Coxiella burnetii actively blocks IL-17-induced oxidative stress in macrophages
Posted on: 16 May 2023
Preprint posted on 15 March 2023
Coxiella burnetii, the pathogen that causes Q fever, demonstrates a strategy to effectively evade the immune system by inhibiting the IL-17-induced oxidative stress in macrophages. preLight Authors: Abigail Page & Farhana Afrin Mohona
Selected by UofA IMB565Categories: cell biology, immunology, microbiology
preLight Authors: Abigail Page & Farhana Afrin Mohona
Background: Coxiella burnetii is a highly infectious bacterium responsible for Q fever, a potentially fatal disease that displays flu-like symptoms or progresses into life-threatening endocarditis. The treatment for this life-threatening condition involves a two-year regimen of antibiotic combination therapy as well as valve replacement surgery. Although there is a vaccine, it is not accepted world-wide. The insufficient understanding of the bacterium’s pathogenesis imposes restrictions on these therapeutic approaches, resulting in a high mortality rate. (1-7)
Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular pathogen that primarily targets alveolar macrophages. During infection, the bacterium forms phagolysosome-like vacuoles called the Coxiella-Containing Vacuole (CCV) that support their replication. Within the vacuole, the pathogen uses the Dot/Icm type IVB secretion system (T4BSS) to deliver effector proteins to control host signaling pathways and cellular processes. This T4BSS pathway helps maintain the vacuole fusogenicity, prevents host cell death, and activates inflammasomes, which are important for the immune response. But how Coxiella burnetii evades the host innate immune response is unclear.
Previous work has shown that the bacterium restricts the host immune response by blocking the signaling pathway of interleukin-17 (IL-17), a proinflammatory cytokine that aids the production of antimicrobial peptides and chemokines, leading to pathogen eradication. In this preprint, the researchers found that T4BSS downregulates the expression of IL-17 target genes and blocks IL-17-induced chemokine secretion, protecting the pathogen from the bactericidal effect of IL-17, and promoting survival. (8-18)
In this preprint, the authors illustrate that C. burnetii T4BSS prevents the transcription pathway activated by IL-17 and disrupts the IL17RA/ACT1/TRAF6 pathway. Additionally, if the IL17R-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway is disrupted, the bactericidal effect of IL-17 is reduced. They also show that alveolar macrophage produce high numbers of reactive oxygen species in response to IL-17, but C. burnetii T4BSS proteins completely inhibit IL-17 oxidative stress, hinting that the bacterium downregulates IL-17 signaling to avoid being killed by reactive oxygen species. (Figure 1)
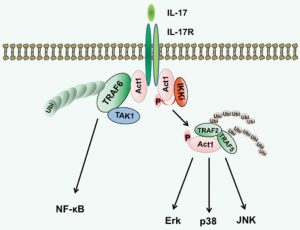
Figure 1: The binding of IL-17 to the IL-17RC/IL-17RA receptor recruits ACT1, which is necessary for all known IL-17 dependant pathways. TRAF6 coordinates with ACT1 to activate NFkB, vital for the induction of proinflammatory genes. The phosphorylation of ACT1 reduces the affinity of Act1 for TRAF6, promoting TRAF2/5 interactions. This binding activates MAP kinase signaling, leading to the transcription of chemokine mRNAs. [26]
Key Findings:
Coxiella burnetii blocks activation of IL-17 signaling in alveolar macrophages
The researchers theorized that the T4BSS effector proteins block the ACT1/TRAF6 pathway downstream of the IL-17 transcription receptor. To test this, they conducted a colorimetric enzyme assay using HEK-Blue IL-17 cells, which stably express the IL-17RA/IL-17RC heterodimer IL-17 receptor, ACT1, and secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The authors showed that IL-17 binding to the IL-17 receptor triggers the ACT1/TRAF6 signaling cascade to activate NFkB, inducing SEAP expression. They revealed a more than 70% decrease in SEAP expression in cells infected with WT C. burnetii compared to mock and T4BSS defective mutant (ΔdotA)-infected cells. This indicated that C. burnetii inhibits the activation of the ACT1- TRAF6/ NFkB and AP-1 pathways via T4BSS effector proteins.
