After traumatic brain injury oligodendrocytes regain a plastic phenotype and can become astrocytes
Posted on: 6 August 2021
Preprint posted on 18 June 2021
Article now published in Developmental Cell at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2023.04.016
Categories: cell biology, neuroscience
Background:
The degree of neuron insulation by lipid-rich membranes (myelination) is a major factor in determining the rate of propagation of action potentials along neurons. Myelination ensures rapid conduction of electrical impulses which is necessary for efficient information processing in the brain. Oligodendrocytes, generated from Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells (OPCs), are the myelin-forming cells in the brain that can generate up to 50 myelinating processes, each capable of independently wrapping around axons (1). While oligodendrocytes are terminally differentiated cells, a plastic phenotype within the lineage was first demonstrated by Raff and colleagues in 1983, who showed that O-2A precursor cells have a microenvironment-dependent ability to generate either oligodendrocytes or type 2 astrocytes (2). Nerve/Glia Antigen 2 (NG2) expressing glial precursor cells (of oligodendroglial lineage) also demonstrate such plasticity in an age-dependent manner in vivo (3). Besides precursor cells, plasticity of mature oligodendrocytes has also been demonstrated in the goldfish optic tract. Upon axonal injury, these cells revert to a precursor-like bipolar morphology, and eventually remyelinate the axons (4). However, the plasticity of mature oligodendrocytes in the adult mammalian brain remains elusive. In this preprint, Bai et al. demonstrate a novel type of cell generated from the oligodendroglial lineage, including mature oligodendrocytes, in an acutely injured brain that can potentially become astrocytes.
Key results:
The authors made use of the Cre/loxP transgenic system to investigate the potential contribution of oligodendroglial lineage cells (OPCs and/or mature oligodendrocytes) towards generation of astrocytes upon acute stab-wound injury (SWI). Using double transgenic mice expressing Cre recombinase in oligodendroglial cells (NG2-CreERT2; R26flSTOPfltdTomato reporter), it was observed that stab wounds after tamoxifen-induced recombination cause an increase in the expression of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP), a marker for astrocytes, in about 25% of recombined (oligodendroglial) cells. Of these, about 28.5% of cells were newly generated astrocytes that not only extended elaborate processes, but also expressed another astrocytic marker, Glutamine synthetase (GS). Increasing the duration of tamoxifen-induced recombination before SWI substantially increased the number of newly generated astrocytes from recombined cells, suggesting these cells are distinct from astrocytes already present in the brain.
In order to understand the origin of astrocytes, the authors used a split Cre system, where the presence of a functional recombinase enzyme depends on the complementation of N- and C- terminals of Cre (NCre and CCre) expressed under different promoters. Transdifferentiation, or direct conversion of one terminally differentiated cell type to another without the involvement of a dedifferentiated state, is brought about by a downregulation, and simultaneous upregulation of former (cell type that transdifferentiates) and latter (new cell type that is formed) cells respectively. As such, the authors utilized transgenic mice differentially expressing NCre and CCre in astrocytes (GFAP-NCre) and oligodendrocytes (PLP-CCre) respectively. SWI induces Cre complementation, with recombined cells immunopositive for both astrocyte and oligodendrocyte markers. This points towards the potential of mature oligodendrocytes to express astrocytic genes. These astrocytes also respond to injury by undergoing astrogliosis, thereby validating their functionality in the brain.
Using a double transgenic mice line (PLP-DsRed1/GFAP-EGFPGFEA), the authors were able to detect a subset of cells, referred to as AO cells, that expressed both fluorophores in the injured brain, suggesting co-expression of Astrocytic and Oligodendrocytic genes (hence the name). These cells also expressed several oligodendrocyte-specific proteins, but not astrocyte or other glial markers, indicating an oligodendrocytic lineage. During their conversion to astrocytes, AO cells show upregulation of the GFAP promoter, and downregulation of the PLP promoter, leading the authors to classify them as a “transitioning cell”.
