Saturation variant interpretation using CRISPR prime editing
Posted on: 20 October 2021
Preprint posted on 14 May 2021
Article now published in Nature Biotechnology at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41587-021-01201-1
Saturation prime editing: a new twist on performing highly efficient reclassification of variants of uncertain significance at scale
Selected by Jeffrey CalhounCategories: bioinformatics, genetics, molecular biology
Background
Our understanding of the genes associated with genetic disorders has advanced considerably with the advent of next generation sequencing technologies including gene panels, microarrays, and exome sequencing. Clinical genetic testing has become routine for obtaining precise genetic diagnoses in many clinical disciplines from oncology to cardiology to neurology. The rate of clinical genetic testing is expected to continue to increase as the cost of next generation sequencing continues to decline and the benefits of early genetic testing become more widely appreciated.
An ideal outcome of a clinical genetic test is the identification of a pathogenic variant which explains the individual’s phenotype and has an associated precision medicine treatment, such as combination lumacaftor/ivacaftor for the F508del CFTR variant in cystic fibrosis. Currently, the most likely outcome is the discovery of a variant of uncertain significance (VUS), i.e., a genetic change in a potentially relevant gene is detected, but lacks the sufficient evidence to determine whether the genetic variant is pathogenic or benign. Functional assays, in which a VUS is expressed in a cell model to evaluate its activity, have been used for many years to determine whether a particular VUS significantly impacts gene function. However, these experiments are time-consuming and only test one VUS at a time. Developing a new technology is therefore necessary to scale this experiment to tackle the large number of VUS observed in clinical genetic testing.
Multiplexed assays of variant effects (MAVEs) allow for the simultaneous functional characterization of large libraries of VUS generated with techniques such as saturation mutagenesis or saturation genome editing (SGE). In SGE, a genome editor such as SpCas9 is used in concert with a library of guide RNAs (gRNAs) and oligo donors to make many different mutations in a region of a gene. SGE is typically paired with a functional assay, such as cell growth, and next generation sequencing to identify variants with normal or altered function. One of the first MAVEs used SGE to reclassify VUS in the tumor suppressor BRCA1.1 However, there are several technical limitations of SGE, especially (1) an over-reliance on the haploid cell line HAP1 which is known to spontaneously revert to a diploid state and (2) the use of homology-directed repair (HDR) with low editing efficiency due to the frequent occurrence of nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). In this preprint, Erwood S et al. sought to address both of these technical limitations through the development of novel haploidized cell lines and the adaptation of prime editing for high-throughput variant characterization.
Key findings
Locus specific haploidization
Haploid HAP1 cells are typically used in SGE experiments to limit each cell to expressing a single variant, which is essential for determining the function of the variant after sorting or selecting cells based on a cellular phenotype. However, this has restricted SGE experiments to genes endogenously expressed in HAP1 cells. In order to overcome this limitation, the authors hypothesized that making cells haploid at a specific locus (a single gene) would enable SGE experiments in many cell lines. A pair of gRNAs specific to heterozygous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) native to HEK293T (HEK) cells were designed using publicly available genome sequencing data. The authors co-transfected HEK cells and selected a line with only a single remaining functional copy of the NPC1 gene associated with a lysosomal storage disorder known as Niemann-Pick disease type C1. The cell line was validated by experiments to confirm the haploidized line had reduced NPC1 expression by Western blotting and normal cholesterol homeostasis by filipin staining. In theory, a similar approach could be used in virtually any cell line that endogenously expresses a particular gene of interest.
Saturation Prime Editing (SPE) of NPC1 and BRCA2
The authors developed an assay based on staining with LysoTracker, a cell-permeable fluorescence dye that stains lysosomal compartments. The assay was validated using well-characterized missense (p.I1061T and p.P1007A) and nonsense (p.C909X) NPC1 variants. Qualitative and quantitative increases in LysoTracker staining in variant expressing cells were observed relative to parental haploidized HEK cells. Next, prime editing gRNAs (pegRNA) libraries encoding NPC1 variants were generated; importantly, each library contained a silent substitution to disrupt the PAM site and prevent further editing (Figure 1). The mutant pegRNA libraries were cotransfected into haploidized HEK cells with expression constructs for the SpCas9 prime editor as well as a nicking gRNA to increase editing efficiency. Cells were FACS sorted based on LysoTracker signal, followed by DNA extraction and sequencing of the target region of the NPC1 gene. 251/256 (98%) variants were successfully classified as either functional or non-functional based on whether these variants were enriched in the sorted pool of cells with high LysoTracker signal. 14/14 (100%) of control nonsense variants were classified as non-functional, while 60/61 (98%) of control synonymous variants were classified as functional. Interestingly, the majority (121/180) of NPC1 missense variants were classified as non-functional. Editing efficiency in libraries was high, ranging from about 45-73% of the sequencing reads with programmed edits and few of the sequencing reads (about 5-17%) containing small indels.