C. burnetii T4BSS blocks IL-17 activation of NFkB p65, MAPK, and SAPK/JNK pathways
The researchers then sought to assess whether C. burnetii targets NFkB and/or Map kinases following stimulation by IL-17 by measuring the phosphorylation levels of NFkB p-65, JNK/SAPK, and p38 MAPK in infected mouse alveolar macrophages (MH-S cells). Observed through immunoblots, the researchers observed less activation of NFkB p-65 and p38 MAPK, and a drastic reduction in JNK/SAPK activation. These findings imply that during IL-17 stimulation, C. burnetii T4BSS targets the NFkB and MAP kinase pathways, namely JNK/SAPK, as a means of preventing the transcription of IL-17 downstream genes.
Disruption of the IL17R-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway neutralizes the IL-17 bactericidal effect
The researchers sought to find out whether the IL-17R-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway is required for the bactericidal effects of IL-17. While wild type macrophage stimulated with IL-17 were able to restrict C. burnetii growth (32.7%) and reduce CCV size, knockouts of IL-17RA and TRAF6 abrogated the IL-17-mediated restriction. Depletion of ACT1 protein with siRNA resulted in recovery of bacterial growth and size of CCV which stands in contrast to the effects observed in the presence of IL-17. These contrasting outcomes strongly indicate that the IL-17-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway is essential for the bactericidal effects against Coxiella burnetii.
Coxiella burnetii T4BSS inhibits IL-17-mediated oxidative stress in macrophages
IL-17 can trigger reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by activating NADPH-oxidases (NOX) through ACT1 and TRAF6. High ROS levels inhibit growth of the bacterium. The researchers aimed to see whether Coxiella burnetii T4BSS inhibits IL-17 signaling in macrophages to avoid elevated ROS levels. They conducted a fluorometric assay and found a significant increase in NOX activity in macrophages in WT cells in the presence of IL-17, compared to untreated cells (Δil-17ra). Further, using CellROX Green, they measured ROS levels in mock, WT and ΔdotA mutant-infected cells and found a significant increase in ROS in the mutated cells and not the WT. This suggests that Coxiella burnetii employs the T4BSS to block IL-17 mediated ROS.
Conclusion:
This study shows that Coxiella burnetii targets the IL-17R-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway to inhibit transcription of IL-17 target genes and block the activity of NOX enzymes to prevent ROS, ultimately to protect themselves during immune invasion.
Why we chose this preprint:
Q fever is a zoonotic disease caused by Coxiella burnetii that causes severe chronic illness and is transmitted through inhaling contaminated aerosols. The diagnosis and treatment of Q fever has been met with difficulty, as there is no licensed vaccine or therapy available. As researchers interested in health and medicine, this is very concerning, and this is what made this preprint so intriguing.
Essentially, Coxiella burnetii is able to combat oxidative stress and survive in the host body. This study is vital to the understanding of the physiological relevance of how these pathogens interact with the host immune system. The authors paint a well put together picture of how this bacterium targets the IL-17R-ACT1-TRAF6 pathway. The research on how this bacterium combats oxidative stress to promote survival adds to the knowledge of how reactive oxygen stress works in the host-microbe relationship and could potentially lead to novel therapeutics. This aspect of the paper attracted us personally, as we have a great interest in understanding cell signaling mechanisms, which would enable us to better comprehend the disease prognosis and the drug mechanisms used in treating this disease.
Questions for the Authors:
Q1. It is stated that C. burnetii has been found to use one or more T4BSS effector proteins, do you think that C. burnetii evolved to use varying numbers of T4BSS effectors to adapt to different host environments, such as when the host has an elevated or decreased immune system?
Q2. Could this process of ROS combatants be utilized for a potential therapy in battling ROS synthetically in the human body in relation to combating ROS-elevating disorders, such as cancers and chronic diseases?
Q3. What approach would be taken to discern the virulence determinants excreted by the C. burnetii T4BSS system that effectively impede the IL-17 pathway?
Q4. Do you intend to perform Real-time quantitative PCR assay for the purpose of ascertaining the quantitative levels of NFkB p65, MAPK, and SAPK/JNK subsequent to the induction of IL-17?
Q5. How might the ability of Coxiella burnetii to inhibit IL-17-mediated oxidative stress impact the development of Q fever?
References:
1. Million, M., et al., Evolution from acute Q fever to endocarditis is associated with underlying valvulopathy and age and can be prevented by prolonged antibiotic treatment. Clin Infect Dis, 2013. 57(6): p. 836-44.
2. Kampschreur, L.M., et al., Chronic Q fever diagnosis— consensus guideline versus expert opinion. Emerg Infect Dis, 2015. 21(7): p. 1183-8.
