Anti-bat ultrasound production in moths is globally and phylogenetically widespread
Posted on: 27 October 2021
Preprint posted on 22 September 2021
Article now published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences at http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2117485119
Screaming your toxicity: ultrasound production in moths as a warning to bats massively more prevalent than previously thought
Selected by Thomas Neil, Baheerathan MurugavelCategories: biophysics, ecology, evolutionary biology
Background
Bats and moth are embroiled in an acoustic arms-race between predator and prey which has been raging on since bats first evolved echolocation, some 65 million years ago. Echolocating bats are excellent hunters of nocturnal insects, they localise and target their prey using a sophisticated series of ultrasonic clicks to illuminate their prey with sound and listen for the echoes bouncing off them. The presence of echolocating insectivorous bats has led to a host of defences in insects which fly by night, with moths in particular evolving a diverse range of strategies to help them survive. Many moths have evolved ultrasound sensitive ears, allowing them to detect approaching bats and take evasive manoeuvres. Some of these moths have even evolved the ability to produce ultrasound of their own, warning a bat that they are toxic and not to be eaten. Some moths do not have ears, yet have evolved passive defences to increase their chances of survival, such as acoustic decoys and acoustic camouflage. Now, a preprint on acoustic defences in moths has revealed that certain adaptations are much more widely spread amongst the group than previously thought.
Findings
Warning signals are well known in visual systems, but less so in other sensory modalities. Ultrasonic signalling amongst moths was mostly thought to occur in one group, the tiger moths, with a few other examples dotted amongst other moth families. However, the current study lead by Jesse Barber of Boise State University has revealed that this type of signalling is much more widespread than previously thought, with their study identifying ultrasound production in an additional 52 new genera and 8 subfamilies previously unknown to produce ultrasound.
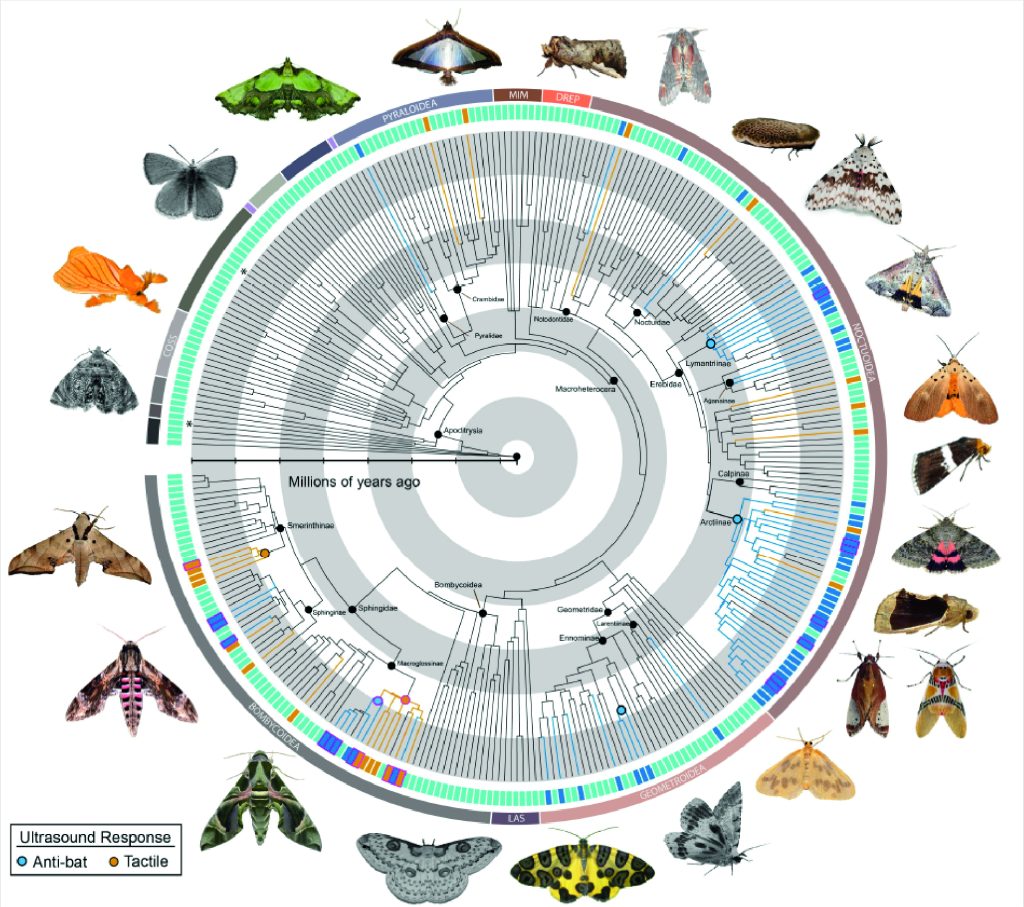
Figure 1. A molecular phylogeny of Lepidoptera indicating anti-predator ultrasound either in response to bat-like ultrasound (light blue bars) or to tactile stimulation (orange bars). Asterisks indicate taxa known to produce ultrasound, but not in response to either tactile stimulus nor bat ultrasound. Grayscale images indicate taxa that do not produce ultrasound (taken from preprint).
