NLR immune receptor-nanobody fusions confer plant disease resistance
Posted on: 4 November 2021 , updated on: 20 April 2023
Preprint posted on 24 October 2021
Article now published in Science at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abn4116
Pikobodies with huge potential: One giant leap toward ready-to-order plant resistance genes
Selected by Marc SomssichCategories: bioengineering, cell biology, immunology, molecular biology, pathology, plant biology
Updated 19 April 2023 with a postLight by Marc Somssich
The bioRxiv preprint highlighted here has now been republished in Science, where it has already attracted some attention from the mainstream media. My favorite headline comes from German magazine Spektrum, which writes “This is how Alpacas can protect plants from disease”.
And while we are on the topic of Alpacas, this is also where my main criticism of the republished and peer reviewed version of this article comes in: The original preprint ended with a figure (Fig. 4), illustrating the pipeline of how to generate the synthetic Pikobodies that can provide plant disease-resistance. This figure, anchored by a mildly annoyed Llama (or Alpaca), and adopted with minimal (but pointed) change for Fig. 2 of our preLight, was not just beautiful and eye-catching, but also a very well executed and easy-to-grasp summary of the manuscript. Such a figure is not only informative, it is also useful in illustrating and communicating scientific advances to the scientific community, and, maybe even more important, to the general public. It is clear that the figure was moved to the supplementary material because of the word/figure/page restrictions imposed by the journal, but given that these restrictions are an outdated remnant from the time of paper-based journals (and it would be possible to offer online-versions of papers with additional figures), it is a real shame that this figure is now (pretty much) hidden from science communicators and the public.
This criticism aside, it is important to also highlight the work that has replaced our beloved Alpaca as Figure 4 in the journal-version of the paper. One of the main points I raised as “next steps” in my preLight was the necessity to test the functionality of the Pikobodies in stable transgenic plant lines, rather than transiently transformed leaves of N. benthamiana only. I suggested to do this in Arabidopsis thaliana, since the generation of stable plant lines is work and time consuming. However, for their Science paper, Kourelis and Marchal et al. (2023) took this a step further and produced stable transgenic N. benthamiana lines. These transgenic plant lines expressed their GFP-targeting PikobodyEnhancer, and when challenged with GFP– or mCherry-expressing Potato virus X indeed conferred resistance against the GFP-expressing variant of the virus, but not the mCherry-version. This acquired resistance was independent of the infection method (lab-based infiltration, or, closer to a real-life situation, leaf wounding).
Given that the Pikobodies need to work in stable transgenic plants, should they be used in the field to confer resistance to crops, this additional experiment is extremely valuable and has improved this paper significantly. It will be very interesting to see the further developments around Pikobodies, particularly in crops and in the field.
Background
In his talk ‘Beyond single genes: receptor networks underpin plant immunity’ Prof. Sophien Kamoun points out one of the main differences between the immune systems of plants and animals (to any animal researcher reading this: Yes, plants really have an immune system): While animals have an adaptive immune system, enabling them to acquire immunity against new pathogens and creating an immunological memory through the production of antibodies, plants find themselves in a continuous evolutionary arms race with their pathogens, having to evolve new receptors to sense newly evolved pathogen effectors (1,2).
The plant immune system is assumed to be a two-tiered system, with the two tiers, pattern- and effector-triggered immunity (PTI & ETI), being tightly interconnected (1,3). PTI is centred around plasma membrane-localized pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which sense extracellular pathogens trying to breach the membrane and enter the cell. On tier 2, ETI is an intracellular surveillance system to detect avirulence (AVR) effector proteins that were injected into the cell by pathogens that successfully escaped PRR-detection (1,2). Both detection systems launch the plant’s defence response, with activated ETI leading to an amplification of the PTI-triggered response, that can eventually result in controlled death of the infected cell in order to protect the cells around it (hypersensitive cell death response (HR), which is used as the main readout for an immune reaction in the new preprint discussed here (4)) (1,2).
The receptors involved in ETI are mainly nucleotide binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins, which are generally composed of three domains (Fig. 1): on their N-terminus there can be a coiled-coil (CC) or Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/R protein (TIR) domain, necessary for the NLR to oligomerise and activate an immune response (5). In the centre is a nucleotide-binding (NB) domain involved in effector-binding, and located on the C-terminus is an LRR domain with an auto-inhibitory function, and involvement in effector-binding (5). There are exceptions to this canonical structure, of course, and some NLRs sense the pathogen effectors via an additional integrated domain (ID) (Fig. 1) (5). While such IDs generally are highly specific to a certain effector, recent work led by Juan Carlos de la Concepcion has provided proof of concept that their specificity can also be manipulated (6). In their study, de la Concepcion et al. (2019) use the ID of the NLR Pikp and engineer it to bind several AVR-Pik effector variants, rather than just its specific AVR-Pik effector (6). Similarly, Liu et al. (2021) have engineered the ID of the rice NLR RGA5 to recognize related variants of its specific effector AVR-Pib (7).
