Aurora A depletion reveals centrosome-independent polarization mechanism in C. elegans
Posted on: 9 September 2018 , updated on: 21 November 2019
Preprint posted on 9 August 2018
Article now published in eLife at http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/elife.44552
Centrosome Aurora A gradient ensures a single PAR-2 polarity axis by regulating RhoGEF ECT-2 localization in C. elegans embryos
Posted on: , updated on: 21 November 2019
Preprint posted on 21 August 2018
Article now published in Development at https://dev.biologists.org/content/early/2019/10/21/dev.174565
A new light shines bright in the polarity field: two preprints investigate the contribution of Aurora A in symmetry breaking and polarity establishment in the early C. elegans embryo.
Selected by Giuliana ClementeCategories: cell biology, developmental biology
Context and Background:
Asymmetric cell division is universally used in development to ensure cell fate diversity and to orchestrate axes formation and embryonic body plan patterning. The early C. elegans embryo is one of the most widely used systems to gain genetic and molecular insights into the processes that underlie symmetry breaking (Rose L. et al., 2014). In this model organism, asymmetric cell division is evident from the very first cleavage of the zygote and goes on for the next 4 rounds, during which the major body axes are established. The A-P axis rises upon fertilisation and the position of the paternal centrosome marks the future posterior side of the embryo. At the molecular level, symmetry breaking derives from a change in the uniform contraction of the acto-myosin cortex, involving the small GTPase RHO-1 and its activator ECT-2. At the onset of polarity establishment, upon a still unknown signal, ECT-2 is displaced from the future posterior cortex and Myosin-II is disassembled, leading to cortex relaxation and increased acto-myosin flow towards the anterior (Motegi F. et al., 2006; Zonies S. et al., 2010). This unbalance favours the recruitment of PAR-2 at the posterior pole while pushing the anterior PAR complex (PAR-3/PAR-6/PKC-3) to the opposite end.
Whether and how centrosomes dictate symmetry breaking and how they signal the cell cortex to recruit polarity complexes is still unclear and under investigation. Two recent preprints from the Gönczy and the Kotak labs look at the centrosome as a signalling hub for the establishment of polarity and identify the Aurora A kinase (AIR-1 in C. elegans) as a central player in polarity establishment.
Key findings:
Both studies start with the observation that inhibition of AIR-1, either by RNAi or using a dead kinase variant, results in the formation of two PAR-2 domains, one at each pole of the zygote. This unusual distribution of PAR-2 is also accompanied by a delocalisation of the anterior PAR-3/PAR-6/PKC-3 complex in the middle, suggesting that, under normal conditions, Aurora A controls the spatial distribution of the PAR complexes within the embryo.
As the cortical acto-myosin flow is critical for the asymmetric distribution of the PAR components, the two groups analyse this variable by image velocimetry (PIV) analysis and found that AIR-1 knockdown results in reduced cortical flow. Specifically, they registered two flows of small intensity that start from both poles and propagate towards the centre. The reduction of cortical flow nicely correlates with no changes in the localisation of Myosin-II at the posterior cortex upon polarity establishment.
Next, both preprints address whether centrosomes play a role in symmetry breaking. Previous studies found these organelles indispensible for setting up polarity in the C. elegans zygote. The work from the Gönczy lab now questions this assumption given that in the AIR-1 RNAi background, in which centrosomes are not functional, polarity is altered but yet established. They observed that eggs fertilised with sperm from such-1 (t1668) mutants (which do not harbour centrioles) still form a PAR-2 crescent either at the anterior or at both poles, indicating that centrioles are not required for symmetry breaking. Nevertheless, the data suggest that localisation of AIR-1 at the centrosome provides a spatial cue to organise a posterior PAR domain. To test this idea, Klinkert et al. force the localisation of a RNAi-resistant AIR-1 to an immature, non-functional centriole (SPD-2 RNAi) to test whether it would rescue the defective asymmetry upon RNAi of endogenous AIR-1. Surprisingly, centrioles lacking SPD-2 establish a unique, posterior PAR2 domain, rescuing the AIR-1 RNAi phenotype. This set of experiments suggests therefore that the C. elegans one-cell embryo has an intrinsic ability to polarise; however, AIR-1 at the centrosome provides the spatial information for proper PAR-2 localisation at the posterior pole, ensuring the uniqueness of symmetry breaking. Kapoor et al. reach a similar conclusion using a different approach. They explore symmetry breaking in zyg-12 mutants, in which centrosomes do not keep their association to the nucleus and move freely in the cytoplasm towards the anterior pole, resulting in an anterior PAR-2 domain. Down-regulation of the kinase leads to anterior and posterior cortical PAR-2 localisation, no matter the position of the centrosome. These results reinforce the notion that centrosomal Aurora A instructs the posterior cortex to allocate PAR-2.
