SIV and Mycobacterium tuberculosis synergy within the granuloma accelerates the reactivation pattern of latent tuberculosis
Posted on: 23 April 2020
Preprint posted on 21 February 2020
Article now published in PLOS Pathogens at http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008413
What drives TB reactivation during HIV infection? In vivo non-human primate models may provide some answers.
Selected by Louise FraserCategories: cell biology, immunology, microbiology, pathology, systems biology
Background:
Despite decades of research, tuberculosis (TB) still caused approximately 1.5 million deaths in 2018. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is the causative agent of TB and has remarkable immune evasion capabilities. In 90% of cases, patients develop an asymptomatic latent infection that can last a lifetime. Why a select group of patients develop active infection remains unclear, however human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is well known to increase susceptibility to TB. This largely has been attributed to HIV-induced CD4 T cell loss. However, this is not the full story.
Following infection, the host immune system surrounds TB-infected macrophages and forms a granuloma. This structure is a two-edged sword – it prevents further spread of bacteria and allows immunological control, but also provides a prime site for bacterial survival and replication. Maintaining the granuloma requires a delicate balance that can be disrupted by many factors. Using cynomolgus macaques infected with Mtb and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), Diedrich et al shed light on some of the intricacies at work within the immune granuloma.
Key Findings:
CD4+ loss alone does not explain all the pathology observed during Mtb reactivation.
By comparing the reactivation and resulting pathology in TB-infected macaques treated with either SIV or anti-CD4 antibody, the authors found that, while αCD4 treatment resulted in greater CD4 T cell depletion in the animals, it was the SIV treated macaques that had higher bacterial numbers and a more severe pathology. Mtb/SIV treated macaques also had a higher number of new granulomas than the Mtb/CD4 animals, suggesting greater dissemination of bacteria.
A T cell balancing act
If CD4 T cell loss alone does not explain increased pathology, what does? According to Diedrich et al’s research, it is the proportion of CD4 to CD8 T cells that matters, not the absolute number of T cells within the granuloma. CD8 T cell numbers were increased in the granulomas of animals that experienced reactivation (in both SIV and αCD4 treatment groups), but SIV infection increased the absolute number of both CD4 and CD8 T cells in granulomas. Interestingly, while CD8 T cell numbers were increased in the granulomas during reactivated infection, CD4 T cells were decreased in both Mtb/SIV and Mtb/αCD4 groups. Together, it appears that the functional effect of CD4/CD8 T cell proportional differences may be more important in inducing TB reactivation than the absolute number of T cells. Of course, this raises a new question. What are the T cells doing?
It’s all in the cytokines
To study the changes in T cell activity within lung granulomas, Diedrich et al performed principal component analysis, with IFN-α, IFN-γ, TNF, IL-2, IL-17, IL-10, IL-4 and granzyme B included as markers of T cell activation. Overall, both CD4 and CD8 T cells had a higher score in Mtb/SIV-treated animals, whether reactivated or not. In addition, animals that underwent reactivation had a higher score than those that did not in Mtb/SIV animals, whereas Mtb/αCD4 animals showed no difference between activation states. Altogether, Mtb/SIV induced greater immune activation than either Mtb alone or Mtb/αCD4, and this heightened immune activation correlated with increased growth of Mtb and replication of SIV.
It’s a symbiotic relationship (but not for us).
Perhaps of greatest interest from a therapeutic perspective is this finding: Mtb-positive granulomas had higher SIV RNA copy numbers, and animals who underwent TB reactivation had higher SIV RNA copy numbers than those that did not. In addition, Mtb-positive granulomas from reactivated animals also had a higher proportion of live bacteria, compared to those of animals whose infection remained in latency. Together, these findings suggest that Mtb and SIV co-operate – within the granuloma, Mtb provides an optimised environment for SIV replication, while SIV reduces Mtb death. This confirms earlier in vitro research suggesting that HIV replication could be improved by Mtb. Exactly how these two achieve symbiosis remains unclear, but it provides an insight into the complex innerworkings of the TB granuloma that may prove invaluable for future therapeutic developments.
