Coordination of Tissue Cell Polarity by Auxin Transport and Signaling
Posted on: 4 August 2019
Preprint posted on 11 July 2019
Article now published in eLife at http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.51061
Leave no PIN standing – vein patterning in Arabidopsis involves more than PIN-mediated auxin transport
Selected by Martin BalcerowiczCategories: developmental biology, plant biology
Background: Auxin transport shapes the Arabidopsis vein network
The plant vascular system, which transports water, nutrients and assimilates, represents a network of cell files extending through all organs. In leaves, these vascular strands are referred to as veins or nerves and are arranged in a ramified pattern with a central midvein, lateral loops and higher order terminating and connecting veins1. They are inherently polar structures as their cells are elongated along the vein axis and the vein network connects the leaf with stem vasculature. In agreement with this, vein formation requires coordination of cell polarity, and the plant hormone auxin has long been established as a central player in this process2.
In particular, polar auxin transport defines the site of vein formation: from a local maximum, auxin flows towards the basal part of the plant, and this flow determines where vascular strands are formed1. This polarity in auxin flux is controlled by auxin efflux carriers of the PIN-FORMED (PIN) family, especially PIN1, and directed auxin flux feeds back on PIN1 asymmetrical distribution1,3. How polar PIN1 distribution is established is not fully understood, but the guanine-nucleotide exchange factor GNOM (GN), which regulates vesicle formation in membrane trafficking, is thought to play a pivotal role in this process. gn mutants display altered venation patterns as well as changes in PIN1 subcellular trafficking, suggesting that GN controls PIN1 distribution during vein pattern formation4.
Key findings: Not only auxin transport, but also auxin signalling contributes to vein patterning downstream of GN.
The authors decided to test the prevailing hypothesis that GN controls vein patterning via polar distribution of PIN proteins. They first confirmed that vein patterning is severely compromised in gn mutants. Intermediate gn alleles displayed generally thicker veins, lateral veins running parallel to instead of joining the midvein and narrow clusters of vascular elements forming near the leaf margin. In several strong gn mutant alleles the vein network was reduced to a central, shapeless cluster of vascular elements (Fig. 1). Furthermore, a PIN1::PIN1-GFP reporter showed a broader expression domain and displayed strongly reduced polarity in gn compared to the wild-type background. These observations agree with previous reports and with the idea that GN controls venation via PIN1 polar localisation.
PIN1 is part of an eight-member family, and plasma membrane-localised PIN3, PIN4 and PIN7 as well as ER-localised PIN6 and PIN8 contribute to vein patterning. Simultaneous mutation of these six PIN genes causes strong vein patterning defects, with many lateral veins failing to connect to the midvein and running parallel instead; this phenotype is also observed when plants are treated with the PIN auxin transport inhibitor NPA (Fig. 1). However, neither pin1,3,4,6,7,8 mutants nor NPA-treated wild type fully phenocopied the vein patterning defects of gn mutants, suggesting that additional factors act downstream of GN.
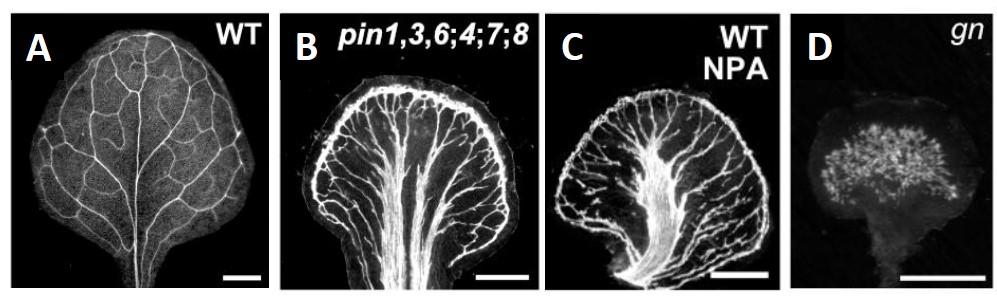
Figure 1: Dark-field illumination of mature first leaves of wild type (A), the pin1,3,4,6,7,8 mutant (B), wild type treated with the auxin transport inhibitor NPA (C) and the severe gn-13 mutant (D). Scale bars represent 0.5 mm (reproduced with altered numbering from Verna et al., Fig. 5A, C, D and Fig. 8A).
