Prenatal exposure to environmental stressors alters gut macrophage development and gastrointestinal function of male offspring
Posted on: 9 April 2025 , updated on: 10 April 2025
Preprint posted on 24 March 2025
’Listen to your gut’ – lessons from the brain. How prenatal environmental stressors disrupt gut immune cells, impair synaptic pruning in the gut and contribute to neurodevelopmental issues
Selected by Jeny JoseCategories: developmental biology, immunology, neuroscience
Introduction
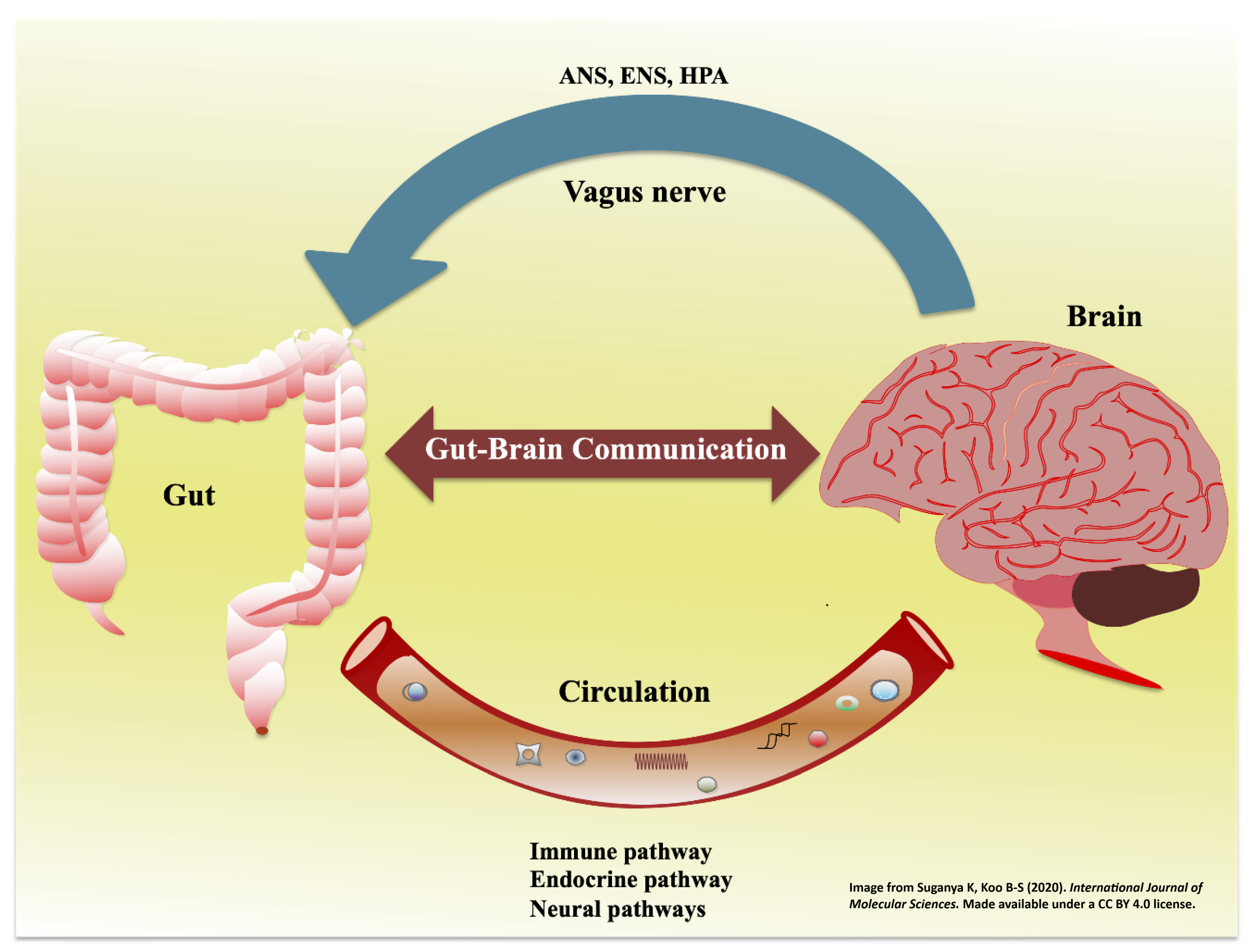
More and more studies point at the critical role of environmental factors in shaping developmental outcomes. To give but one example, exposure to immune challenges during pregnancy, whether through infections, toxicants, or maternal health issues, can significantly increase the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) like autism. What’s particularly intriguing is that recent findings point to the gut-brain axis as a central player in this process.
Many individuals diagnosed with NDDs also experience common gastrointestinal problems, such as gastritis, diarrhea, or acid reflux. Interestingly, these symptoms often appear around the same time as behavioural changes associated with NDDs. This suggests that there may be a link between brain development and GI health, with potential implications for understanding how environmental factors impact both.
Despite a growing body of evidence, the biological mechanisms behind this gut-brain connection remain unclear, especially in relation to how environmental exposures might contribute to these disruptions. Understanding these connections could be key to unlocking better prevention and treatment strategies for NDDs.