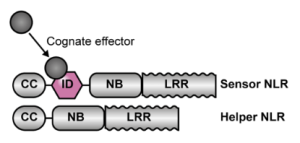 Fig. 1: Structure of plant NLR effector receptors. Canonical NLRs carry a CC (or TIR), NB and LRR domain, and form a heterodimer made up of a sensor and a helper NLR. Some atypical NLRs have an additional ID to bind the cognate pathogen effector protein. From ref. 4.
Fig. 1: Structure of plant NLR effector receptors. Canonical NLRs carry a CC (or TIR), NB and LRR domain, and form a heterodimer made up of a sensor and a helper NLR. Some atypical NLRs have an additional ID to bind the cognate pathogen effector protein. From ref. 4.
As a result of this work, the Pik NLR gained a wider effector recognition profile (6,7). But maybe more importantly, these studies demonstrated that the ID is tolerant of manipulation and therefore may function as a scaffold to engineer completely new designer effector-recognition domains. And by engineering NLR gene stacks that readily provide crop plants with resistance to several pests common to a geographical area or season, a pseudo-adaptive immune system for plants could potentially be created. And this is exactly the direction Jiorgos Kourelis and Clémence Marchal (equal contribution) from the lab of Sophien Kamoun are heading with their new preprint: They engineer a completely new and adaptable(!) effector-recognition domain for a plant NLR (4).
In this Preprint
The authors used nanobodies, the minimal antigen-binding fragment of camelid antibodies, raised against GFP or mCherry and inserted these in the position of the ID of the Pik-1 NLR. In case these NLR-nanobody fusions (named Pikobodies) are functional resistance proteins, the engineered GFP/mCherry-Pik-1 NLRs would trigger an immune reaction in the plant in response to the detection of GFP or mCherry. But first the authors checked for any autoimmune activities of the engineered Pikobodies, which manipulated NLRs often have, by expressing them in Nicotiana benthamiana leaf epidermal cells. Pikobodies that trigger an autoimmune response will cause necrotic lesions around the infiltration site, as a result of local cell death. Several of the designed Pikobodies did not show such an autoimmune response, and thus were selected for further analyses.
These potentially functional Pikobodies included Pikobody(Enhancer) recognizing GFP, and Pikobody(LaM-4) recognizing mCherry. The authors then co-expressed these with GFP and mCherry proteins, to see if the Pikobodies recognized their respective target. And indeed, co-expression of Pikobody(Enhancer) with GFP resulted in cell death, while co-expression with mCherry showed no effects. On the other hand, expression of Pikobody(LaM-4) only resulted in cell death when expressed with mCherry, but not GFP. To see if these Pikobodies would also react to actual infection by a pathogen, the authors infected N. benthamiana leaves expressing the different Pikobodies with a GFP– or mCherry-expressing potato virus X. Again, the Pikobodies appeared to recognize their intended target protein and seemed to provide protection against viral infection.
Finally, the authors checked if their Pikobodies were compatible with gene stacking. Should the Pikobodies be used to provide ready-to-order resistance (R) genes in the future, crop plants would ideally be protected against several pathogens, which would require the introduction of more than one R gene (i.e., a stack of genes) (8). To test the compatibility of the Pikobodies to R gene stacking, the authors co-transformed N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells with their Pikobody(Enhancer) or (LaM-4), in combination with the wild type Pik NLRs, or the two Pikobodies(Enhancer) and (LaM-4) together, and showed that this co-expression indeed resulted in an immune response to the two different recognized effectors.
