Phospho-seq: Integrated, multi-modal profiling of intracellular protein dynamics in single cells
Posted on: 19 April 2023 , updated on: 1 April 2025
Preprint posted on 28 March 2023
Article now published in Nature Communications at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56590-7
Blair and colleagues present a novel scalable sequencing-based multi-omics technique callled Phospho-Seq that involves simultaneous measurement of chromatin accessibility and proteomics, followed by a computational integration of expression data.
Selected by Benjamin Dominik MaierCategories: bioinformatics, genomics, molecular biology
Updated 1 April 2025 with a postLight by Benjamin Maier
Congratulations to John Blair and colleagues on their manuscript now published in Nature Communications! The peer review file is available here, though it only includes details from the review process at Nature Communications, as the manuscript was previously reviewed at another journal. While the main findings remain unchanged, the manuscript has been extensively restructured and multiple sections have been added. Additional data and analyses have been incorporated to further strengthen and refine their conclusions. Below is my (naive) summary of key updates:
-
Quantitative Benchmarking of Phospho-seq: The authors benchmarked Phospho-seq against flow cytometry and ASAP-seq to assess its accuracy in protein measurements. Phospho-seq performed comparably to flow cytometry across multiple proteins, with a slightly higher but not statistically significant staining index. When compared to ASAP-seq using flow cytometry as a reference, Phospho-seq demonstrated a strong correlation (R² = 0.90) with ground truth measurements, while ASAP-seq showed a much weaker correlation, highlighting Phospho-seq’s superior accuracy and dynamic range.
-
Expansion to Retinal Organoids: The authors introduced human iPSC-derived retinal organoid models as a second dataset alongside the previously used three-month-old brain organoids. In a new section, “Intracellular Protein Staining Highlights Cell Type Differences in Human Retinal Organoids,” they describe how Phospho-seq identified 16 distinct cell clusters with differential protein marker expression and chromatin accessibility patterns. Notably, they discovered a previously unreported difference in pRPS6 phosphorylation between rods and cones, showcasing Phospho-seq’s potential for uncovering cell type-specific signaling variations.
-
Integration with Transcriptomic Profiling: The section “Extending Phospho-seq to Incorporate Transcriptomic Measurements” was rewritten to more accurately describe the integration of Phospho-seq with transcriptomic profiling using the 10X scATAC + RNA multiome kit. This approach enabled the simultaneous capture of protein, RNA, and chromatin accessibility data in retinal organoids. However, while it allowed for cell type identification, it came at a significant cost in data quality and throughput, with reduced molecular sensitivity across all modalities.
-
Identification of Transcriptional Co-factors: A new section, “Identification of Transcriptional Co-factors Through ADT-Motif Correlation,” was added, where the authors used Phospho-seq alongside a bulk GLI3 CUT&Tag dataset and a paired scRNA-seq + scATAC-seq dataset (10X multiome) from WT and GLI3 KO cells to identify GLI3 co-factors. Their analysis demonstrated that Phospho-seq data for GLI3 could predict genomic regions responsive to perturbation, highlighting its ability to identify putative co-factors and distinguish functionally regulated regions and genes.
Background:
Profiling of proteins using “multiomic” technology
Multimodal omics techniques involve the simultaneous readout of multiple types of omics data (such as transcriptomics and proteomics) to generate a more comprehensive understanding of biological systems. The first generation of methods to quantify proteins alongside other omics modalities [see CITE-seq (Stoeckius et al., 2017), REAP-seq (Wong et al., 2022), DOGMA-seq (Mimitou et al., 2021) and TEA-seq (Swanson et al., 2021)] were limited to the detection of surface proteins. Although hematopoietic samples can be characterised very effectively with these methods, there is a need for experimental protocols to measure intracellular and intranuclear protein levels in order to inter alia identify signalling cascades and characterise disease states. Some pioneering approaches [see ASAP-seq (Mimitou et al., 2021), inCITE-seq (Chung et al., 2021), NEAT-seq (Chen et al., 2022) and QuRIE-seq (Rivello et al., 2021)] to measure proteins inside cells have been published recently. However, they are limited in scalability due to reliance on commercially available conjugated antibodies and do not allow for trimodal readout in the same biological system.