The lack of a definitive cytological state was also observed in the electrophysiological properties of AO cells (in PLP-DsRed1/GFAP-EGFP mice), which were found to be quite distinct in comparison to astrocytes or oligodendrocytes. Although these cells exhibited mostly K+ currents (whole-cell patch-clamp recordings at -80 mV holding voltage) which are typical of glia, the type of these currents (voltage-gated, non-rectifying; outwardly or inwardly rectifying K+ currents) varied a great deal between individual AO cells, indicating a transitional cell state without a definitive physiological property.
To go beyond the fixed time-point based experimental approaches, the authors used a 2-photon microscope to visualize the transition to astrocytes. In PLP-DsRed1/GFAP-EGFP mice, AO cells were detected as early as 3 days post injury (dpi) (Figure 1). Upon tracing a single oligodendrocyte (DsRed1+EGFP-), AO cell identity (DsRed1+EGFP+) could be seen by 5 dpi, which eventually converted to an astrocyte by 6 dpi (DsRed1 EGFP+). However, not all AO cell transitioned to astrocytes; some reverted to the oligodendrocyte fate, suggesting a potential heterogeneity in committing to becoming an astrocyte.
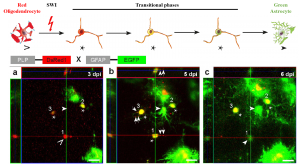
Figure 1: Conversion of oligodendrocytes to astrocytes via transitional phases upon SWI. In vivo 2-photon microscope facilitates the visualization of a newly formed astrocyte (arrowhead, c) from oligodendrocyte (open triangle, a) via AO cell (asterisk, b). Modified from Bai et al., Figure 5a-c (made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 international license).
Although acute SWI is an efficient approach for the detection of AO cells, two physiological injury models (Pial Vessel Disruption, PVD and transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion, MCAO) were assessed for their fidelity in identifying cell fate transition. Under both of these injury conditions, AO cells were observed near the lesion sites, providing substantial evidence for the physiological relevance of this process. Since these injuries also affected the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB), which would lead to an elevated level of cytokines in the affected region, the authors hypothesized inflammatory molecules to be a key player in the generation of AO cells. Not only was Interleukin-6 (IL-6) level increased after SWI, cortical injection of IL-6 also induced the formation of AO cells, which could be reduced by Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF). Such regulation by cytokines provides a possible mechanism that could act in concert with each other, or other molecular players yet unknown, to generate astrocytes from oligodendrocytes.
The reason behind choosing this preprint:
The generation of different cell types during development requires fate determination of stem/progenitor cells, which is provided by several intrinsic and extrinsic cues. Fate switch, however, remains an underexplored avenue. In an organ that mostly comprises post-mitotic cells (neurons), the plastic potential of non-neuronal cells becomes an important aspect of the efficient maintenance of homeostasis. Bai and colleagues quite elegantly demonstrate the conversion of mature oligodendrocytes and their progenitors into astrocytes upon injury. This paper also brings to attention another class of heterogeneous astrocytes (AO cells) that might have a distinct response to injury. Consequently, oligodendrocyte plasticity could emerge as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of brain trauma/injuries.
Questions for the authors:
• Given the variations in electrophysiological properties of individual AO cells, are the genes coding for different ion channels differentially expressed?
• What factors determine if an AO cell will be converted to an astrocyte, or back to an oligodendrocyte?
• Do the astrocytes generated from AO cells become functionally integrated into the glio-vascular network?
References:
1. Baumann N, Pham-Dinh D. Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiological reviews. 2001.
2. Raff MC, Miller RH, Noble M. A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature. 1983;303(5916):390-6.
3. Zhu X, Hill RA, Dietrich D, Komitova M, Suzuki R, Nishiyama A. Age-dependent fate and lineage restriction of single NG2 cells. Development. 2011;138(4):745-53.
4. Ankerhold R, Stuermer CA. Fate of oligodendrocytes during retinal axon degeneration and regeneration in the goldfish visual pathway. Journal of neurobiology. 1999;41(4):572-84.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.30269
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the cell biology category:
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Also in the neuroscience category:
PPARδ activation in microglia drives a transcriptional response that primes phagocytic function while countering inflammatory activation
Isabel Paine
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
preLists in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the neuroscience category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)