The force loading rate drives cell mechanosensing through both reinforcement and fluidization
Posted on: 20 March 2021 , updated on: 24 March 2021
Preprint posted on 8 March 2021
Article now published in Nature Communications at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24383-3
Categories: biophysics, cell biology
Background
Physical forces play a key role in governing biological processes such as cell migration (du Roure et al., 2005; Trepat et al., 2009), differentiation (Engler et al., 2006; Park et al., 2011), and tissue morphogenesis (Heisenberg and Bellaiche, 2013). Examination of cellular and tissue level behaviors in response to either cell-extrinsic or cell-intrinsic mechanical stress show that forces can act as a cue to preserve tissue integrity (Acharya et al., 2018; Polacheck et al., 2017) as well as maintain tissue homeostasis (Teo et al., 2020a; Teo et al., 2020b). To convert extrinsic mechanical forces into intrinsic biochemical signals (mechanotransduction), cells must sense mechanical stimuli (mechanosensing) and translate these stimuli into biochemical signals that elicit specific cellular outcomes.
Notably, cells undergo fluidization when stretched at high amplitudes or rates (Krishnan et al., 2009; Nava et al., 2020; Peyret et al., 2019; Trepat et al., 2007). This process involves a drastic change in the stiffness of cells and disintegration of the cell cytoskeleton (Chen et al., 2010; Krishnan et al., 2009). While we are beginning to understand the effects of static force magnitudes on cellular mechanosensing, the effects of loading rate (i.e. the rate at which force is applied) on cells remain unclear. In this new preprint, Andreu et al. sought to investigate the contribution of loading rate on cellular mechanosensing by using a myriad of tools such as substrate stretching, optical tweezers, atomic force microscopy, a computational clutch model as well as an in vivo differential rat lung ventilation model.
Key findings
To investigate the effects of loading rate on cellular mechanosensing, the authors first seeded mouse embryonic fibroblasts on soft fibronectin-coated polyacrylamide substrates (0.6 kPa). Under this condition, cells displayed small punctate paxillin-containing adhesions, a largely cytosolic population of YAP, and fast actin retrograde flow (~50nm/s). Since the loading rate is derived from deformation speed and substrate stiffness, two strategies were employed to increase loading rate. In the first strategy, cells were seeded on substrates with increased stiffness (3.4 kPa). This activated cellular mechanosensing as evidenced by YAP nuclear translocation. In the second strategy, loading rate was directly increased by stretching cells seeded on soft substrates (0.6 kPa). In this approach, cells were first subjected to a mild 2.5% biaxial cyclic stretch in a progressive triangular wave at a frequency of 0.125Hz for 1h. Cellular mechanosensing was not activated as paxillin-containing adhesions remained small and YAP was mainly cytosolic. However, when the stretch frequency was increased to 1 and 2Hz while maintaining a constant stretch amplitude, YAP translocated to the nucleus and paxillin-containing adhesions grew into larger focal adhesions. These experiments show that increasing loading rate can activate cellular mechanosensing.
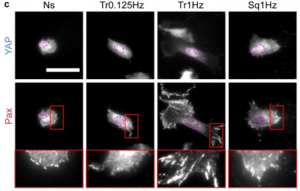
Figure 1. Immunofluorescence staining of YAP and paxillin in mouse embryonic fibroblasts that are not stretched (Ns), stretched at 10% using triangular (Tr) and square (Sq) signals at different frequencies. Adapted from Figure 1C from Andreu et al. 2020.