Former research shows a fascinating difference between the two genders. Prenatal exposure to air pollution and maternal stress, which are two major risk factors for NDDs, affects male and female mice differently. While male mice exhibit significant social deficits, females appear to be resilient. Moreover, changes in the gut microbiome and gut architecture were observed in the males, and remarkably, normalizing the gut microbiome at birth prevented the emergence of these social deficits later in life. This suggests that the gut plays a key role in the development of behaviour through its influence on brain function and the gut-brain connection as a potential therapeutic target for NDDs
In this preprint, Nguyen and colleagues explored the effects of combined prenatal stressors on intestinal macrophages and gastrointestinal function in mice during the early postnatal period, specifically at postnatal day 4 (P4) and P14. Their findings highlight how prenatal environmental stressors can induce gastrointestinal dysfunction and offer potential insights into the mechanisms behind this dysmotility, particularly in males.
Key Results
Gastrointestinal Architecture:
Pregnant mice were exposed to chronic air pollution and maternal stress. Their male offspring showed significant changes in small intestine architecture including shorter villi and a thinner muscularis layer with no similar changes in female offspring.
Macrophage Activity:
The male offspring had reduced F4/80 expression, a macrophage surface receptor, in intestinal macrophages, with no significant changes in macrophage density. This suggests altered macrophage function rather than population size in response to exposure to chronic air pollution and maternal stress.
Impaired Synaptic Pruning and Disrupted Enteric Nervous System Development:
Gene expression studies revealed an upregulation of motor neuron markers (SNAP25, ChAT, nNOS, DBH) in the small intestine of male offspring at P14, suggesting disrupted enteric motor neuron development. These changes were not seen in sensory neurons or other neuron subtypes. Besides this, the preprint authors also noticed an impairment of macrophages’ synaptic pruning function, where macrophages engulf and clear synaptic material, in the muscularis layer of the small intestine. This impairment in synaptic engulfment, particularly in the muscularis layer of males, may directly affect the development and function of the enteric nervous system. Notably, the synaptic pruning function of these macrophages may be compromised due to their origin from the yolk sac, a precursor to immune cells, which could further contribute to the developmental abnormalities observed in the enteric nervous system.
They found that male mice exhibited unique responses to these stressors, with notable transcriptional changes linked to gut motor function starting in the second postnatal week. A striking male-specific deficit was identified in the ability of intestinal macrophages to refine synapses within the muscularis externa, the part of the gut responsible for smooth muscle contractions. Furthermore, accelerated GI transit was observed in prenatally stressed males at P14, indicating enteric neuron hyperactivity, a symptom of GI dysmotility.
Gastrointestinal Motility:
The GI transit rate in male offspring was accelerated at P14, indicating potential gastrointestinal dysmotility linked to disrupted enteric nervous system function. This observation was again specific for male offspring of mothers exposed to chronic air pollution and maternal stress.
Why This Research is Important
Children with neurodevelopmental disorders often experience various GI problems, such as gastritis, bloating, and motility disorders. While the immune system is thought to play a role in these issues, most research has focused on inflammatory pathways in later life, neglecting the developmental functions of immune cells in the gut. This study found that intestine-resident macrophages, which typically help maintain homeostasis by engulfing synaptic material, were impaired by prenatal exposure to air pollution and maternal stress, a model for environmental factors linked to neurodevelopmental disorders. This impairment disrupted the normal development of the enteric nervous system, particularly affecting synaptic pruning in the muscularis layer of the small intestine. The impaired macrophage function, specifically in synaptic engulfment, could be responsible for dysmotility in the gut, contributing to GI disorders observed in NDDs.
These findings suggest that environmental exposures during gestation can affect the development of both the central nervous system and the gut-brain axis, potentially leading to long-term GI and behavioural issues.
The study showed that males were particularly affected, with disruptions in macrophage function leading to changes in motor neuron activity in the small intestine, and females, when affected, were affected to a lesser degree.
While not a complete 100%, mice share around 85-90% of their genes with humans. This makes them valuable for studying human biology, genetics, and diseases. Many biological processes, such as immune function, metabolism, and neurodevelopment, are conserved between humans and mice.
Glossary
Enteric nervous system = a complex network of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Enteric neuron synapses = synaptic connections between neurons in the enteric nervous system, often called the “second brain,” and other neurons or target cells within the digestive system.
Macrophage = a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. It is part of the body’s defense mechanism and is involved in several important functions such as phagocytosis, tissue repair, and regulating other immune signals.
Microglial pruning = the process by which microglia, a type of immune cell in the brain, remove or “prune” unnecessary or excess synapses during brain development.
Muscularis layer = a layer of smooth muscle found in the walls of most parts of the digestive tract. It plays a crucial role in the movement of food through the gastrointestinal system.
Synapse = the junction or connection between two neurons (or between a neuron and another type of cell, such as a muscle or gland cell) where communication occurs.
Synaptic engulfment = the process in which one cell, typically a glial cell, surrounds and engulfs synaptic components, such as parts of a synapse or the whole synapse. This process is important for the maintenance and proper functioning of synapses in the brain. The cells that perform synaptic engulfment are usually microglia or astrocytes, which are types of glial cells in the brain.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.40037
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
Also in the immunology category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
Scalable transcription factor mapping uncovers the regulatory dynamics of natural and synthetic transcription factors in human T cell states
Inês Caiado
Also in the neuroscience category:
Electrophysiological correlates of conscious experiences during sleep: Lucid dreams, sleep paralysis, out-of-body experiences, and false awakenings
uMontreal Neuro preLighters et al.
PPARδ activation in microglia drives a transcriptional response that primes phagocytic function while countering inflammatory activation
Isabel Paine
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
preLists in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the immunology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the neuroscience category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)