3. Raoult, D., Treatment of Q fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 1993. 37(9): p. 1733- 474 6.
4. Dahlgren, F.S., D.L. Haberling, and J.H. McQuiston, Q fever is underestimated in the United States: a comparison of fatal Q fever cases from two national reporting systems. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2015. 92(2): p. 244-6.
5. Maor, Y., et al., Coxiella burnetii Endocarditis and Aortic Vascular Graft Infection: An Underrecognized Disease. Ann Thorac Surg, 2016. 101(1): p. 141-5.
6. Keijmel, S.P., et al., A fatal case of disseminated chronic Q fever: a case report and brief review of the literature. Infection, 2016. 44(5): p. 677-82.
7. Botelho-Nevers, E., et al., Coxiella burnetii infection of aortic aneurysms or vascular grafts: report of 30 new cases and evaluation of outcome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2007. 26(9): p. 635-40.
8. Voth, D.E., D. Howe, and R.A. Heinzen, Coxiella burnetii inhibits apoptosis in human THP-1 cells and monkey primary alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun, 2007. 75(9): p. 4263-71.
9. Cunha, L.D., et al., Inhibition of inflammasome activation by Coxiella burnetii type IV secretion system effector IcaA. Nat Commun, 2015. 6: p. 10205.
10. Curtis, M.M. and S.S. Way, Interleukin-17 in host defence against bacterial, mycobacterial and fungal pathogens. Immunology, 2009. 126(2): p. 177-85.
11. Khader, S.A. and R. Gopal, IL-17 in protective immunity to intracellular pathogens. Virulence, 2010. 1(5): p. 423-7.
12. Onishi, R.M. and S.L. Gaffen, Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology, 2010. 129(3): p. 311-21.
13. Amatya, N., A.V. Garg, and S.L. Gaffen, IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol, 2017. 38(5): p. 310-322.
14. McGeachy, M.J., D.J. Cua, and S.L. Gaffen, The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity, 2019. 50(4): p. 892-906.
15. Barin, J.G., et al., Macrophages participate in IL-17-mediated inflammation. Eur J Immunol, 2012. 42(3): p. 726-36.
16. Lin, Y., et al., Interleukin-17 is required for T helper 1 cell immunity and host resistance to the intracellular pathogen Francisella tularensis. Immunity, 2009. 31(5): p. 799-810.
17. Kimizuka, Y., et al., Roles of interleukin-17 in an experimental Legionella pneumophila pneumonia model. Infect Immun, 2012. 80(3): p. 1121-7.
18. Chen, J., et al., IL-17A induces pro-inflammatory cytokines production in macrophages via MAPKinases, NF-κB and AP-1. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2013. 32(5): p. 1265-74.
19. Gu, C., L. Wu, and X. Li, IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine, 2013. 64(2): p. 477-85.
20. Leonardi, A., et al., CIKS, a connection to Ikappa B kinase and stress-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000. 97(19): p. 10494-9.
21. Mahapatra, S., et al., Coxiella burnetii Employs the Dot/Icm Type IV Secretion System to Modulate Host NF-κB/RelA Activation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2016. 6: p. 188.
22. Burette, M., et al., Modulation of innate immune signaling by a Coxiella burnetii eukaryotic-like effector protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020. 117(24): p. 13708- 13718.
23. Voth, D.E. and R.A. Heinzen, Sustained activation of Akt and Erk1/2 is required for Coxiella burnetii antiapoptotic activity. Infect Immun, 2009. 77(1): p. 205-13.
24. Jansen, A.F.M., et al., Viable Coxiella burnetii Induces Differential Cytokine Responses in Chronic Q Fever Patients Compared to Heat-Killed Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun, 2018. 86(10).
25. Ammerdorffer, A., et al., Coxiella burnetii isolates originating from infected cattle induce a more pronounced proinflammatory cytokine response compared to isolates from infected goats and sheep. Pathog Dis, 2017. 75(4)
- Shembade, N., Harhaj, E. IKKi: a novel regulator of Act1, IL-17 signaling and pulmonary inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol8, 447–449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2011.4
doi: Pending
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the cell biology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
Also in the immunology category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
Scalable transcription factor mapping uncovers the regulatory dynamics of natural and synthetic transcription factors in human T cell states
Inês Caiado
Also in the microbiology category:
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
Citrobacter rodentium infection activates colonic lamina propria group 2 innate lymphoid cells
André Luiz Amorim Costa, Marcus Oliveira
preLists in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the immunology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the microbiology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |











 (3 votes)
(3 votes)