Next, the authors applied different stretch amplitudes ranging from 2.5% to 20%. Concurring with their previous observations, increasing stretch amplitudes at most frequencies activated cellular mechanosensing. Strikingly, for stretch amplitudes above 5% and stretch frequencies above 1Hz, cells fail to display adhesion growth and YAP nuclear localization. These observations led the authors to hypothesize that the cells could have fluidized due to cytoskeletal network disruptions at such high stretch rates. To test this hypothesis, cells were stretched at different rates and actin organization was quantified. At very low and high rates, actin was largely disorganized. However, when cells were stretched using a condition that activated cellular mechanosensing (10% stretch, 1Hz triangular wave), actin fibers were organized with enhanced actin anisotropy. To further confirm the role of cytoskeletal fluidization, the authors were able to inhibit fluidization and restore cellular mechanosensing at high stretch rates by treating cells with an actin-stabilizing drug, Jasplakinolide.
To explore the interplay between loading rate, mechanosensing, and fluidization, the authors developed a computational clutch model. By modifying only stretch frequency and amplitude, the model largely concurred with the experimental observations. This indicates that depending on the magnitude of the loading rate, cells can either mechanosense or fluidize. To further confirm this hypothesis, the authors proceeded to test the assumptions in their model. Firstly, loading rate and not cell deformation rate should be responsible for triggering mechanosensing or fluidization. Secondly, these effects are expected to occur at cellular and subcellular levels. To test if these assumptions hold, cells expressing GFP-paxillin were seeded on glass, and forces were applied by displacing an optical trap horizontally with triangular signals of the same amplitude but different frequencies. Gradually, bead displacement and speed were progressively reduced. Simultaneously, there was an increase in applied force, loading rates, effective stiffness of beads, and recruitment of paxillin to the beads. Remarkably, unlike the stretch experiments, there was no reduction in paxillin recruitment even at very high frequencies. The authors reasoned that the lack of fluidization could be due to 1) insufficient force applied by the optical tweezers on cells (optical tweezers can only apply forces <~100pN) and 2) since cells have adhered to the glass and optical tweezer experiments were performed on the lamellar region of cells which contains structured actin networks, the forces applied to the beads are probably well-distributed across the network, reducing the chances of fluidization. To overcome these limitations, the authors adopted a different strategy. They attached cells in suspension to a flat Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) cantilever, brought cells into contact with a fibronectin-coated glass, and pulled the cells at different speeds. With this approach, they observed an initial increase in cell stiffness which decreased sharply at pulling speeds of 5 and 6um/s- suggestive of fluidization.
Finally, to determine if the effects of loading rate on cellular mechanosensing can also be seen in vivo, the authors subjected each of the two lungs of a rat to independent mechanical ventilation frequencies. When the right and left lungs were ventilated at the same frequency, no significant differences in YAP localization were seen. However, when ventilation frequency was increased, nuclear YAP levels were also increased indicating that mechanosensing was activated.
What I like about this preprint
I thoroughly enjoyed reading this preprint! The authors used multiple creative experimental approaches to address the longstanding question of whether loading rate affects cell mechanosensing. To see loading rate affecting mechanosensing in vivo is exciting as it gives relevant context on why this question is important. It is also nice to read about puzzling results and learn how the authors navigate the limitations of experimental techniques by thinking out-of-the-box.
Questions for the authors
- The observation that cells fluidize when loading rate goes over a particular threshold is interesting. Do you observe fluidization effects in vivo?
- I wonder if cells have a memory of changes in loading rate? For instance, what happens to cells that are exposed to sustained levels of loading rate that trigger cellular mechanosensing? Do they continue to mechanosense or would mechanosensitivity be dampened?
References:
Acharya, B.R., Nestor-Bergmann, A., Liang, X., Gupta, S., Duszyc, K., Gauquelin, E., Gomez, G.A., Budnar, S., Marcq, P., Jensen, O.E., et al. (2018). A Mechanosensitive RhoA Pathway that Protects Epithelia against Acute Tensile Stress. Dev Cell 47, 439-452 e436.
Chen, C., Krishnan, R., Zhou, E., Ramachandran, A., Tambe, D., Rajendran, K., Adam, R.M., Deng, L., and Fredberg, J.J. (2010). Fluidization and resolidification of the human bladder smooth muscle cell in response to transient stretch. PLoS One 5, e12035.
du Roure, O., Saez, A., Buguin, A., Austin, R.H., Chavrier, P., Silberzan, P., and Ladoux, B. (2005). Force mapping in epithelial cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 2390-2395.
