unsupervised hierarchical clustering, the researchers identified two clusters with the biggest EC similarity. In cluster 1, ECs were more similar within the same vessel type. In cluster 2, ECs were more similar within the same tissue type.
The authors noticed that within cluster 1 of the atlas, ECs from different tissues within the same vessel type exhibited high variability. Building on this observation and previous studies, they constructed a computational pipeline to investigate how tissue-specific signals are associated with EC tissue heterogeneity through CCC. This method implements two types of cell-cell communication: metabolite-mediated and protein-mediated. They first implemented advanced bioinformatics tools, such as MEBOCOST and LIANA+, to detect metabolite-mediated CCC and protein-mediated CCC events. They then used an unsupervised machine learning method called ‘topic modeling’ to find common patterns of CCC across all tissues, grouping similar communication events together into “topics”. With this model, the authors were able to determine how likely each CCC event is part of a CCC pattern and how strongly a tissue shows a particular CCC pattern.
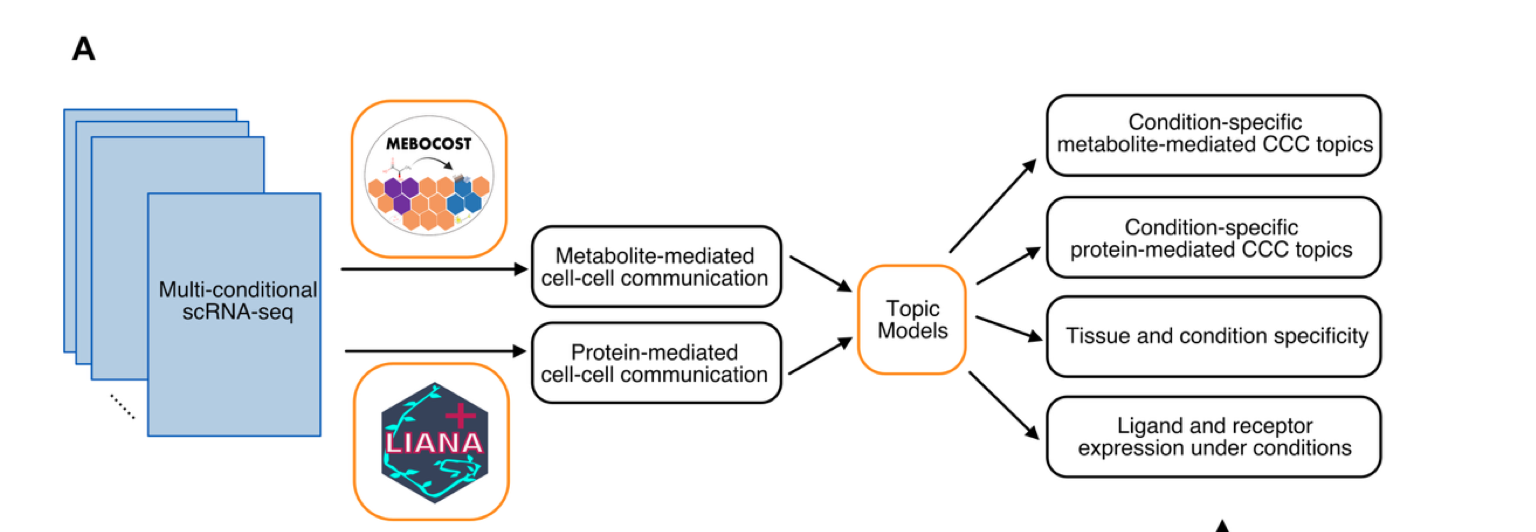
Figure 2A from the preprint – A visual representation of the computational pipeline developed to understand EC tissue heterogeneity through CCC using scRNA-seq data. Figure made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
The researchers examined the number of EC-associated CCC events in different tissues. Using their computational method, they found that the CCC number for EC differs across tissues. For instance, the ovary and intestine had many more CCC events than the kidney and adipose tissue. However, they found that both protein-mediated and metabolite-mediated CCC showed the same tissue-specific pattern, suggesting that ECs communicate differently depending on the tissue rather than the CCC levels. The authors further computed the percentage of ECs and the overall cell type count across different tissues. They found that the percentage of ECs in a tissue was weakly correlated with the number of CCC events, whereas the number of cell types in the tissue showed a strong correlation. Even after normalizing CCC counts by the number of cell types, there were still differences across tissues, emphasizing tissue-specific CCC patterns.
