Tandem duplication of serpin genes yields functional variation and snake venom inhibitors
Posted on: 9 October 2025 , updated on: 14 October 2025
Preprint posted on 10 January 2025
Article now published in Molecular Biology and Evolution at http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf290
This study shows coevolutionary adaptation in Neotoma macrotis, where duplicated SERPINA3 genes inhibit Crotalus venom proteases, revealing functional diversification and potential use in antivenom development.
Selected by Daniel Osorno Valencia, Marcus OliveiraCategories: biochemistry, evolutionary biology, genetics
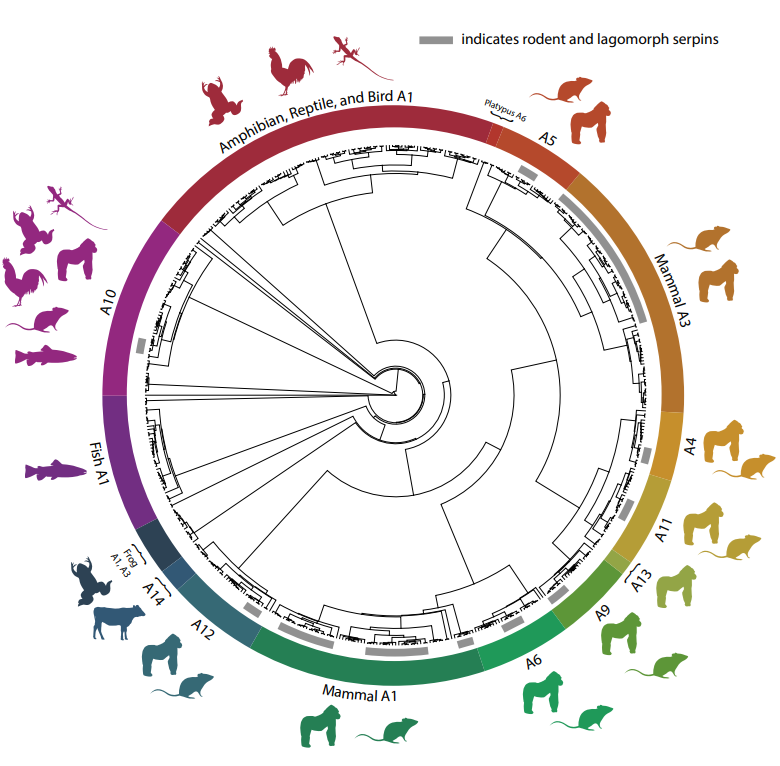
Figure from preprint made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
Why I think this preprint is important:
This study uncovers a novel mechanism underlying snake venom resistance in Neotoma macrotis, showing that tandem duplications of SERPINA3 genes have produced variants capable of inhibiting venom serine proteases (SVSPs) from Crotalus species. Phylogenetic and functional analyses reveal that paralogs like SERPINA3-3 and SERPINA3-12 form stable inhibitory complexes, suggesting adaptive neofunctionalization. These findings highlight gene duplication as an evolutionary defense strategy and offer potential biomedical applications for antivenom development.
Background:
Snake venom resistance is a classic example of coevolution between the predator and the prey. Some animals have developed it through evolution, by obtaining molecular tools that can serve as a defense mechanism against venom. This includes changes in the expression of some receptors that are normally recognized by toxins, expression of proteins in blood that can neutralize toxins, or even specific immune responses [1], [2], [3].
In some mammals, like the squirrel Otospermophilus beecheyi, proteins have been identified in blood serum that are capable of binding to the venom toxins and neutralizing their effects[4]. Similarly in the rodents Dipodomys ordii and Neotoma floridana factors have been found in their blood capable of neutralizing the toxic effects of metalloproteinases [5]. Furthermore, in Caecilians (amphibians) it has been documented that convergent evolution has led to mutations in acetylcholine receptors that prevent the action of neurotoxins found in snake venom [6].
In this study, the authors explore how the tandem duplication of genes from the family SERPINA, a serine protease inhibitor in rodents, have generated variants with the capability to inhibit serine proteases from snake venom of different species. They analyze the evolution of these genes across clades and demonstrate that some variants found in the species Neotoma macrotis can inhibit serine proteases found in snake venom in vitro, showing how tandem duplications are related to venom resistance in mammals.