Engler, A.J., Sen, S., Sweeney, H.L., and Discher, D.E. (2006). Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126, 677-689.
Heisenberg, C.P., and Bellaiche, Y. (2013). Forces in tissue morphogenesis and patterning. Cell 153, 948-962.
Krishnan, R., Park, C.Y., Lin, Y.C., Mead, J., Jaspers, R.T., Trepat, X., Lenormand, G., Tambe, D., Smolensky, A.V., Knoll, A.H., et al. (2009). Reinforcement versus fluidization in cytoskeletal mechanoresponsiveness. PLoS One 4, e5486.
Nava, M.M., Miroshnikova, Y.A., Biggs, L.C., Whitefield, D.B., Metge, F., Boucas, J., Vihinen, H., Jokitalo, E., Li, X., Garcia Arcos, J.M., et al. (2020). Heterochromatin-Driven Nuclear Softening Protects the Genome against Mechanical Stress-Induced Damage. Cell 181, 800-817 e822.
Park, J.S., Chu, J.S., Tsou, A.D., Diop, R., Tang, Z., Wang, A., and Li, S. (2011). The effect of matrix stiffness on the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in response to TGF-beta. Biomaterials 32, 3921-3930.
Peyret, G., Mueller, R., d’Alessandro, J., Begnaud, S., Marcq, P., Mege, R.M., Yeomans, J.M., Doostmohammadi, A., and Ladoux, B. (2019). Sustained Oscillations of Epithelial Cell Sheets. Biophys J 117, 464-478.
Polacheck, W.J., Kutys, M.L., Yang, J., Eyckmans, J., Wu, Y., Vasavada, H., Hirschi, K.K., and Chen, C.S. (2017). A non-canonical Notch complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function. Nature 552, 258-262.
Teo, J.L., Gomez, G.A., Weeratunga, S., Davies, E.M., Noordstra, I., Budnar, S., Katsuno-Kambe, H., McGrath, M.J., Verma, S., Tomatis, V., et al. (2020a). Caveolae Control Contractile Tension for Epithelia to Eliminate Tumor Cells. Dev Cell 54, 75-91 e77.
Teo, J.L., Tomatis, V.M., Coburn, L., Lagendijk, A.K., Schouwenaar, I.M., Budnar, S., Hall, T.E., Verma, S., McLachlan, R.W., Hogan, B.M., et al. (2020b). Src kinases relax adherens junctions between the neighbors of apoptotic cells to permit apical extrusion. Mol Biol Cell 31, 2557-2569.
Trepat, X., Deng, L., An, S.S., Navajas, D., Tschumperlin, D.J., Gerthoffer, W.T., Butler, J.P., and Fredberg, J.J. (2007). Universal physical responses to stretch in the living cell. Nature 447, 592-595.
Trepat, X., Wasserman, M.R., Angelini, T.E., Millet, E., Weitz, D.A., Butler, J.P., and Fredberg, J.J. (2009). Physical forces during collective cell migration. Nature Physics 5, 426-430.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.27751
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biophysics category:
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation is Stimulated by Red Light Irradiation
Rickson Ribeiro, Marcus Oliveira
Also in the cell biology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
preLists in the biophysics category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
66th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, 2022
Preprints presented at the 66th BPS Annual Meeting, Feb 19 - 23, 2022 (The below list is not exhaustive and the preprints are listed in no particular order.)
| List by | Soni Mohapatra |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Biophysical Society Meeting 2020
Some preprints presented at the Biophysical Society Meeting 2020 in San Diego, USA.
| List by | Tessa Sinnige |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Biomolecular NMR
Preprints related to the application and development of biomolecular NMR spectroscopy
| List by | Reid Alderson |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
Also in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)