Machine learning method uncovers tissue-specific metabolite- and protein-mediated CCC patterns
The researchers used topic modeling to study tissue-specific EC heterogeneity in the context of metabolite-mediated CCC. Specifically, they used topic modeling to group CCC events identified in each tissue, with each topic representing a pattern of metabolite-mediated communication. They identified 15 metabolite-mediated CCC topics, with 9 topics being strongly associated with specific tissues. Within each topic, the authors looked into metabolite-sensor pairs and saw that each pair was strongly associated with CCC topic specificity. For example, topic 13 was closely linked to the ovary, with five metabolite-sensor pairs showing elevated CCC events and expression in this tissue. These findings are supported by previous studies demonstrating the significance of the identified metabolites and sensors in tissue-specific functions.
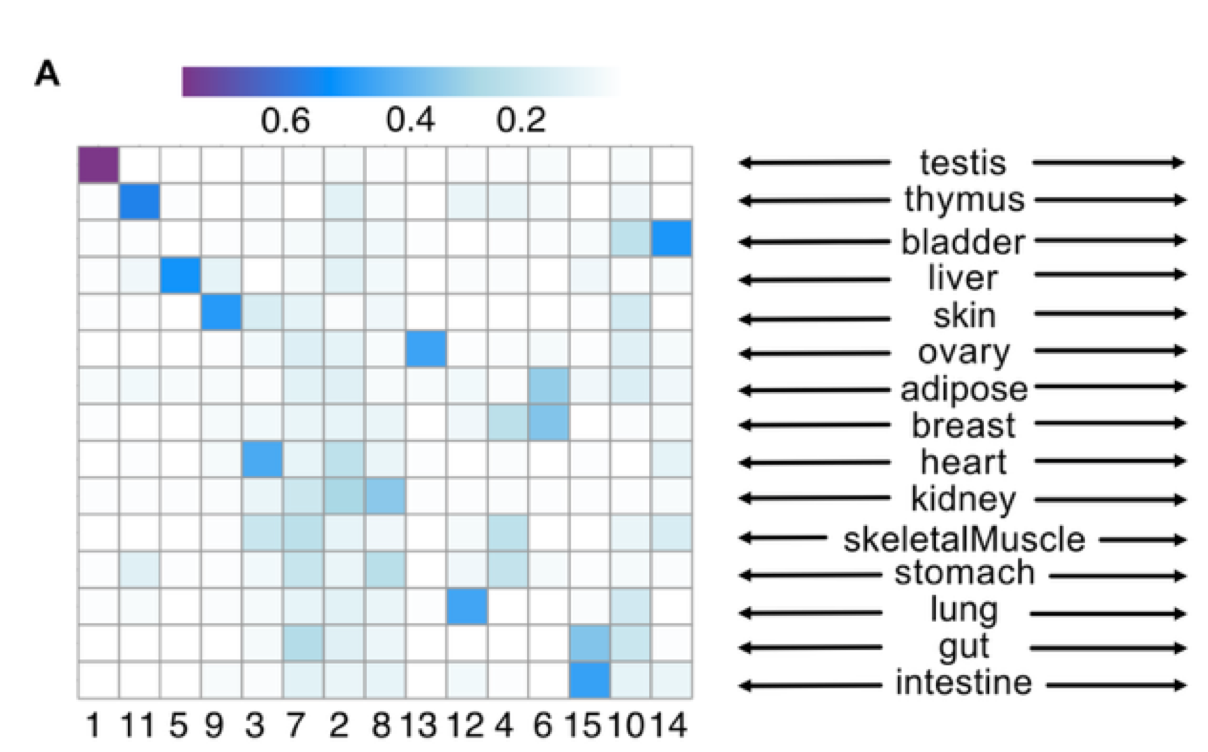
Figure 4A from the preprint – This figure visualizes the results of topic modeling on metabolite-mediated CCC networks. The heatmap illustrates the strength of the correlation between the 15 topics identified by the model and the tissues type under study. Figure made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
The research team also used topic modeling to study tissue-specific EC heterogeneity in the context of protein-mediated CCC. Using the same pattern-detecting method as for metabolite-mediated CCC, they identified 15 protein-mediated CCC topics. 13 out of these topics are strongly associated with tissue types. An analysis into the ligand-receptor pairs showed that each pair was specific to a topic. They further investigated topic 15, which is closely associated with the heart, and found that six ligand-receptor pairs stood out. Published literature reveals that these ligand-receptor pairs have crucial roles in the heart. These results indicate that different tissues have unique ligand-receptor pairs involving ECs and offer insights into why ECs vary across tissues.
