Suppressor of Fused controls perinatal expansion and quiescence of future dentate adult neural stem cells
Posted on: 20 December 2018 , updated on: 21 December 2018
Preprint posted on 27 October 2018
Article now published in eLife at http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/elife.42918
What drives establishment of the quiescent neural stem cell pool in the dentate gyrus? The answer lies in the unusual activity of Sufu, a well-known regulator of Shh signalling
Selected by Ekaterina DvorianinovaCategories: developmental biology
Background
In the adult rodent brain, new neurons are produced in two areas – the cortical subventricular zone (SVZ) and dentate subgranular zone (SGZ) – and adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (DG) is associated with learning processes (Deng et al., 2010). Neurons originate from neural stem cells (NSCs) throughout life, first by asymmetric, then by symmetric self-consuming divisions. While the latter leads to NSC pool exhaustion, it suggests that a population of quiescent NSCs have to be established earlier in development for proper maintenance of neurogenesis during adulthood.
Indeed, long-lived NSCs appear in the DG at E17.5, migrating from the hippocampus to the ventral and dorsal DG. One of the interesting pathways involved in long-lived NSC regulation is Shh signalling, with Shh ligand secreted by neurons in the embryonic amygdala and postnatal DG (Li et al., 2013). Previous studies have shown that deletion of Smoothened (Smo, which acts as Shh signalling transductor) from responsive cells in the DG, as well as Shh ligand removal from local neurons, undermines the emergence of long-lived NSCs and decreases the NSC pool (Han et al., 2008; Li et al., 2013). However, the following questions remain unanswered:
1) How is Shh activity regulated in space and time to provide the enlargement of the NSC pool in DG development?
2) What is the role of Shh signalling in the shift of NSCs to a quiescent state?
The authors focused their study on Sufu, a known negative regulator of the Shh pathway. They investigated Sufu’s role in the regulation of Shh signalling during DG development, expansion of long-lived NSCs and their transition to the quiescent state.
Key findings
To test whether Sufu regulates Shh signalling activity, the authors conditionally deleted Sufu from NSCs in mice harbouring a Gli1-LacZ (Shh-responding) transgene. A decrease in Shh signalling response of NSCs was observed during DG development, which is the exact opposite of the situation in the neocortex, where deletion of Sufu escalates Shh signalling activity. A significant reduction of Shh-responding cells in the ventral hippocampus of KO mice was confirmed in both prenatal (E15.4-P0) and postnatal (P7) development. Moreover, expression of Gli1, one of the transcription factors that transduce Shh signalling to downstream targets, was also significantly down-regulated in Sufu-KO mice at P0, demonstrating that removal of Sufu decreases Shh signalling activity. While the number of NSCs (in SGZ) labelled with a stem cell marker did not vary between control and Sufu-KO mice, the percentage of proliferating NSCs was lower in KO. This is in contrast to Smoothened (Smo2) mutant mice in which Shh signalling is constitutively active and the pool of proliferating NSCs is increased. Given that Sufu KO is expected to upregulate Shh pathway, we would expect more similarity between Sufu-KO and SmoM2 mice. Instead, Shh downregulation is described after Sufu KO in NSCs. This observation allows us to hypothesize that the way in which Sufu is involved in Shh signalling may differ between specific NSC subtypes.
Since neurogenic competence of NSCs in adult DGs was not affected by Sufu deletion at
developmental stages in hGFAP-Sufu-KO (astrocyte-specific Sufu knock-out) and hGFAP-Sufu-
KO;Gli1-lacZ/+ 8-week old mice, and at the same time, the latter group showed a lower number of newborn neurons, it led to the assumption that this mutant line has a reduced NSC pool. As expected, the amount of Sox2- and GFAP-positive (with Sox2 serving as a marker of stemness) radial NSCs in SVZ was diminished in hGFAP-Sufu-KO;Gli1-lacZ/+ mice, but also in hGFAP-Sufu-KO line. The latter can signify that the absence of Sufu provokes failure of NSC expansion in the first postnatal week since this period tends to be crucial in NSCs pool establishing. Experiments corroborated a compromised level of NSCs proliferation, which sequentially resulted in a smaller number of quiescent NSCs in adult DG.
