daf-42 is an evolutionarily young gene essential for dauer development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Preprint posted on 24 April 2023 https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.04.24.538107v1
DAFining dauer – a novel secreted factor determines developmental trajectory in nematode.
Selected by Chee Kiang EweCategories: developmental biology
Background:
Dauer diapause – a state of hypobiosis – is widely conserved in many nematodes and appears to have driven the evolution of parasitism. For over five decades, free-living C. elegans has provided a convenient model to study the molecular mechanism of dauer formation. Dauers exhibit a distinct morphology which includes a specialized thickened cuticle with alae. Their body is constricted, and they develop a buccal plug that seals the mouth – all to promote survival in harsh environments (Cassada & Russell, 1975; Fielenbach & Antebi, 2008).
In C. elegans, the dauer developmental decision occurs at the late L1 stage though the commitment to dauer formation does not occur until mid-late L2d stage (Figure 1). Dauer entry is influenced by environmental factors (food availability, temperature, and pheromone) and is regulated by multiple signaling pathways, including the conversed insulin signaling pathway, TGFβ, and others. Mutants that show a dysfunctional dauer/adult developmental switch can be broadly divided into two classes: dauer-constitutive (Daf-c) and dauer-defective (Daf-d). While Daf-c mutants always enter dauer diapause, Daf-d animals never form dauer even in the presence of environmental triggers (Fielenbach & Antebi, 2008).
In this preprint, Lim and colleagues report a novel regulator of dauer development – DAF-42. Unlike the “classical” Daf-c and Daf-d that regulate the dauer entry decision, DAF-42 promotes L2d-to-dauer transition. Interestingly, despite the essential role of DAF-42 in dauer development, it is poorly conserved outside of the Caenorhabditis genus, suggesting rapid evolution of the dauer gene regulatory network.
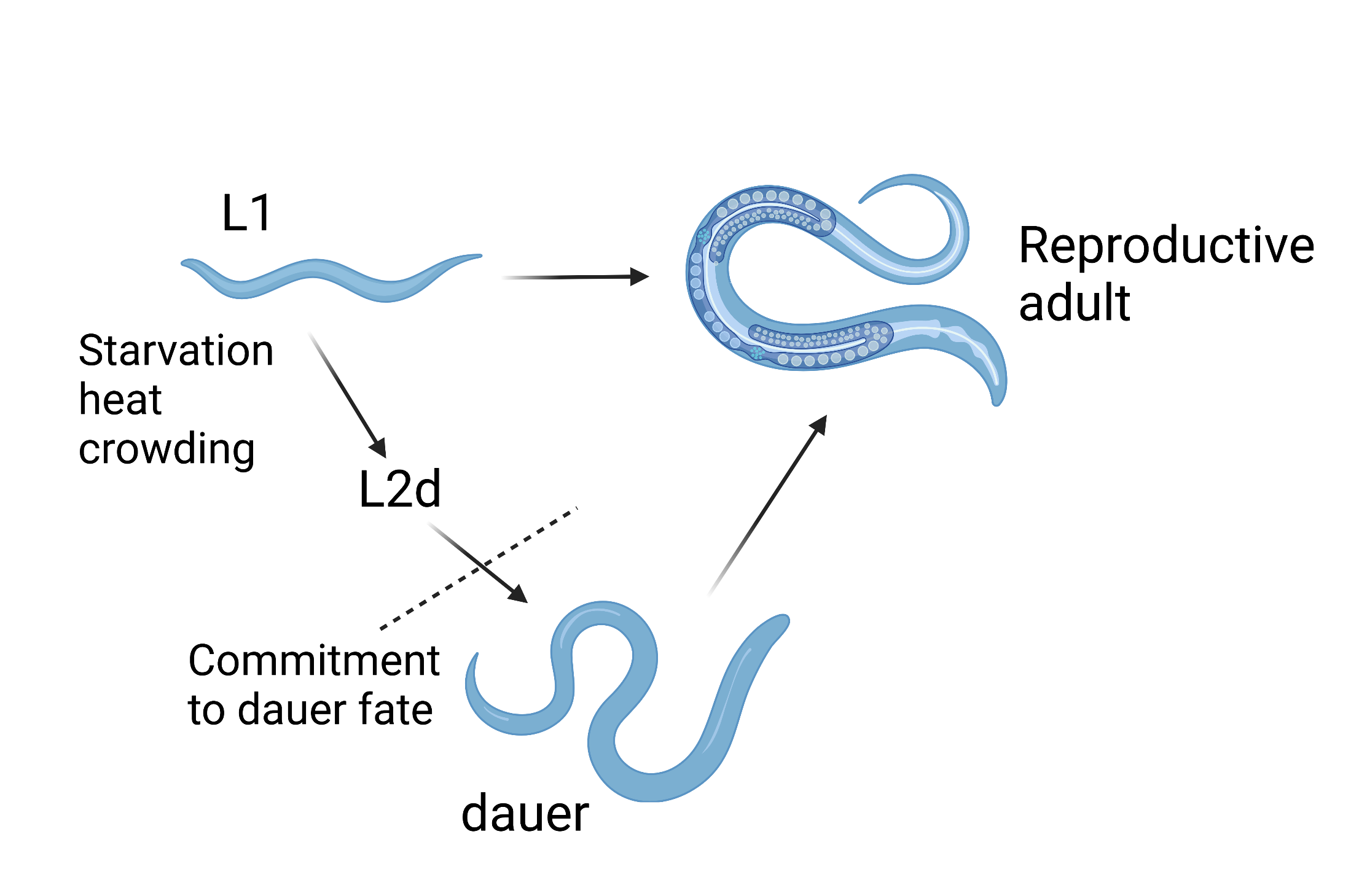 Figure 1: C. elegans life cycle. C. elegans first stage (L1) larvae grows into reproductive adults in ~3 days at 20OC. In unfavorable growth conditions, the L1 animal can develop to form dauer, which can live several months without food. The dauer can resume reproductive development when the environment recovers.
