A direct and widespread role for the nuclear receptor EcR in mediating the response to ecdysone in Drosophila
Posted on: 4 February 2019
Preprint posted on 10 January 2019
Article now published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences at http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1900343116
Here, there, everywhere: extensive and dynamic genome binding by a steroid hormone receptor highlights the interconnection between systemic and local cues for organ development
Selected by Natalie DyeCategories: developmental biology, genetics
Hormones regulate so much of our physiology and development. Just think back to those gloriously awkward times at puberty or consider what happens during pregnancy– so many changes in the body happening at once, all in response to changing hormones. But of course, every tissue responds differently – some tissues grow while others shrink or change shape. How does that work?
The authors of this preprint start addressing this question by profiling gene expression changes and genome-wide binding of the steroid hormone receptor in the Drosophila wing during the transition from larval to pupal life stages – the fly’s puberty, if you will. The steroid in flies is called ecdysone and it is received by a nuclear hormone receptor called EcR.
Drosophila has long been a favorite model for studying hormone signaling, and (for once) it wasn’t because of the fly’s genetic tractability (at least not at first). Researchers in the 1950s-60s figured out how to culture salivary glands ex vivo to directly study the response to exogenously added hormone. The glands have huge chromosomes that make visible bulges when gene expression is activated, so researchers didn’t even need fancy microscopy to track the response to hormone. From these experiments, Michael Ashburner proposed that ecdysone binds to a (then unknown) receptor that activates relatively few targets, who then go on to activate many additional downstream targets. Thus, Ashburner proposed that much of ecdysone’s effects on the tissue are only indirectly mediated by its receptor.
While this model provided an influential framework for hormone-induced gene expression, it remained unclear how tissue-specific responses are elicited. After all, the salivary glands die after larval stages, while “imaginal” tissues like the wing undergo dramatic morphogenesis to make adult structures. Previous works have profiled gene expression changes occurring in the wing at pupariation, but the mechanisms and direct role of EcR were not addressed. Thus, we are overdue for a systems-level analysis of EcR’s role in eliciting steroid dependent expression in the wing.
Summary of the preprint:
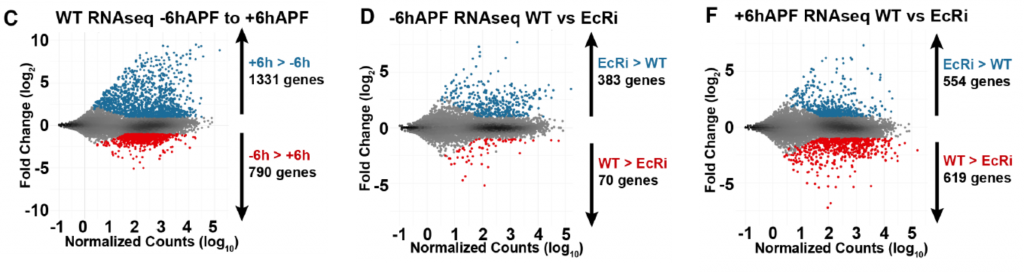
- Authors perform RNA-seq on wild type and EcR-depleted wing discs at two timepoints: 6hr before and 6hr after the larval-to-pupal transition (Fig 1C). Their results suggest that:
- Before the transition, EcR mostly prevents the precocious activation of ~400 genes whose expression will increase at pupariation (Fig 1D).
- After the transition, EcR affects both the activation and repression of >1000 genes. Most of these genes either increase or decrease during the larval-to-pupal transition (Fig 1F).
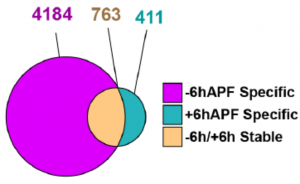
- Using CUT&RUN (a recently developed alternative to ChIP-seq) to identify the sites on the genome where EcR binds, authors find that:
- Before the larval-to-pupariation transition, EcR binds extensively to the genome at numerous sites, both canonical and wing-specific genes.
- After, EcR is lost from most of its previous targets but gained at hundreds of new sites.