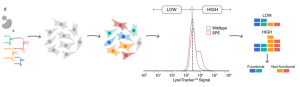
Figure 1. Establishment of a functional assay for variants in NPC1.
To show that this strategy is generalizable to other genes, the authors further developed a cell growth assay for SPE in the tumor suppressor BRCA2. Through a similar haploidization method followed by SPE and downstream sequencing at two timepoints, the authors assayed 465 different BRCA2 variants. In this case, most (252/300) missense variants were classified as functional, while all nonsense (59/59) were classified as nonfunctional. These data suggest that pairing locus-specific haploidization with SPE enables highly efficient functional characterization at scale.
Why I selected this preprint
I have performed research for a number of years aimed at functional characterization of individual missense variants in epilepsy-associated genes such as SCN3A or SZT2. I have been closely monitoring the literature on different strategies for functional characterization at scale as I believe this is a critical new technology for genetics to manage the large numbers of VUS coming from clinical genetic testing. This preprint addresses a number of significant technical limitations associated with SGE and it will be interesting to see whether other laboratories adopt and perhaps even improve upon some of the techniques reported in this preprint.
Questions for the authors
Q: Is there a concern that locus-specific haploidization alone will induce a cellular phenotype, such that sorting cells based on variants introduced by SPE is not possible? For example, in cases of haploinsufficiency where a 50% reduction is protein expression is sufficient to cause a genetic disorder. It may be that prime editing of a single allele may not produce significant effects beyond the difference seen between that haploidized cell line relative to its parental control line. Do you have an alternative strategy for these genes which may work?
Q: Are the costs of performing SPE similar to SGE? I would imagine with the more complex nature of pegRNAs relative to sgRNAs, there might be additional costs associated, but these costs may also be recouped later by the relative lack of indels (ie. Wasted cells).
References
- Findlay, G.M., Daza, R.M., Martin, B., Zhang, M.D., Leith, A.P., Gasperini, M., Janizek, J.D., Huang, X., Starita, L.M., and Shendure, J. (2018). Accurate classification of BRCA1 variants with saturation genome editing. Nature 562, 217-222.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.30851
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioinformatics category:
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the genetics category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
Also in the molecular biology category:
'Preprints by preLighters': Cell loss disrupts mechanical homeostasis to drive retinal pigment epithelium ageing-like phenotype in vitro
Reinier Prosee, Teodora Piskova
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
preLists in the bioinformatics category:
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the genetics category:
Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology 2026
The Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology, 2026, was organised by Jun Wu (UT Southwestern), Jianping Fu (University of Michigan) and Miki Ebisuya (TU Dresden) and held at Asilomar Conference Grounds in California (US). The meeting discussed recent advances made in establishing stem-cell-based embryo models, what fundamental insights into developmental processes have been gleaned from them, as well as how they are beginning to be applied more widely. This prelist contains preprints by presenters at the talk and poster sessions at the conference, which our Reviews Editor in attendance spotted. Please do reach out to preLights@biologists.com if you notice any that we’ve missed.
| List by | Ingrid Tsang |
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the molecular biology category:
Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology 2026
The Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology, 2026, was organised by Jun Wu (UT Southwestern), Jianping Fu (University of Michigan) and Miki Ebisuya (TU Dresden) and held at Asilomar Conference Grounds in California (US). The meeting discussed recent advances made in establishing stem-cell-based embryo models, what fundamental insights into developmental processes have been gleaned from them, as well as how they are beginning to be applied more widely. This prelist contains preprints by presenters at the talk and poster sessions at the conference, which our Reviews Editor in attendance spotted. Please do reach out to preLights@biologists.com if you notice any that we’ve missed.
| List by | Ingrid Tsang |
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (3 votes)
(3 votes)