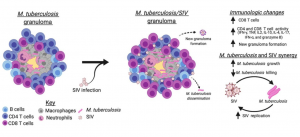
From PrePrint Figure 7: Illustration of how SIV affects the immunological function of lung granulomas. SIV co-infection results in increased CD8 T cells and increased Th1 cytokine production in the Mtb granuloma. Co-infection with SIV also increases the number of granulomas formed and Mtb growth, and reduces Mtb killing within the granuloma.
Why is this work important?
TB remains a dominant player in the world of infectious disease. While it does enter latency in 90% of cases, any stress to the immune system can leave infected individuals vulnerable to reactivation. HIV, which specifically targets immune cells, presents a major risk factor to individuals with latent TB. Understanding how HIV triggers TB reactivation, along with the resulting pathology, is imperative for patient treatment. In addition, understanding how TB and HIV might benefit one another when co-infected could provide crucial information for the development of new therapies against both diseases. This work, which seeks to understand such mechanisms, is therefore of great importance.
Why did I choose it?
Even if you exclude third parties, Mtb/host interactions are complex. In vivo research is paramount if we are ever to truly understand them. Using non-human primates as a model reduces the genetic variability that limits the clarity in human data and increases the potential for direct transference of results to humans (something that is difficult to do in other model species). This study includes time points that occur before pathology can be readily observed. While this may not be directly beneficial to human TB, where the development of symptoms usually precedes diagnosis, it will provide crucial information about disease development that is missed in human studies.
Questions for the Authors:
- You mention that there is a large variation in time between SIV infection and TB reactivation. Assuming this holds true in humans, is this allowed for during treatment regimens?
- You included a mixture of both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine activation int your principal component analysis and saw an increase in overall activation in Mtb/SIV animals compared to Mtb/CD4, and in reactivated compared to latent infection. My question is, was there an observed change in this over the infection period? And is such analysis a potential indicator of future reactivation?
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.19132
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the cell biology category:
Cell cycle-dependent mRNA localization in P-bodies
Mohammed JALLOH
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
Roberto Amadio
Notch3 is a genetic modifier of NODAL signalling for patterning asymmetry during mouse heart looping
Bhaval Parmar
Also in the immunology category:
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
Roberto Amadio
G6b-B antibody-based cis-acting platelet receptor inhibitors (CAPRIs) as a new family of anti-thrombotic therapeutics
Simon Cleary
Feedback loop regulation between viperin and viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus through competing protein degradation pathways
UofA IMB565 et al.
Also in the microbiology category:
Characterization of natural product inhibitors of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals competitive inhibition of RhlR by ortho-vanillin
UofA IMB565 et al.
Lytic bacteriophages interact with respiratory epithelial cells and induce the secretion of antiviral and proinflammatory cytokines
UofA IMB565 et al.
Streptococcus pneumoniae augments circadian clock gene expression in zebrafish cells
UofA IMB565 et al.
Also in the pathology category:
LINC complex alterations are a hallmark of sporadic and familial ALS/FTD
Megane Rayer et al.
Hypoxia blunts angiogenic signaling and upregulates the antioxidant system in elephant seal endothelial cells
Sarah Young-Veenstra
H2O2 sulfenylates CHE linking local infection to establishment of systemic acquired resistance
Marc Somssich
Also in the systems biology category:
Modular control of time and space during vertebrate axis segmentation
AND
Natural genetic variation quantitatively regulates heart rate and dimension
Girish Kale, Jennifer Ann Black
Expressive modeling and fast simulation for dynamic compartments
Benjamin Dominik Maier
Clusters of lineage-specific genes are anchored by ZNF274 in repressive perinucleolar compartments
Silvia Carvalho
preLists in the cell biology category:
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the immunology category:
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the microbiology category:
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the pathology category:
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
Also in the systems biology category:
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)