Tardigrades dramatically upregulate DNA repair pathway genes in response to ionizing radiation
Posted on: 18 October 2023 , updated on: 19 October 2023
Preprint posted on 7 September 2023
What doesn’t kill you makes you stronger: @ArthropodQueen and team characterize a novel mechanism of ionizing radiation tolerance in the tardigrade H. exemplaris
Selected by Isabella CisnerosCategories: genomics, molecular biology
Background:
Colloquially known as water bears or moss piglets, tardigrades are fascinating invertebrate organisms with the ability to survive a variety of extreme conditions, including extreme temperature, desiccation, and even the harsh environment of outer space [1]. When exposed to these conditions, tardigrades can enter a state called cryptobiosis, in which their metabolism comes to a reversible standstill until more suitable conditions are reached [1,2]. This aspect of tardigrade biology has become a subject of great interest and is increasingly being studied, with genomes for the tardigrade species Ramazzottius varieornatus and Hypsibius exemplaris already available [3,4].
Researchers have already begun to characterize the mechanisms underlying cryptobiosis, particularly in the case of DNA repair. Previous studies in the tardigrade species R. varieornatus found a DNA damage suppressing protein—termed Dsup—that confers resistance to ionizing radiation (IR) by binding to nucleosomes and protecting DNA from hydroxyl radicals [3,5]. However, little else is known about the mechanisms that tardigrades use to survive DNA damage resulting from extreme conditions. In this preprint, the authors sought to understand how the tardigrade H. exemplaris survives the DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation. Using sequencing and molecular techniques, the authors describe a novel mechanism underlying IR tolerance in tardigrades.
Main Findings:
Messenger RNA sequencing reveals significant upregulation of DNA repair genes following exposure to ionizing radiation
After confirming that IR induces DNA damage in H. exemplaris and that the tardigrade is able to repair its damaged cells post-exposure, the authors set out to understand the mechanisms underlying this repair. To do so, the authors performed messenger RNA sequencing (mRNA-seq) on tardigrades post-exposure to either 100, 500, or 2180 Gray (Gy) doses of IR. These doses range from a level with proven survival and reproduction post-exposure to an LD50 dose (a dose of IR at which 50% of humans would die).
Analysis of differential expression showed a robust response from H. exemplaris, with about half of the most enriched transcripts encoding proteins found in DNA repair pathways. Additionally, these transcripts were found to be involved in base excision repair (BER) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), two important DNA repair processes that lend themselves to repairing the damage caused by IR. The authors also analyzed transcript enrichment for genes associated with other reparative processes such as mismatch repair (MMR), nucleotide excision repair (NER), homologous recombination (HR) and theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). They found transcripts associated with HR as well as TMEJ, revealing specificity in the tardigrade transcriptional response to IR damage.
DNA repair transcripts identified through sequencing are expressed throughout the tardigrade but are also enriched in specific tissues
Having characterized the transcriptional response to IR, the authors next asked whether this response is tissue-specific or an overall response. They performed in situ hybridization on a few of the enriched DNA repair transcripts identified through mRNA-Seq. Following IR exposure, all of the transcripts observed were enriched in nearly all tissues, validating their sequencing results. However, some transcripts were particularly enriched in secretory tissues, such as the salivary glands and the hindgut, while nearly all were enriched in storage cells called coelomocytes. Given that secretory tissues are believed to be active in transcription and translation, the authors attributed this enrichment to the fact that transcriptionally active tissues are more sensitive to damage caused by IR.
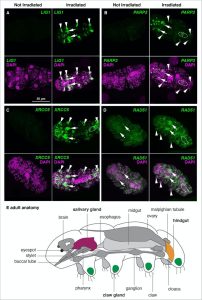
Figure 1: In situ hybridization of enriched DNA repair transcripts. (A-D) Detection of the DNA repair transcripts LIG1, PARP3, XRCC5, and RAD51 under two treatment conditions: no exposure to ionizing radiation or exposure to 100 Gy. Arrows indicate salivary glands, arrowheads indicate claw glands, and dashed circles correspond to the hindgut. (E) Schematic of an adult tardigrade showing the regions highlighted above as well as other major anatomical features.
Heterologous expression of DNA repair transcripts in bacteria confers resistance to radiation—but degree of expression matters
The authors next chose to test whether the DNA repair genes that showed increased expression in H. exemplaris confer protection against IR. They expressed these genes heterologously in E. coli and exposed colonies to 2,180 Gy. They then observed these colonies to see how their survival compared to negative controls as well as a positive control vector expressing Dsup, a previously characterized tardigrade gene shown to improve radiation survival in human cells.
All but one of the introduced genes that increased survival of E. coli colonies after IR encoded proteins in the BER pathway. For some of these genes, expression resulted in the same levels of protection as that of the Dsup protectant. The authors were curious to see if high levels of expression of these genes were necessary for the survival of tardigrades after IR exposure, which they tested by using RNA interference (RNAi). The gene XRCC5 was selected as it was the most significantly enriched transcript following IR exposure. They found that tardigrades injected with dsRNA targeting this gene show more lethality compared to controls, indicating that dramatic upregulation of DNA repair genes plays a significant role in the overall response to IR.
Why I Chose This Preprint:
I find the novel mechanism of tardigrade IR tolerance characterized in this preprint to be absolutely fascinating, especially given both the current gap of knowledge regarding tolerance mechanisms as well as the fact that this mechanism differs from the previously characterized Dsup. While tardigrades are not a commonly used model organism, there is quite a lot to be learned from them, particularly when it comes to survival under extreme conditions. Further characterization of tardigrade tolerance could have significant applications in a variety of contexts, from climate change to future space exploration. This study marks an exciting step forward in the characterization of tolerance responses and I am excited to see how this research continues to develop.
Questions For The Authors:
- How did you decide upon the 24hr post-exposure timepoint for your experiments? Did you consider incorporating later timepoints for sequencing and/or in situ experiments?
- In the discussion, you mention the possibility of synergy between multiple protective mechanisms. However, heterologous expression of exemplaris Dsup does not confer the protection given by R. varieornatus Dsup. How likely do you think the occurrence of synergy is, and what could be the benefit of not having it?
- While it is possible that strong IR tolerance developed from cross-tolerance for another threat, how do we account for the significant upregulation of DNA repair genes shown by the tardigrades? Is it possible that the upregulation of DNA genes seen in this study is tied to the extent of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation (as compared to the damage caused by desiccation, for example)?
References
[1] Møbjerg, N. & Cardoso Neves, R. New insights into survival strategies of tardigrades. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 254:110890 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110890
[2] Halberg, K. A., Jørgensen A., Møbjerg, N. Desiccation Tolerance in the Tardigrade Richtersius coronifer Relies on Muscle Mediated Structural Reorganization. PLoS ONE, 8(12): e85091 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085091
[3] Hashimoto, T., Horikawa, D., Saito, Y. et al. Extremotolerant tardigrade genome and improved radiotolerance of human cultured cells by tardigrade-unique protein. Nat Commun 7, 12808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12808
[4] Koutsovoulous, G., Kumar, S., Laet, D. R. et al. No evidence for extensive horizontal gene transfer in the genome of the tardigrade Hypsibius dujardini. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(18):5053-5058 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1600338113
[5] Chavez, C., Cruz-Becerra, G., Fei, J., Kassavetis, G. A., Kadonaga, J. T. The tardigrade damage suppressor protein binds to nucleosomes and protects DNA from hydroxyl radicals. eLife 8:e47682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47682
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.35733
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the genomics category:
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the molecular biology category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
preLists in the genomics category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the molecular biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)