One of the possible explanations for a decreased level of NSC proliferation during the first postnatal
week could be a premature transition of NSCs into a quiescent state. Double-labelling with
thymidine analogues revealed that while in control mice NSCs enter quiescence at P3-P7, in hGFAP-Sufu-KO and hGFAP-Sufu-KO;Gli1-lacZ/+ mice it happens earlier around P0-P3. In addition, NSCs in
control mice displayed a lower proliferation rate at P3 compared to mutants, pointing at the fact
that deletion of Sufu precociously lessens proliferation of NSCs and aggravate premature transition
to the quiescent state.
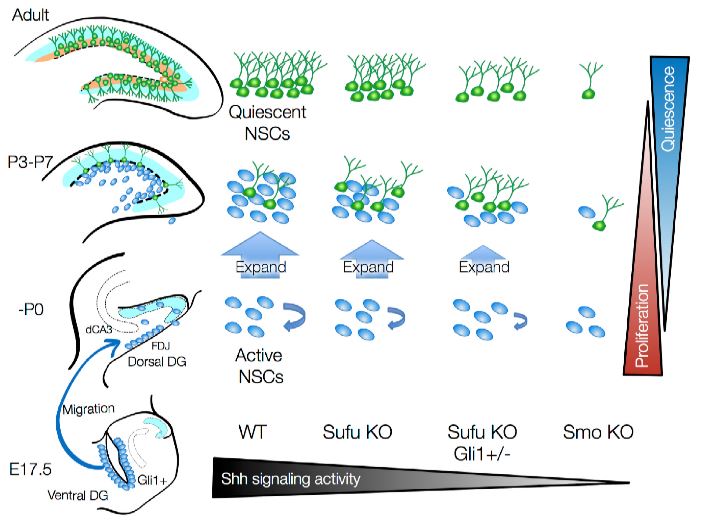
Fig. 1: Schematic summary illustrating the role of Sufu and Shh signaling activity in initial production, expansion and quiescent state transition of NSCs during DG development (Fig. 7 of the preprint)
Taken all together, these results demonstrate that regulation of Shh signalling through Sufu is vital
for the expansion of long-lived NSCs and the timely transition to a quiescent state during DG
development.
Further questions
The most impressive part I would underline in this paper is that Sufu behaves differently in various
NSC populations, playing in DG a role of an activator rather than a suppressor of Shh signalling.
Prominently, there is even a distinction in the response to Sufu-KO in different sub-locations of the
same region, like the dorsal DG and ventral DG, where the only proliferation of NSCs in the dorsal DG was affected.
In the future, I will be interested in getting answers to these questions:
1) Which mechanisms are involved in expansion and transition to quiescence in NSCs from
ventral DG? Since Sufu does not seem to take part in these processes, are they still mostly
driven by Shh signalling, or other pathways play the more important role there?
2) What is the exact trigger that switches Sufu from inhibitor to activator of Shh pathway? Are
there any intermediate signal transducers regulating this?
3) How will cells respond to Sufu-KD? Will we observe the same effect on NSCs in dorsal DG in
case of 30%/50%/70% decrease of Sufu expression, or only full ablation of Sufu can ensure
activation of Shh signalling in this cell population?
References
1) Deng, W., Aimone, J.B., and Gage, F.H. (2010). New neurons and new memories: how does adult
hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11, 339-350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2822
2) Han, Y.-G., Spassky, N., Romaguera-Ros, M., Garcia-Verdugo, J.-M., Aguilar, A., Schneider-
Maunoury, S., and Alvarez-Buylla, A. (2008). Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for
the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 11, 277-284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2059
3) Li, G., Fang, L., Fernández, G., and Pleasure, S.J. (2013). The ventral hippocampus is the embryonic
origin for adult neural stem cells in the dentate gyrus. Neuron 78, 658-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.019
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.6630
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
preLists in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)