Figure 1: C. elegans life cycle. C. elegans first stage (L1) larvae grows into reproductive adults in ~3 days at 20OC. In unfavorable growth conditions, the L1 animal can develop to form dauer, which can live several months without food. The dauer can resume reproductive development when the environment recovers.
Major findings:
- daf-42 is a novel gene required for dauer entry.
By combining a screen for C. elegans mutants defective in dauer formation with genetic mapping-by-sequencing, the authors found that mutants lacking daf-42 failed to develop into dauer and would die when grown under dauer-inducing conditions. Next, the authors introduced the daf-42 mutation into worms carrying daf-2(e1370), a temperature sensitive Daf-c mutation, and could show that daf-2(-); daf-42(-) double mutants arrest at the L2d stage, while daf-2(-) single mutants robustly developed into dauers at 25oC. daf-2(-); daf-42(-) double mutants showed a degraded pharynx and molting defects. Moreover, dauer alae and cuticles were not properly formed in daf-2(-); daf-42(-) animals, indicating that daf-2(-); daf-42(-) animals can initiate the dauer formation program but fail to complete the developmental transition. Supporting this notion, removing DAF-7 (TGFβ ligand) or DAF-9 (cytochrome p450 enzyme in the steroid hormone pathway), both of which regulate the dauer entry decision, failed to rescue daf-42(-) lethality as DAF-42 functions downstream of the decision point influenced by harsh environmental conditions.
- DAF-42 is an unstructured secreted protein that promotes L2d-to-dauer transition.
The authors reported that DAF-42 is a large protein with 17 isoforms. It is largely disordered and contains a signal peptide at the N terminus.
By examining transcriptomic data and transgenic reporters, the authors found that daf-42 is expressed in the seam cells (specialized hypodermal cells) during dauer entry. Indeed, expressing daf-42 under the control of a seam cell promotor could partially rescue the lethality of daf-2(-); daf-42(-) double mutants. The authors could show that DAF-42 is secreted from the seam cell to the peripheral hypodermis and cuticle during L2d stage, perhaps to promote molting during the L2d-to-dauer transition.
Next, the authors examined the transcriptomic differences between daf-2(-) single and daf-2(-); daf-42(-) double mutants and found that daf-2(-); daf-42(-) worms showed significant changes in gene expression during L2d, but not at an earlier point, supporting the model in which DAF-42 acts after dauer commitment in L2d. Intriguingly, many genes upregulated in daf-2(-); daf-42(-) are related to immune system and defense response.
- daf-42 is a newly evolved gene in the Caenorhabditis
It is clear that DAF-42 plays an essential role in dauer development. Surprisingly, however, DAF-42 homologs are not found in nematodes outside of the Caenorhabditis genus. Within Caenorhabditis, the DAF-42 protein sequences exhibit substantial variation. These results indicate that the gene regulatory network for dauer development is highly plastic and a young gene has quickly evolved to gain essential developmental functions.
What I like about this preprint:
This preprint identifies an unusual daf gene that promotes dauer development. The data presented is solid. Most surprisingly, daf-42 appears to be evolutionary young and to have quickly evolved to adopt an essential developmental role. This study has shed light on the evolution of the nematode dauer signalling pathway and provides an interesting paradigm to further study the evolutionary trajectory of young genes.
Questions for the authors:
- For the translational reporter, is it possible that not all isoforms are tagged, and daf-42 expression is not fully captured?
- Have you looked closer at the fate of DAF-42 in the target tissues? Does it, for example, get taken up by the hypodermal cells?
- It appears that DAF-42 may play an important role in molting as evident by the mutant phenotype and daf-42 expression pattern. Did you observe changes in the expression of genes regulating molting in the mutant?
References:
Cassada, R. C., & Russell, R. L. (1975). The dauerlarva, a post-embryonic developmental variant of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Developmental Biology, 46(2), 326–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-1606(75)90109-8
Fielenbach, N., & Antebi, A. (2008). C. elegans dauer formation and the molecular basis of plasticity. Genes & Development, 22(16), 2149–2165. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1701508
Posted on: 11 May 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.34630
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Alteration of long and short-term hematopoietic stem cell ratio causes myeloid-biased hematopoiesis
Temporal constraints on enhancer usage shape the regulation of limb gene transcription
OGT prevents DNA demethylation and suppresses the expression of transposable elements in heterochromatin by restraining TET activity genome-wide
preLists in the developmental biology category:
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (1 votes)
(1 votes)