Epiblast formation by Tead-Yap-dependent expression of pluripotency factors and competitive elimination of unspecified cells
Posted on: 29 November 2018
Preprint posted on 21 October 2018
Article now published in Developmental Cell at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.05.024
Differentiate or die! A new role for cell competition and Hippo signalling in the early mouse embryo
Selected by Sarah Bowling, Teresa RayonCategories: developmental biology
Background of the preprint
During animal development, one single cell divides to generate every cell type in the body. This process is incredibly complex, highly robust, but perhaps most remarkable it is very flexible. For example, embryos containing mutant cells from early developmental stages are able to develop normally (Tam and Rossant, 2003 and references therein). Understanding how developing systems succeed in generating millions of distinct cell types while withstanding perturbation is an intriguing and poorly investigated question in biology.
Cell competition has emerged in recent years as one potential mechanism through which developing tissues tolerate disturbances and achieve quality control. During cell competition, less fit but viable cell types are selectively eliminated when in the presence of more fit cells. The process was initially described to remove mutant cells in developing Drosophila tissues and has since been described in mouse development. Specifically, during mouse gastrulation (around embryonic day (E) 6.0), cells that are karyotypically abnormal or mutant (Sancho et al, 2013; Bowling et al, 2018), those that have differentiated precociously (Diaz-Diaz et al, 2017), or those that have elevated p53 levels (Zhang et al, 2017) are eliminated, resulting in a selected epiblast cell pool (Claveria et al, 2013).
In this preprint, the authors investigate the mechanisms which safeguard cell fitness at an earlier stage of mouse development: the blastocyst (E3.5). During this stage, around 10 cells exist in the inner cell mass and specify to either epiblast fate (becoming all cells of the future embryo), or to primitive endoderm fate (contributing to extra-embryonic tissues). The authors propose that since such a small number of cells seed the entire body, it is likely that quality control mechanisms act to boost cellular fitness. Furthermore, the authors investigate roles of Hippo signalling, a pathway that has important roles in early fate decision events, in mediating pluripotency in the blastocyst. In doing so, the preprint reveals both a novel role for Hippo signaling in regulating pluripotency and the existence of cell competition mechanisms in the blastocyst.
Key findings of the preprint
- Hippo mutant cells are eliminated through cell competition in the blastocyst
Initially the authors demonstrate that cell competition is triggered by differences in Hippo pathway activity: deletion of Hippo signalling components Tead or Yap in a small number of cells leads to their apoptotic elimination during mid-blastocyst development (embryonic day (E) ~3.75). Importantly, the elimination is cell non-autonomous as Tead-/- and Yap-/- embryos survive until embryonic day (E) 11.5 and E8.5, respectively.
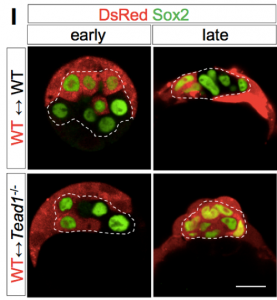
Elimination of Tead-/- cells from wild-type embryos during blastocyst development
- Hippo signaling regulates cell pluripotency
Next the authors investigate the role Hippo signaling could play in the blastocyst. First, the authors identify a strong correlation between Yap and pluripotency factor expression (particularly Sox2) in the developing blastocyst, hinting at a potential link between Hippo signaling and pluripotency. Supporting this, the authors demonstrate that Tead-/- cells have lower Sox2 expression than surrounding wild-type cells in chimeric blastocysts. Finally, culturing chimeras in 2i media, which maintains naïve pluripotency, rescues the competitive elimination of Tead-/- cells. Together, these data indicate a role for Hippo in regulating pluripotency in the inner cell mass, but also suggest that cell competition could act to remove unspecified cells during blastocyst development.
- Cell competition removes unspecified cells in the embryo
Finally, the authors further probe the possibility that cell competition functions to remove unspecified cells from the blastocyst in normal conditions. During blastocyst development, cells either specify to epiblast fate and express Sox2, or specify to primitive endoderm fate and express Sox17. When the authors inhibit cell death in wild-type blastocysts and analyse the expression of these two markers, a new population of cells emerge that lack either Sox2 or Sox17 expression. The authors suggest that these ‘unspecified’ cells are normally eliminated through cell competition.
What we like about this preprint
- Use of mosaics to confront populations during pre-implantation (and generated by electroporation instead of microinjection!)
- Evidence of endogenous cell competition: a particularly high frequency of apoptosis was observed in early mid-blastocyst stage (64–95-cell) embryos in cells with weak nuclear levels of YAP.
- Novel mechanism for Hippo signalling pathway that couples growth control and fate choice, since embryos treated with inhibitors of apoptosis show a higher degree of unspecified cells and increased cell numbers in the inner cell mass.
Questions to the authors:
- What proportion of cells undergoing apoptosis during blastocyst development do you think are being subject to endogenous cell competition rather than cell-autonomous death?
- Do you expect to see the same effects on cell competition in primed mESCs versus naïve?
- What could be the cause some cells failing to specify during epiblast formation? Would this be expected to be intrinsic or extrinsic factors?
References
Tam and Rossant (2003) Mouse embryonic chimeras: tools for studying mammalian development. Development 2003 130: 6155-6163
Sancho, M et al (2013). Competitive Interactions Eliminate Unfit Embryonic Stem Cells at the Onset of Differentiation. Developmental Cell 26, 19-30.
Bowling, S et al (2018) P53 and mTOR signalling determine fitness selection through cell competition during early mouse embryonic development. Nature Communications 9(1):1763
Díaz-Díaz, C. et al. Pluripotency Surveillance by Myc-Driven Competitive Elimination of Differentiating Cells. Dev. Cell (2017)
Zhang, G. et al (2017). p53 pathway is involved in cell competition during mouse embryogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 114, 498-503.
Claveria, C (2013). Myc-driven endogenous cell competition in the early mammalian embryo. Nature 500, 39-44.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.6078
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
preLists in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)