Besides PINs, transport proteins of the ATP BINDING CASSETTE B (ABCB) and AUXIN1/LIKE AUX1 (AUX1/LAX) families are known to control polar auxin efflux and influx, respectively. To test whether these transporters contribute to GN-mediated vein patterning, Verna et al. analysed the phenotype of various combinations of pin, abcb and aux1/lax mutants as well as of NPA-treated abcb and aux1/lax mutants. None of the respective mutants displayed gn-like vein pattern defects, suggesting that ABCBs and AUX1/LAX transporters are not the missing component regulating venation downstream of GN.
Local auxin application can induce the formation of additional veins in the wild type, but intriguingly, Verna et al. also observed this effect in pin1,3,4,6,7,8 mutants. This implies that in the absence of PINs, there is still an auxin-dependent, yet apparently auxin transport-independent, mechanism inducing vein formation. Double mutants of TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1 (TIR1) and AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX 2 (AFB2) as well as mutants of AUXIN RESISTANT 1 (AXR1), which are both severely compromised in auxin signalling, display vein pattern defects such as open loops and fragmented veins. Treatment of these mutants with NPA to inhibit PIN function generated phenotypes similar to those of intermediate gn alleles. These phenotypes were also observed in axr1 pin1,3,4,6,7,8 and tir1 afb2 pin1,3,4,6,7,8 mutants, while combining gn and axr1 mutations did not further enhance the vein pattern defects. Finally, PIN1-GFP distribution is similarly altered in NPA-treated tir1 afb2 mutants and in intermediate gn mutants. Taken together, these observations suggest that AXR1- and TIR1/AFB2-mediated auxin signalling contributes to vein patterning and establishment of polarity downstream of GN.
What I like about this preprint
There is one word that came to mind after reading this preprint: thorough. The authors have performed an extremely comprehensive genetic and pharmacological analysis of vein patterning and thereby revealed that our knowledge about this process does not stretch as far as we previously thought it does.
Open questions/future directions
This study has raised many more questions about vein pattern formation since it has shown us that our previous concepts, while not incorrect, were clearly incomplete. As the authors state, the obvious follow-up question will be how auxin signalling, being inherently unpolar, can promote polarity in vein patterning, but this will potentially require years of investigation. Other questions more directly related to the present preprint are:
- Compromising PIN-mediated auxin transport and auxin signalling phenocopies intermediate, but not strong, gn mutant alleles. Is this difference due to residual auxin signalling in the tested mutant backgrounds, or could there be an auxin-independent component to GN function as well? In this regard, have the authors tested whether auxin application can still induce vein formation in NPA-treated tir1 afb2 or axr1 mutants?
- PIN1-GFP localisation is one read-out for polarity during the vein patterning process. It would be interesting to know whether the authors have looked at the subcellular localisation of any other PIN protein in a gn mutant background.
References/Further reading
- Scarpella E, Barkoulas M, Miltos Tsiantis M (2010) Control of Leaf and Vein Development by Auxin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001511.
- Sachs T (1981) The control of the patterned differentiation of vascular tissues. Adv Bot Res 9:151–262
- Linh NM, Verna C, Scarpella E (2018) Coordination of cell polarity and the patterning of leaf vein networks Curr Opin Plant Biol 41:116–124
- Richter S, Anders N, Wolters H, Beckmann H, Thomann A, Heinrich R, Schrader J, Singh MK, Geldner N, Mayer U, Jürgens G (2010) Role of the GNOM gene in Arabidopsis apical-basal patterning – From mutant phenotype to cellular mechanism of protein action. Eur J Cell Biol 89:138-144
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.12862
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
Also in the plant biology category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Actin Counters Geometry to Guide Plant Cell Division
Jeny Jose
The nucleus follows an internal cellular scale during polarized root hair cell development
Jeny Jose
preLists in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the plant biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)