Key findings:
Duplication and evolution of the SERPINA genes in rodents
The authors found that the genes SERPINA1 and SERPINA3 have undergone a lot of gene duplication events in rodents, especially in comparison to other classes of vertebrates. The resulting variations occurred independently in different lineages, especially in the genus Neotoma where the species N. macrotis, for example, has 12 paralogs of SERPINA3 and various of SERPINA1 (preprint Fig 2). Through phylogenetic analysis, the authors identified a birth–death evolutionary pattern, with multiple recent duplications in Neotoma and copy losses in other lineages. This diversification has generated species-specific gene families, suggesting that these duplications are not neutral but may be under adaptive selective pressure, possibly in response to ecological challenges such as envenomation by predators. These results provide the genomic basis to study the evolutionary function of SERPINAs as potential resistance mechanisms.
Functional expression of paralogs of SERPINA3 and inhibition patterns
The authors were able to express and isolate with high purity the recombinant version of the 12 paralogs of SERPINA3 found in N. macrotis. Most of the recombinant proteins showed a functional activity against diverse serine proteases (preprint Fig 3). It was observed that SERPINA 3-3, 3-5, 3-8, 3-10 and 3-12 formed complexes with chymotrypsin and cathepsin G, which the authors believe indicates an inhibitory capacity of the serine proteases. Additionally, it was observed that the degradation pattern of each SERPINA was different, indicating a diverse functionality. For example, SERPINA3-6 was degraded by proteases without forming complexes, showing that some copies may have lost inhibitory function. This functional diversity among paralogs suggests that gene duplication has allowed the exploration of new biochemical functions, possibly related to adaptation to external challenges such as venom exposure.
Inhibition of snake venom proteases by SERPINA3
Two paralogs, SERPINA3-3 and SERPINA3-12, were shown to inhibit snake venom proteases (SVSPs), forming covalent complexes with purified toxins such as RVV-V and Protac (preprint Fig 4 A and D), as well as with fractions of SVSPs from Crotalus oreganus, C. molossus and C. adamanteus. The authors indicate that SERPINA3-3 formed complexes with all venom samples (preprint Fig 5), being most effective against venoms from non-sympatric snakes (such as C. adamanteus), whereas venoms from local predators (C. oreganus) generated less inhibition, suggesting a possible case of counter-adaptation by the predator. The authors suggest that duplicated SERPINAs not only maintain general inhibitory function but have acquired the specific ability to neutralize venom toxins, representing a potential mechanism of adaptive resistance. Furthermore, the formation of multiple complexes suggests that a single paralog may inhibit several isoforms of SVSPs, increasing their efficacy.
Questions:
Q1: The authors identified SERPINA gene duplications, particularly in rodents (preprint Fig. 1, 2), suggesting a role in lineage-specific adaptations like venom resistance in N. macrotis. However, gene presence does not guarantee protein expression in relevant tissues or dynamic regulation upon venom exposure [7,8]. Have the authors considered RNA-seq or qPCR on tissues like the liver of N. macrotis before and after venom exposure? As the liver is the primary source of circulating SERPINs, this could clarify whether these gene duplicates are functionally relevant and part of a regulated defensive response.
Q2: The authors found that the SERPINA variants are capable of forming complexes with different serine proteases, indicating their ability to bind to these enzymes (preprint Fig 4 and 5). To further complement these findings, the authors could consider incorporating enzymatic inhibition assays using fluorogenic or chromogenic substrates. Such approaches are widely used to quantify the inhibitory efficiency and specificity of protease inhibitors in a quantitative manner [9], [10]. For example, fluorescence-based microplate assays or spectrophotometric methods could provide additional insights into the functional differences among the SERPINA paralogs. While the complex formation demonstrates binding capacity, these kinetic assays could help determine how effectively each variant inhibits target proteases, offering a more detailed functional characterization and strengthening the conclusions regarding their potential role in venom resistance.
Q3: Have the authors considered incorporating structural modeling approaches, such as homology modeling, molecular docking, or structure prediction tools like AlphaFold, to further explore the specificity and inhibitory mechanism of the SERPINA variants interacting with serine proteases? Given that SERPINs inhibit serine proteases through a well-characterized conformational mechanism involving insertion of the reactive center loop (RCL) into β-sheet A, structural analyses could provide valuable insight into the molecular determinants of target specificity and potential neofunctionalization among the paralogs. Tools like AlphaFold, which have demonstrated remarkable accuracy in protein structure prediction, could be particularly useful for visualizing differences in the RCL region. These structural predictions could complement the biochemical assays presented here and help validate hypotheses about binding modes, specificity, and functional divergence. Similar structural approaches have been successfully applied in other studies to investigate protease-inhibitor interactions [11].