Bridge Integration
The Satija lab recently published a preprint (Hao et al., 2022) to computationally harmonise unimodal single-cell measurements from two omics modalities (RNA and protein, chromatin, histone, or methylation) using separate multi-omics datasets as molecular bridges. The bridge dataset measures both modalities simultaneously, enabling the mapping of single-omics datasets onto each other. This enables the study of relationships between multiple omics readouts and facilitates experimental designs, as multi-omic technologies may only be applied to a subset of the experimental samples while cheaper/high-quality single-omics can be performed for all samples. In this preprint, Blair and colleagues use bridge integration to integrate single cell transcriptomics readouts into Phospho-seq.
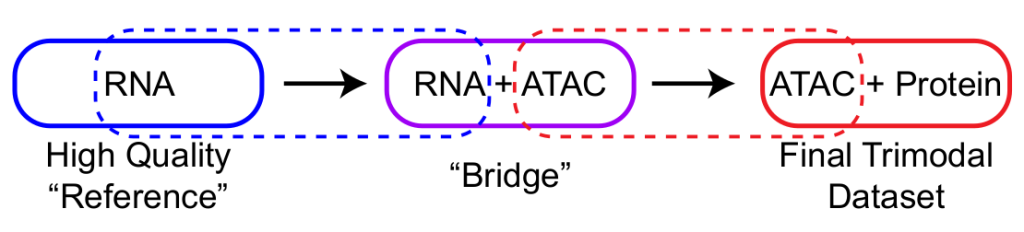
Fig. 1 Bridge Integration. Figure taken from Blair et al. (2023), BioRxiv published under the CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
Key Findings
Benchtop Preparation of Barcoded Antibodies for Protein Staining
Phospho-seq adapts a benchtop conjugation strategy described in van Buggenum et al. (2016) to generate large custom uniquely-indexed DNA-bound antibody panels for protein staining. As this method is easy to use, cost-efficient and compatible with commercially available antibodies (unconjugated and conjugated), the approach is scalable and suitable for many experimental settings.
Phospho-Seq Workflow
Following dissociation, single cells are subjected to fixation to maintain structural integrity and detergent-based permeabilization enabling oligonucleotide-tagged (barcoded) antibodies to enter the nucleus and the cytoplasm to bind their target proteins. Single-stranded DNA binding protein is added to the antibody pool to prevent nonspecific binding of cellular components to the barcoded antibodies thereby reducing background noise.
Finally, scATAC seq is performed using the Tn5 transposase enzyme and the 10x scATAC-seq kit to identify regions of chromatin that are accessible to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins. The method involves the use of a transposase enzyme that can insert sequencing adapters into open chromatin regions, followed by sequencing to identify the location and accessibility of these regions across the genome.
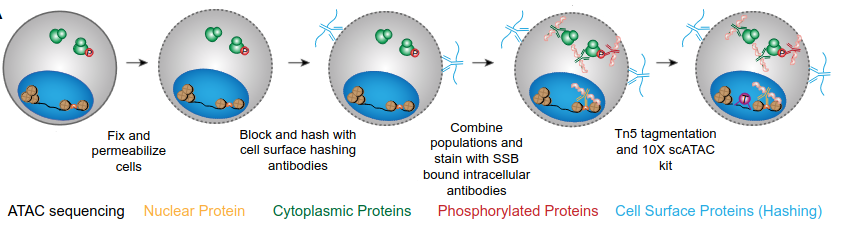
Fig. 2 Phospho-Seq Workflow. Figure taken and from Blair et al. (2023), BioRxiv published under the CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license and converted into landscape orientation.
In order to improve cell annotation and construct gene regulatory networks, single cell transcriptomics data is required alongside chromatin accessibility and proteomics readouts. Initially, the authors tried to directly generate trimodal readout in Phospho-seq, however they observed a considerable decrease in data quality due to incompatible fixation and permeabilization conditions for RNA and ATAC readout. Hence, they used a recently developed computational approach, bridge integration, to map single cell transcriptomics data to the Phospho-seq data yielding high quality trimodal data.
Phospho-seq Measurements Improve Biological Understanding
The authors demonstrated that the proteomics readout alongside a chromatin accessibility measurement is suitable to distinguish cell types. For instance, they found that the segregation and differentiation capacity of different induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines can be better explained by their readout instead of epigenetic differences.
Moreover, different distributions of unphosphorylated and phosphorylated proteins were measured upon activation of a signalling cascade indicating that the readout can be used as a proxy for stimulation even when the total abundance of the proteins remained the same.
This is highly relevant as it was also shown in the preprint that for some transcription factors (TFs), phosphorylation levels of nuclear TFs correlated with its activity while no correlation was found between the total abundance and the activity. The authors therefore suggested that phosphorylated TF levels may be more informative with regards to TF activity and reflect cellular states. Finally, the authors demonstrated that Phospho-seq is applicable to a broad range of samples as could be seen by its suitability to cell cultures, iPSCs and organoids.
