Activation of intracellular transport by relieving KIF1C autoinhibition
Posted on: 7 January 2019
Preprint posted on 6 December 2018
Article now published in Nature Communications at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10644-9
Straightening out: KIF1C is activated by the binding of scaffolding proteins PTPN21 or HOOK3
Selected by Ben Craske, Gaetan Dias Mirandela, Thibault Legal and Toni McHughCategories: biochemistry, cell biology
Context:
The molecular motor KIF1C is a fast plus end-directed kinesin which is important for cargo transport in several cell types, delivering dense core vesicles to the dendrites of neurons and trafficking integrins to the actin-rich adhesions of macrophages and smooth muscle cells. It has been suggested that like other kinesin-3 motors KIF1C may cooperate with dynein to enable bidirectional cargo transport, but how this mechanism is regulated is unclear. Most kinesin-3 motors are inactive, diffusive monomers which dimerise upon cargo binding, activating their processive movement. This mechanism of autoregulation is distinct to kinesin-1 and kinesin-7 motors, which are regulated through direct interactions between the tail domains and the motor and neck regions, inactivating them until cargo binding relieves inhibition.
Key Findings:
In this paper Siddiqui et al. show that unlike other Kinesin-3 motors, purified KIF1C is intrinsically dimeric. In high salt concentrations, KIF1C adopts a more elongated conformation than in physiological conditions which suggests that the non-motor regions may fold into a compact, self-interacting structure. Using crosslinking mass spectrometry the authors show that the microtubule-binding interface of the motor domain interacts with the FHA domain and the third coiled-coil in the stalk. This indicates that such self-interactions may block the motor domain from associating with the microtubule and subsequent processivity(Fig. a). They also find that depletion of a previously characterized KIF1C interactor, PTPN21 (protein tyrosine phosphatase N21), phenocopies KIF1C depletion resulting in a reduction in the frequency of podosome formation. Interestingly, rescue is not dependent on the catalytic activity of PTPN21, as a minimal region of PTPN21 containing only the FERM domain (Fig. a) was sufficient to rescue the phenotype, suggesting that the scaffolding function was important for KIF1C activation. By imaging vesicle-transport in both RPE1 cells and primary hippocampal neurons Siddiqui et al. show that the reduction of both plus and minus end directional transport observed upon partial depletion of KIF1C can be rescued by over expression of the PTPN21 FERM domain. This demonstrates that this activation mechanism is common between different cell types.
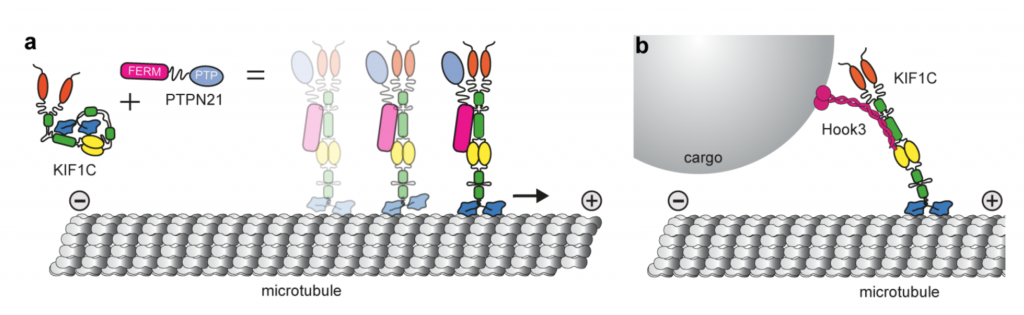
Using in vitro reconstitutions, the authors show that the PTPN21 FERM domain is able to activate KIF1C. This is shown by an increase in both landing rate and frequency of motor movement. Using crosslinking mass spectrometry, they find that PTPN21 FERM domain forms crosslinks with the FHA/coiled-coil 3 (CC3) region of KIF1C responsible for its auto inhibition. To further confirm that this region is important for autoregulation, they generated a KIF1C_delCC3 mutant lacking the CC3 domain. Single molecule motility assays indicate that KIF1C_delCC3 has a higher landing rate than KIF1C in vitro. Additionally, the landing rate of the mutant is no longer increased by inclusion of PTPN21-FERM, indicating that inhibition is fully relieved in the absence of the coiled-coil 3 domain.
Finally, Siddiqui et al. use a BioID to look for other KIF1C stalk interactors. The authors identified 240 proteins which are pulled down with KIF1C-BioID2 but not KIF1C_del623-825-BioID2. Interestingly, their top hit is Hook3, a dynein/dynactin activator that may be involved in mediating bidirectional cargo transport. In vitro they demonstrate that Hook3 is able to activate KIF1C in a similar fashion to PTPN21 and show co-transport of Hook3-Alexa647 with KIF1C in their single molecule kymographs.
Overall this paper shows that KIF1C is a dimeric kinesin-3 motor and is autoinhibited through a direct interaction between the FHA/CC3 stalk region and the microtubule-binding region in the motor domain. This inactive, compact structure can be relieved through interaction with binding partners such as PTPN21 or Hook3, increasing the landing rate of the motor on microtubules in vitro and enabling bidirectional cargo transport in cells (Fig. a,b).
Open questions:
Were there any other interesting candidates in the BioID screen? For example do any other dynein activators appear in the screen?
If Hook3 can simultaneously bind and activate both KIF1C and dynein through non-overlapping binding sites, how might this work to regulate switching from plus to minus end directed movement?
Why we chose this paper:
We chose this preprint as we are interested in the different mechanisms underpinning kinesin regulation and how cargo binding may mediate the activation of such motors through structural changes. This paper demonstrates that KIF1C is regulated in a distinct manner compared to other kinesin-3 family members and uses a combination of biochemistry, in vitro reconstitutions and cell biology to illustrate how inhibition is relieved by binding partners.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.6978
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biochemistry category:
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Snake venom metalloproteinases are predominantly responsible for the cytotoxic effects of certain African viper venoms
Daniel Osorno Valencia
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Also in the cell biology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
preLists in the biochemistry category:
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
Peer Review in Biomedical Sciences
Communication of scientific knowledge has changed dramatically in recent decades and the public perception of scientific discoveries depends on the peer review process of articles published in scientific journals. Preprints are key vehicles for the dissemination of scientific discoveries, but they are still not properly recognized by the scientific community since peer review is very limited. On the other hand, peer review is very heterogeneous and a fundamental aspect to improve it is to train young scientists on how to think critically and how to evaluate scientific knowledge in a professional way. Thus, this course aims to: i) train students on how to perform peer review of scientific manuscripts in a professional manner; ii) develop students' critical thinking; iii) contribute to the appreciation of preprints as important vehicles for the dissemination of scientific knowledge without restrictions; iv) contribute to the development of students' curricula, as their opinions will be published and indexed on the preLights platform. The evaluations will be based on qualitative analyses of the oral presentations of preprints in the field of biomedical sciences deposited in the bioRxiv server, of the critical reports written by the students, as well as of the participation of the students during the preprints discussions.
| List by | Marcus Oliveira et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Also in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)