This is a multi-year study which involved numerous trips to locations to sample the local moths and assess their ability to produce ultrasound. The researchers embarked on field work in South America (Ecuador, French Guiana), Africa (Mozambique), and Asia (Malaysian Borneo). To assess whether moths produce ultrasound in response to a bat attack, the researchers simulated bat predation in two ways. The first simulated capture, whereby the researcher stimulated the moths with tactile handling to imitate the sensation of being captured by a bat. The second was an acoustic test, with the researchers hitting the moth with bat-like ultrasound to simulate the sounds of an approaching echolocating bat. Finally, the researchers conducted experiments on the palatability of the moth, allowing them to gain an understanding of whether the moth might be warning a bat of its toxicity or not. They did this by feeding moths to captive bats and assessing whether the bat would eat the moth or not.
Many species of moths produce ultrasound for reasons such as communication among other moths, attracting mates or to jam the sonar of an attacking bat predator. Here, the researchers show that most moths use ultrasound to communicate with their bat predators, advertising their toxicity. The researchers found that the majority of the moths that produce ultrasound were indeed toxic, suggesting that ultrasound production has evolved as a means of aposematism: that is, the moths are signally distastefulness to the bats, warning them not to eat them. Several other moths have also converged on this acoustic signal, yet are not toxic, indicating that these moths are faking to the bats that they are toxic, despite being perfectly edible, in an evolutionary process known as Batesian mimicry.
In addition to identifying many new ultrasound producing moths, the researchers also identified three new mechanisms of ultrasound production. They discovered that one species of moth will produce sound by scraping modified scales on their abdomen together, another uses its wings to beat against a modified structure near the joint of the wing, and a third species uses tymbals backed by horn like structures to beam ultrasound rearward during flight.
What we like about this preprint
The acoustic battle between bats and moths is possibly the best example of a predator prey arms race in the animal kingdom, with instances of adaptations and counter adaptions on both sides. This study reveals just how little we still know about some of these fascinating evolutionary adaptions and reveals an entire world of ultrasound producing moths that were previously assumed to be silent. Aposematism is usually linked with strong colours and odours in many animal taxa and has been associated with mimicry, an effective anti-predatory strategy against visual predators. However, the existence of aposematism and mimicry based anti-predatory defences in the light-limited nocturnal environment is not well known, especially considering the other sensory modalities used by nocturnal animals. The authors of the study have explored this complex anti-predatory mechanism in the bat-moth acoustic system. By doing so, they not only describe the presence of aposematism in the acoustic world but have opened up interesting avenues in the field of predator-prey sensory ecology. This study should motivate sensory ecologists to undertake similar works to validate previous assumptions about predator prey interactions and work towards a better understanding of their evolutionary origins across different sensory modalities.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.30871
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biophysics category:
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation is Stimulated by Red Light Irradiation
Rickson Ribeiro, Marcus Oliveira
Also in the ecology category:
Cannibalism as a mechanism to offset reproductive costs in three-spined sticklebacks
Tina Nguyen
Trade-offs between surviving and thriving: A careful balance of physiological limitations and reproductive effort under thermal stress
Tshepiso Majelantle
The cold tolerance of an adult winter-active stonefly: How Allocapnia pygmaea (Plecoptera: Capniidae) avoids freezing in Nova Scotian winters
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
Also in the evolutionary biology category:
Morphological variations in external genitalia do not explain the interspecific reproductive isolation in Nasonia species complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae)
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Dissecting Gene Regulatory Networks Governing Human Cortical Cell Fate
Manuel Lessi
preLists in the biophysics category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
66th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, 2022
Preprints presented at the 66th BPS Annual Meeting, Feb 19 - 23, 2022 (The below list is not exhaustive and the preprints are listed in no particular order.)
| List by | Soni Mohapatra |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Biophysical Society Meeting 2020
Some preprints presented at the Biophysical Society Meeting 2020 in San Diego, USA.
| List by | Tessa Sinnige |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Biomolecular NMR
Preprints related to the application and development of biomolecular NMR spectroscopy
| List by | Reid Alderson |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
Also in the ecology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment', organised at EMBL Heidelberg, Germany (May 2023).
| List by | Girish Kale |
Bats
A list of preprints dealing with the ecology, evolution and behavior of bats
| List by | Baheerathan Murugavel |
Also in the evolutionary biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment', organised at EMBL Heidelberg, Germany (May 2023).
| List by | Girish Kale |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)