Suppression of aggregate and amyloid formation by a novel intrinsically disordered region in metazoan Hsp110 chaperones
Posted on: 14 April 2021 , updated on: 21 April 2021
Preprint posted on 13 January 2021
Categories: biochemistry
Written by: Anna Enneking, Simon Hinfelaar, Inge Rothuis and Vincent Spit
Background
Protein misfolding can cause devastating problems in the cell, as exemplified by the formation of amyloid fibrils in neurodegenerative diseases [1]. Chaperones, including the ATP-dependent Hsp70, prevent protein aggregation [2]. Hsp70 needs a nucleotide exchange factor (NEF) such as Hsp110 to promote cycling from ADP to ATP [3]. Interestingly, Hsp110 is part of the Hsp70 superfamily, meaning they share the canonical Hsp70 architecture. They both have a nucleotide binding domain (NBD) that binds ATP, a flexible linker, and a substrate binding domain (SBD) composed of two parts: a β-sandwich-containing substrate binding site (SBD-β) and α-helical sequence (SBD-α).
Hsp110 also has an extended C-terminus, which is conserved in metazoan Hsp110 genes, e.g human Hsp105α and Apg-1, and has an unknown function [4]. Although they share a canonical structure, Hsp110 has no refolding activity as Hsp70 does. However, Hsp110 overexpression can prevent aggregation of the huntingtin protein in a Drosophila model system [5]. It is unknown whether this is a function of Hsp110 as a NEF or as a passive holdase. To understand this, the authors decide to disrupt the Hsp110 holdase function by targeting the SBD-β domain, because they suspect that this domain is responsible for the holdase activity. In their attempts to disrupt the SBD-β, they uncover a secondary binding site.
Key findings
The authors introduce different deletions in the SBD-β domain of Drosophila Hsp110, leaving the regions that interact with Hsp70 (NBD, SBD-α) intact. They monitor protein aggregation by a light scattering aggregation assay using citrate synthase as substrate to test the holdase activity. Surprisingly, the Hsp110 protein in which SBD-β is deleted is more efficient in preventing aggregation than the full-length protein. So, if the SBD-β is not essential for the activity in this assay, then what else is?
The authors now suspect intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), as such regions can act as sites for protein binding and are present in many chaperones [6]. In silico analysis reveals one IDR in the C-terminus and another one in the SBD-α domain. It turns out that it is the C-terminal IDR that is responsible for the holdase activity, because when deleted the holdase activity is lost. Deletion of the SBD-α domain does not affect the holdase activity. The human homologs of Hsp110, Apg1a and Hsp105α, also have an IDR in the C-terminus. These C-termini also prevent protein aggregation when directly linked to the NBD (Fig. 4C), so the presence of an IDR in the C-terminus could indicate a general holdase function in the Hsp110 proteins.
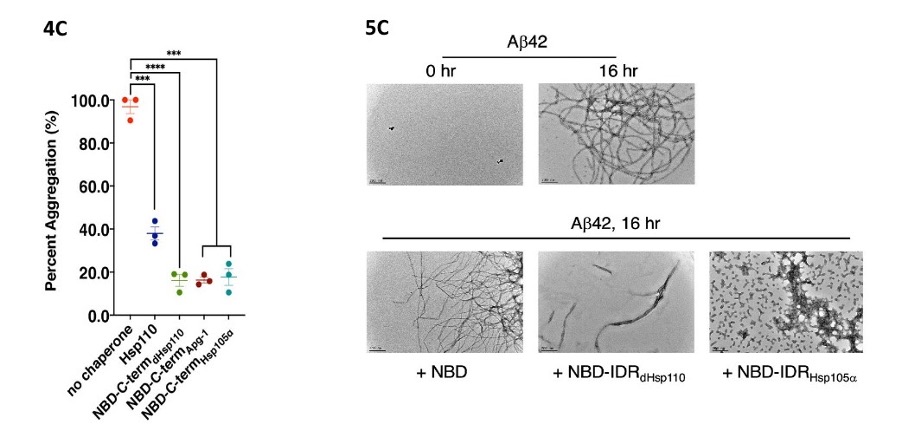
The authors now study whether the IDRs can also prevent amyloid formation, which is associated with various diseases including Alzheimer ‘s [1]. To this end, they examine the impact of variants of Drosophila Hsp110 (dHsp110) and its human homolog Hsp105α on fibril formation of amyloid-β 42 (Aβ42). Negative staining TEM shows that NBDdHsp110 alone does not decrease Aβ42 fibril formation, but the IDR fusions NBDdHsp110-IDRdHsp110 and NBDdHsp110-IDRHsp105α do (Fig. 5C). Thus, the IDR in Hsp110 homologs can also prevent amyloid formation.
What we like about the preprint
We were directly drawn to this article when we read the title. We found the fact that Hsp110 can prevent protein aggregation very interesting, mainly because we previously learned that Hsp110 works as NEF of Hsp70. It was therefore intriguing to read that Hsp70 and Hsp110 share a canonical structure, but that the SBD-β in Hsp110 is not solely responsible for its holdase activity. It was surprising to learn that an IDR contributes to this activity. To our excitement, this paper shows that the IDR in Hsp110 can actually prevent amyloid formation, which is associated with neurodegenerative diseases. This knowledge is important to better understand how chaperones prevent this pathogenic process in the cell.
doi: Pending
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biochemistry category:
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Snake venom metalloproteinases are predominantly responsible for the cytotoxic effects of certain African viper venoms
Daniel Osorno Valencia
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
preLists in the biochemistry category:
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
Peer Review in Biomedical Sciences
Communication of scientific knowledge has changed dramatically in recent decades and the public perception of scientific discoveries depends on the peer review process of articles published in scientific journals. Preprints are key vehicles for the dissemination of scientific discoveries, but they are still not properly recognized by the scientific community since peer review is very limited. On the other hand, peer review is very heterogeneous and a fundamental aspect to improve it is to train young scientists on how to think critically and how to evaluate scientific knowledge in a professional way. Thus, this course aims to: i) train students on how to perform peer review of scientific manuscripts in a professional manner; ii) develop students' critical thinking; iii) contribute to the appreciation of preprints as important vehicles for the dissemination of scientific knowledge without restrictions; iv) contribute to the development of students' curricula, as their opinions will be published and indexed on the preLights platform. The evaluations will be based on qualitative analyses of the oral presentations of preprints in the field of biomedical sciences deposited in the bioRxiv server, of the critical reports written by the students, as well as of the participation of the students during the preprints discussions.
| List by | Marcus Oliveira et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (1 votes)
(1 votes)