Conclusion
Overall, Zhu and team assembled an atlas composed of over 3 million cells from 15 tissues and established a computational pipeline to elucidate the atlas. Using this pipeline of bioinformatics and machine learning approaches, they uncovered how CCC-mediated microenvironments affect EC heterogeneity at the metabolite and protein level. Specifically, they found that EC-related CCC is highly specific to each tissue across both modes of communication. Moreover, the identified CCC patterns grouped in each topic provide a foundation for future studies on how metabolite- and protein-mediated CCC contribute to tissue-specific EC differences.
Questions for the authors:
- How do these tissue-specific EC CCC patterns change in diseased states such as cancer?
- Are sex differences or age-dependent shifts detectable in EC heterogeneity?
- Could integrating spatial transcriptomics or proteomics data validate and refine the CCC topics identified in this study?
References
[1] Krüger-Genge A, Blocki A, Franke R-P, Jung F. Vascular endothelial cell biology: An update. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:4411.
[2] Pi X, Xie L, Patterson C. Emerging roles of vascular endothelium in metabolic homeostasis. Circ Res 2018;123:477–94.
[3] Jalkanen S, Salmi M. Lymphatic endothelial cells of the lymph node. Nat Rev Immunol
2020;20:566–78.
[4] Iglesias MJ, Kruse LD, Sanchez-Rivera L, Enge L, Dusart P, Hong M-G, et al. Identification of endothelial proteins in plasma associated with cardiovascular risk factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2021;41:2990–3004.
[5] Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 2007;100:158–73.
[6] De Val S, Black BL. Transcriptional control of endothelial cell development. Dev Cell
2009;16:180–95.
[7] Potente M, Mäkinen T. Vascular heterogeneity and specialization in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2017;18:477–94.
[8] Lugus JJ, Chung YS, Mills JC, Kim S-I, Grass J, Kyba M, et al. GATA2 functions at multiple steps in hemangioblast development and differentiation. Development 2007;134:393–405.
[9] Shi X, Richard J, Zirbes KM, Gong W, Lin G, Kyba M, et al. Cooperative interaction of Etv2 and Gata2 regulates the development of endothelial and hematopoietic lineages. Dev Biol 2014;389:208–18.
[10] Majewska A, Wilkus K, Brodaczewska K, Kieda C. Endothelial cells as tools to model tissue microenvironment in hypoxia-dependent pathologies. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:520.
[11] Leone P, Malerba E, Susca N, Favoino E, Perosa F, Brunori G, et al. Endothelial cells in tumor microenvironment: insights and perspectives. Front Immunol 2024;15:1367875.
[12] Kalucka J, de Rooij LPMH, Goveia J, Rohlenova K, Dumas SJ, Meta E, et al. Single-cell transcriptome atlas of Murine endothelial cells. Cell 2020;180:764–79.e20.
[13] Paik DT, Tian L, Williams IM, Rhee S, Zhang H, Liu C, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing unveils unique transcriptomic signatures of organ-specific endothelial cells. Circulation 2020;142:1848–62.
[14] Bondareva O, Rodríguez-Aguilera JR, Oliveira F, Liao L, Rose A, Gupta A, et al. Single-cell profiling of vascular endothelial cells reveals progressive organ-specific vulnerabilities during obesity. Nat Metab 2022;4:1591–610.
[15] Schupp JC, Adams TS, Cosme C Jr, Raredon MSB, Yuan Y, Omote N, et al. Integrated single-cell atlas of endothelial cells of the human lung. Circulation 2021;144:286–302.
[16] Li Q, Zhu Z, Wang L, Lin Y, Fang H, Lei J, et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals vascular endothelial cell heterogeneity in human skin. Theranostics 2021;11:6461–76.
[17] Geldhof V, de Rooij LPMH, Sokol L, Amersfoort J, De Schepper M, Rohlenova K, et al. Single cell atlas identifies lipid-processing and immunomodulatory endothelial cells in healthy and malignant breast. Nat Commun 2022;13:5511.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.42083
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioinformatics category:
Also in the genomics category:
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the systems biology category:
Longitudinal single cell RNA-sequencing reveals evolution of micro- and macro-states in chronic myeloid leukemia
Charis Qi
Environmental and Maternal Imprints on Infant Gut Metabolic Programming
Siddharth Singh
Single-Cell Network Analysis Identifies CLEC4E as a Key Mediator of Proinflammatory mDC Responses in Influenza Infection
Charis Qi
preLists in the bioinformatics category:
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the genomics category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the systems biology category:
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)