- The sites that stably bind EcR through the transition have the highest density of the EcR-motif and the highest overlap with sites bound by EcR in the S2 culture cell line. These sites tend to be genes involved in steroid-mediated signaling.
- Most of the sites bound by EcR (except for those relatively few that also bind in S2 cells) are functionally classified as imaginal disc-derived wing morphogenesis genes.
- Not all of the genes found with RNA-seq to vary during the larval-to-pupal transition are bound by EcR – suggesting that there are both direct and indirect effects of ecdysone.
- By examining two EcR target genes, authors conclude that EcR can affect both the temporal and spatial patterns of gene expression in the developing wing:
- The canonical target gene, broad, does not require EcR for its expression and in fact is ectopically high in the absence of EcR, suggesting that EcR is a repressor of broad, preventing its concentration from rising too fast. Interestingly, broad’s expression still increases over time without EcR, suggesting that other factors also regulate this key steroid target.
- The non-canonical target gene, delta, was found to have two EcR-enhancers with spatially restricted expression patterns. Mutant analysis suggests that EcR, together with its binding partner Usp, repress delta. Unlike broad, delta expression does not change through the larval-to-pupal transition. Thus, EcR/Usp is most likely to influence the spatial but not temporal activation of delta – a somewhat surprising role for a hormone receptor.
My 2-cents:
While the authors do identify a relatively small set of core target genes bound by EcR in the wing and in other cell types, what is more striking is that they also find EcR directly, dynamically, and tissue-specifically binding the genome upstream of numerous genes that are required specifically for wing development. Thus, the role of EcR seems much broader than the Ashburner model would have predicted.
The connection between ecdysone and wing development genes is actually not surprising to me. Using culture experiments analogous to those early ones in salivary glands, I previously showed that the expression of numerous genes involved in wing patterning, including delta, are sensitive to steroid during larval stages. But I could not conclude much about the mechanism at the time. This preprint now makes me believe that what I observed is directly attributable to EcR acting as a repressor for many wing patterning genes, and that the low levels of steroid circulating during larval stages partially relieves this repression to control expression in time and/or space.
Importantly, wing patterning was heretofore considered to be largely tissue-autonomous: activity gradients in developmental signaling pathways such as Hedgehog and Wnt collaborate to regionally subdivide the wing tissue, specifying cells that will make, for example, the wing veins. While extensively studied, what controls the timing has remained mysterious. For example, the Hedgehog gradient is present from the very beginning of wing development, so why are veins only specified in late larval stages? Furthermore, morphogen gradients persist through the larval-to-pupal transition, yet the cells do something different with the information, undergoing morphogenesis instead of growth. How?
The intricate connection between ecdysone and wing patterning revealed in this preprint and other recent work suggests that systemic cues like ecdysone provide key tissue-non-autonomous inputs. But importantly, this work also indicates that the information flow is not unidirectional: tissue-specific genes clearly affect the site-specific binding of EcR and thereby the response to steroid. Thus, the picture now emerging is that bidirectional feedback exists between tissue autonomous and non-autonomous signals for wing patterning and growth. The exact nature of these interactions – e.g., which tissue-specific factors interact with EcR – will be interesting to discover in future work.
One last thing that I’m curious about is the potential role of insulin in regulating the dynamics or specificity of EcR genome binding. Insulin is a major signal coordinating systemic development with nutrient availability, and at the larval-to-pupal transition, the animals stop feeding and insulin signaling changes. Crosstalk exists between insulin and steroid signaling pathways in many animals: in humans, consider the link between childhood obesity and the onset of puberty; and in insects, direct interactions have been observed between EcR and the insulin-responsive transcription factor FoxO. Thus, I would be curious to know how EcR binding changes during starvation or mutants of insulin receptor or FoxO.
For more information…
Review of EcR and a little history of the Ashburner model:
Transcriptional profiling of wing discs grown ex vivo +/- ecdysone (NOTE: shameless self-promotion): http://dev.biologists.org/content/early/2017/10/13/dev.155069
Review of inter-organ signaling coordinating growth in Drosophila: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665074/
Ecdysone-induced expression in cell lines:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19237466 &
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.8235
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
Also in the genetics category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
preLists in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the genetics category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)