Given that in the absence of centrosomes the zygote is able to self-organise its polarisation, is there any physical property intrinsic to the system that might drive PAR-2 localisation to the cortex? Klinkert et al. set out to answer this question by using triangular PDMS chambers into which squeeze the embryos and developing an integrated physical model for symmetry breaking. Combining these methods, they reach the conclusion that PAR-2 tends to localise to region of high membrane curvature.
Finally to get at the mechanism of how PAR-2 posterior localisation is spatially controlled by Aurora A, Kapoor et al. investigate whether the kinase works upstream of ECT-2 and thus acts as master regulator of the acto-myosin flow. They find that simultaneous depletion of AIR-1 and ECT-2 rescues the AIR-1 RNAi phenotype restoring the formation of a single PAR-2 domain. Moreover, by monitoring ECT-2 localisation upon polarity establishment, they find that AIR-1 RNAi results in persistent localisation of ECT-2 at the posterior cortex. These data support the idea that Aurora A spatially controls symmetry breaking through the displacement of ECT-2 from the posterior cortex.
Importance: a new working model for Aurora A activity in symmetry breaking:
The data from the preprints advance our knowledge of symmetry breaking and polarity establishment in the C. elegans zygote. This new research suggests that the system is able to self-organise polarity in the absence of functional centrosomes by exploiting areas of high membrane curvature. Nevertheless centrosomes contribute to the process: by controlling ECT-2 localisation, centrosomal AIR-1 provides spatial uniqueness to symmetry breaking by redirecting PAR-2 to only one side of the embryo. AIR-1 acts upstream of the small RHO-GEF ECT-2 and promotes its displacement from the posterior cortex (Figure 1B, B’). This in turn leads to local cortical relaxation and initiates a robust actin flow towards the anterior, pushing the anterior PAR complex to the opposite side, thereby ensuring the formation of a single A/P axis.
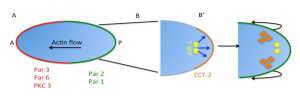
Figure 1: Representation of the sequential steps that lead to a unique A/P axis in the C. elegans zygote. A) Polarised C. elegans one-cell embryo. Upon fertilisation, a dramatic reorganisation results in the formation of a unique A/P axis characterised by the establishment of robust anterior and posterior PAR domains (in red and green, respectively). B, B’) Zoomed-in view of the posterior pole at the time of symmetry breaking. Centrosomal AIR-1 (in yellow) signals the posterior cortex (blue arrows) where ECT-2 (in orange) is uniformly distributed. Following AIR-1 activity, ECT-2 is displaced from the cortex and Myosin-II patches disassemble in the area, leading to cortical relaxation and formation of a region of high membrane curvature. Par-2 localises to this region (in green). Actin flow (black arrows) moves anteriorly, pushing the anterior PAR components in this direction.
Future directions and Questions to the authors:
- Previous work suggested that a pool of AIR-1 is present at the cell cortex. The Gönczy lab exploited the GFP-GBP system to address whether the kinase has any non-centrosomal function and suggested that AIR-1 at the cortex prevents unregulated symmetry breaking events from happening. How does the kinase localise at the cortex? Does it used the same binding mode/domain to localise at the centrosome? What are the targets of AIR-1 at the cortex? Presumably, cortical AIR-1 needs to be cleared solely from the posterior cortex to allow symmetry breaking. Can you speculate on how AIR-1 cortical localisation is fine-tuned?