Conclusion and Perspective
This preprint builds upon recently published multiomics approaches, allowing for the simultaneous characterization of intranuclear, intracellular, and cell surface proteins alongside RNA levels and chromatin accessibility. This method can improve our understanding of intracellular protein dynamics and posttranslational modifications, which cannot be detected by transcriptomics approaches. Furthermore, the method can potentially be combined with other state-of-the-art sequence-based omics approaches to measure more modalities simultaneously. A fixation and permeabilization routine compatible with scATAC and scRNA sequencing techniques could enable direct simultaneous measurement replacing the bridge integration.
Recent advances in sequence-based single-cell transcriptomics have led to the emergence of numerous single-molecule protein sequencing and fingerprinting technologies. This might create the opportunity to study the diversity of proteoforms and to distinguish between different posttranslational modifications, alternative splicing and germline variants in the future.
What I liked about this preprint
It is inspiring to read a preprint in a pioneering field and to see how novel methods build and expand upon previous ones. I found it particularly interesting how the authors integrated their recently published bridge integration into Phospho-seq and how it can help to obtain multimodal data. Additionally, it is beneficial if a method follows the FAIR guidelines, making all machines, reagents, and datasets publicly available and accessible to the community.
References
Chen, A. F., Parks, B., Kathiria, A. S., Ober-Reynolds, B., Goronzy, J. J., & Greenleaf, W. J. (2022). NEAT-seq: simultaneous profiling of intra-nuclear proteins, chromatin accessibility and gene expression in single cells. Nature Methods, 19(5), 547–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01461-y
Chung, H., Parkhurst, C. N., Magee, E. M., Phillips, D., Habibi, E., Chen, F., … Regev, A. (2021). Joint single-cell measurements of nuclear proteins and RNA in vivo. Nature Methods, 18(10), 1204–1212. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01278-1
Hao, Y., Stuart, T., Kowalski, M., Choudhary, S., Hoffman, P., Hartman, A., … Satija, R. (2022). Dictionary learning for integrative, multimodal, and scalable single-cell analysis. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.24.481684
Kelly, R. T. (2020). Single-cell proteomics: Progress and prospects. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics: MCP, 19(11), 1739–1748. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.R120.002234
Mimitou, E. P., Lareau, C. A., Chen, K. Y., Zorzetto-Fernandes, A. L., Hao, Y., Takeshima, Y., … Smibert, P. (2021). Scalable, multimodal profiling of chromatin accessibility, gene expression and protein levels in single cells. Nature Biotechnology, 39(10), 1246–1258. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-021-00927-2
Rivello, F., van Buijtenen, E., Matuła, K., van Buggenum, J. A. G. L., Vink, P., van Eenennaam, H., … Huck, W. T. S. (2021). Single-cell intracellular epitope and transcript detection reveals signal transduction dynamics. Cell Reports Methods, 1(5), 100070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100070
Stoeckius, M., Hafemeister, C., Stephenson, W., Houck-Loomis, B., Chattopadhyay, P. K., Swerdlow, H., … Smibert, P. (2017). Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nature Methods, 14(9), 865–868. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4380
Swanson, E., Lord, C., Reading, J., Heubeck, A. T., Genge, P. C., Thomson, Z., … Skene, P. J. (2021). Simultaneous trimodal single-cell measurement of transcripts, epitopes, and chromatin accessibility using TEA-seq. ELife, 10. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.63632
van Buggenum, J. A. G. L., Gerlach, J. P., Eising, S., Schoonen, L., van Eijl, R. A. P. M., Tanis, S. E. J., … Mulder, K. W. (2016). A covalent and cleavable antibody-DNA conjugation strategy for sensitive protein detection via immuno-PCR. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 22675. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22675
Wong, M., Kosman, C., Takahashi, L., & Ramalingam, N. (2022). Simultaneous quantification of single-cell proteomes and transcriptomes in integrated fluidic circuits. In Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.). Methods in Molecular Biology (pp. 219–261). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1771-7_15
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.34400
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioinformatics category:
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Computational design of pH-sensitive binders
Mohammed JALLOH
Longitudinal single cell RNA-sequencing reveals evolution of micro- and macro-states in chronic myeloid leukemia
Charis Qi
Also in the genomics category:
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the molecular biology category:
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
preLists in the bioinformatics category:
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the genomics category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the molecular biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)