Bibliography
[1] E. O. Martinson, Mrinalini, Y. D. Kelkar, C. H. Chang, and J. H. Werren, “The Evolution of Venom by Co-option of Single-Copy Genes,” Current Biology, vol. 27, no. 13, pp. 2007-2013.e8, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.032.
[2] K. W. Barbour, R. L. Goodwin, F. Guillonneau, Y. Wang, H. Baumann, and F. G. Berger, “Functional Diversification During Evolution of the Murine 1-Proteinase Inhibitor Family: Role of the Hypervariable Reactive Center Loop,” Mol. Biol. Evol, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 718–727, 2002, [Online]. Available: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/19/5/718/1067846
[3] V. Župunski, D. Kordiš, and F. Gubenšek, “Adaptive evolution in the snake venom Kunitz/BPTI protein family,” FEBS Lett, vol. 547, no. 1–3, pp. 131–136, Jul. 2003, doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00693-8.
[4] H. L. Gibbs et al., “The molecular basis of venom resistance in a rattlesnake-squirrel predator-prey system,” Mol Ecol, vol. 29, no. 15, pp. 2871–2888, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1111/mec.15529.
[5] N. R. Balchan, C. F. Smith, and S. P. Mackessy, “A plethora of rodents: Rattlesnake predators generate unanticipated patterns of venom resistance in a grassland ecosystem,” Toxicon X, vol. 21, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2023.100179.
[6] M. Mancuso et al., “Resistance Is Not Futile: Widespread Convergent Evolution of Resistance to Alpha-Neurotoxic Snake Venoms in Caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona),” Int J Mol Sci, vol. 24, no. 14, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.3390/ijms241411353.
[7] S. Naephrai, S. Khacha-Ananda, P. Pitchakarn, and C. Jaikang, “Composition and Acute Inflammatory Response from Tetraponera rufonigra Venom on RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells,” Toxins (Basel), vol. 13, no. 4, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.3390/TOXINS13040257.
[8] A. Deka, M. Sharma, R. Mukhopadhyay, A. Devi, and R. Doley, “Naja kaouthia venom protein, Nk-CRISP, upregulates inflammatory gene expression in human macrophages,” Int J Biol Macromol, vol. 160, pp. 602–611, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.169.
[9] J. G. Miyamoto et al., “A novel metalloproteinase-derived cryptide from Bothrops cotiara venom inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme activity,” Biochimie, vol. 216, pp. 90–98, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.10.010.
[10] J. A. Price, “Microplate fluorescence protease assays test the inhibition of select North American snake venoms’ activities with an anti-proteinase library,” Toxicon, vol. 103, pp. 145–154, Jul. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.06.020.
[11] J. Boldrini-França et al., “Beyond hemostasis: a snake venom serine protease with potassium channel blocking and potential antitumor activities,” Sci Rep, vol. 10, no. 1, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61258-x.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.41610
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biochemistry category:
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Snake venom metalloproteinases are predominantly responsible for the cytotoxic effects of certain African viper venoms
Daniel Osorno Valencia
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Also in the evolutionary biology category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Morphological variations in external genitalia do not explain the interspecific reproductive isolation in Nasonia species complex (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae)
Stefan Friedrich Wirth
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Also in the genetics category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
preLists in the biochemistry category:
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
Peer Review in Biomedical Sciences
Communication of scientific knowledge has changed dramatically in recent decades and the public perception of scientific discoveries depends on the peer review process of articles published in scientific journals. Preprints are key vehicles for the dissemination of scientific discoveries, but they are still not properly recognized by the scientific community since peer review is very limited. On the other hand, peer review is very heterogeneous and a fundamental aspect to improve it is to train young scientists on how to think critically and how to evaluate scientific knowledge in a professional way. Thus, this course aims to: i) train students on how to perform peer review of scientific manuscripts in a professional manner; ii) develop students' critical thinking; iii) contribute to the appreciation of preprints as important vehicles for the dissemination of scientific knowledge without restrictions; iv) contribute to the development of students' curricula, as their opinions will be published and indexed on the preLights platform. The evaluations will be based on qualitative analyses of the oral presentations of preprints in the field of biomedical sciences deposited in the bioRxiv server, of the critical reports written by the students, as well as of the participation of the students during the preprints discussions.
| List by | Marcus Oliveira et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Also in the evolutionary biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'EMBO | EMBL Symposium: The organism and its environment', organised at EMBL Heidelberg, Germany (May 2023).
| List by | Girish Kale |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
Also in the genetics category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)