- PAR-2 has high affinity for regions of high membrane curvature. Does PAR-2 bind these regions directly? From a structural point of view, does it have BAR domains? Do you think this is a feature shared with other PAR proteins?
- Is ECT-2 a direct target of AIR-1?
- Both preprints look at the role of the microtubule cytoskeleton in the establishment of polarity. Reduced number of astral microtubules (TBG-1 RNAi) or complete loss of microtubules (Nocadozole treatment) do not impair PAR-2 localisation to the cortex upon AIR-1 RNAi, reinforcing the idea that the system is able to self-organise polarity. However mutation of the PAR-2 microtubule binding motif completely abrogates its binding to the cortex upon AIR-1 RNAi, suggesting that in this context the presence of microtubules is way more detrimental for polarity establishment. To what extent does the microtubule cytoskeleton contribute to symmetry breaking? And how are the actin and microtubule networks integrated to ensure the formation of a single A/P axis?
- The role of the acto-myosin cytoskeleton in regulating polarity establishment and positioning of polarity markers has been tested and proved in other systems, such as the Drosophila neuroblast (Broadus and Doe, 1997; Hannaford et al., 2018). How conserved is the role of Aurora A in dictating symmetry breaking in other developmental contexts? And how relevant is it to physiopathological conditions?
References:
- Rose L. and Gönczy P. – Polarity establishment, asymmetric division and segregation of fate determinants in early elegans embryos- December 30, 2014), WormBook, doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.30.2, http://www.wormbook.org.
- Motegi F. and Sugimoto A. – Sequential functioning of the ECT-2 RhoGEF, RHO-1 and CDC-42 establishes cell polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans – Nature cell biology 8, 978 (Sep, 2006).
- Zonies S. et al.- Symmetry breaking and polarization of the elegans zygote by the polarity protein PAR-2- Development 137, 1669 (May, 2010).
- Broadus and Doe- Extrinsic cues, intrinsic cues and microfilaments regulate asymmetric protein localization in Drosophila neuroblasts- Current Biology 1997 (7)-11: 827-35
- Hannaford MR et al.- aPKC-mediated displacement and actomyosin-mediated retention polarize Miranda in Drosophila neuroblasts- Elife, eLife. 2018; 7:e29939. doi:10.7554/eLife.29939.
Sign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the cell biology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
Also in the developmental biology category:
Cooperation between cortical and cytoplasmic forces shapes planar 4-cell stage embryos
Corentin Mollier, Shivani Dharmadhikari
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Imaging Reveals Spatiotemporal Divergence in Morphogenesis and Cell Lineage Specification between in-vivo and in-vitro Mouse Embryo during Pre- and Peri-implantation
Heather Pollington
preLists in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the developmental biology category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
BSDB/GenSoc Spring Meeting 2024
A list of preprints highlighted at the British Society for Developmental Biology and Genetics Society joint Spring meeting 2024 at Warwick, UK.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
GfE/ DSDB meeting 2024
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the 2024 joint German and Dutch developmental biology societies meeting that took place in March 2024 in Osnabrück, Germany.
| List by | Joyce Yu |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology
Preprints from the 2nd Conference of the Visegrád Group Society for Developmental Biology (2-5 September, 2021, Szeged, Hungary)
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Society for Developmental Biology 79th Annual Meeting
Preprints at SDB 2020
| List by | Irepan Salvador-Martinez, Martin Estermann |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EDBC Alicante 2019
Preprints presented at the European Developmental Biology Congress (EDBC) in Alicante, October 23-26 2019.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Young Embryologist Network Conference 2019
Preprints presented at the Young Embryologist Network 2019 conference, 13 May, The Francis Crick Institute, London
| List by | Alex Eve |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)