Perspectives
The work presented in this preprint is a remarkable proof-of-concept study demonstrating that Pikobodies hold the potential to provide ready-to-order R genes against virtually any pathogen. The pipeline, as outlined by the authors in their final figure (Fig. 2), is simple and straight forward: Pathogen effectors are isolated and used to immunize a camelid (llamas or alpacas are often used, Sophien Kamoun made it clear on social media that he prefers camels). Anti(nano)bodies produced by the camelid are then isolated and integrated into the ID of a Pik NLR-scaffold. Finally, the resulting Pikobody NLRs are introduced into plants to provide resistance against one or more pathogens
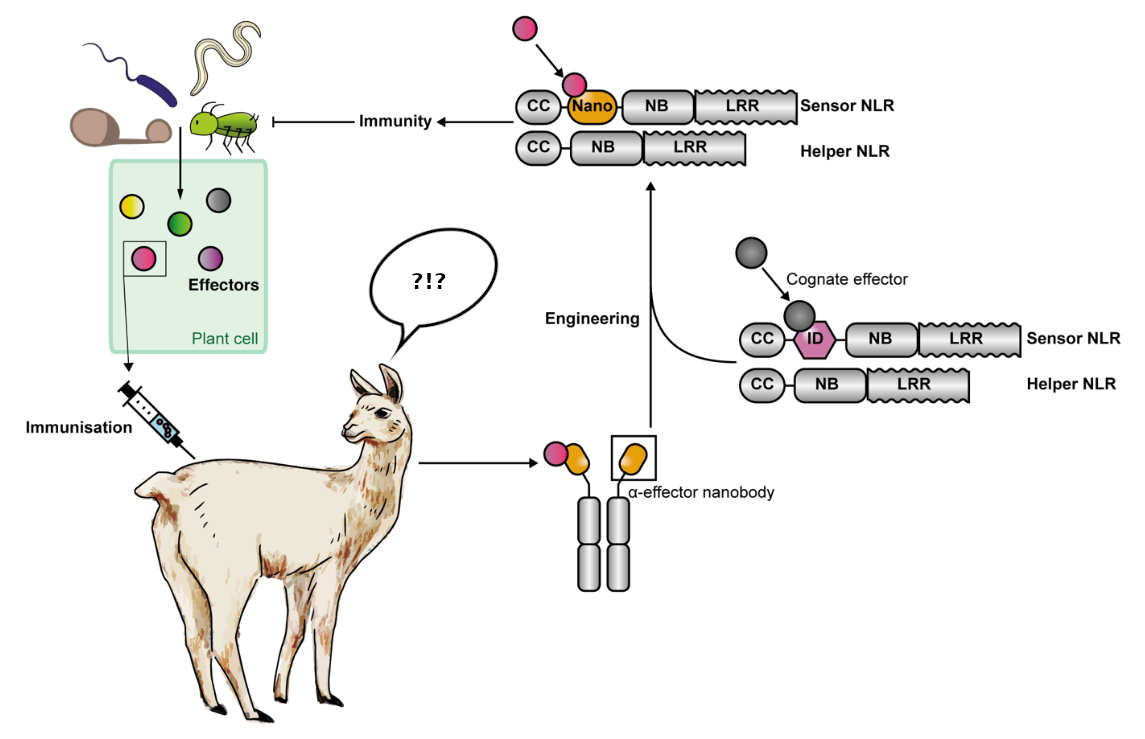 Fig. 2: Pipeline to produce Pikobodies (counterclockwise from top left). Adapted from ref. 4.
Fig. 2: Pipeline to produce Pikobodies (counterclockwise from top left). Adapted from ref. 4.
The next steps toward this aim are clear: First, the Pikobodies must be shown to work in stably transformed plants, first in Arabidopsis thaliana, then in an actual crop plant, and the resistance must persist over several generations. Then, of course, Pikobodies must be produced that contain nanobodies against actual pathogen effectors; effectors from wheat and rice blast or potato late blight are some prime candidates that will be tested first. Such Pikobodies would then be expressed as R gene stacks in crop plants and hopefully provide resistance against these pathogens.
Should this concept indeed prove working and efficient in crop plants, it could be a revolution for the agricultural sector.
References:
- Jones JDG, Dangl JL. The plant immune system. Nature. 2006;444: 323–9. Available at doi:10.1038/nature05286
- Kamoun S. NLR receptor networks: filling the gap between evolutionary and mechanistic studies. Zenodo. 2021;: 5504058. Available at doi:10.5281/zenodo.5504058
- Ngou BPM, Ahn H, Ding P, Jones JDG. Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature. Springer US; 2021; Available at doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03315-7
- Kourelis J, Marchal C, Kamoun S. NLR immune receptor-nanobody fusions confer plant disease resistance. bioRxiv. 2021;: 465418. Available at doi:10.1101/2021.10.24.465418
- Duxbury Z, Wu C, Ding P. A Comparative Overview of the Intracellular Guardians of Plants and Animals: NLRs in Innate Immunity and Beyond. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2021;72: annurev-arplant-080620-104948. Available at doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-080620-104948
- De la Concepcion JC, Franceschetti M, MacLean D, Terauchi R, Kamoun S, Banfield MJ. Protein engineering expands the effector recognition profile of a rice NLR immune receptor. Elife. 2019;8: 1–19. Available at doi:10.7554/eLife.47713
- Liu Y, Zhang X, Yuan G, Wang D, Zheng Y, Ma M, et al. A designer rice NLR immune receptor confers resistance to the rice blast fungus carrying noncorresponding avirulence effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118: e2110751118. Available at doi:10.1073/pnas.2110751118
- Ghislain M, Byarugaba AA, Magembe E, Njoroge A, Rivera C, Román ML, et al. Stacking three late blight resistance genes from wild species directly into African highland potato varieties confers complete field resistance to local blight races. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;: 1–11. Available at doi:10.1111/pbi.13042
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.30993
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioengineering category:
Scalable and efficient generation of mouse primordial germ cell-like cells
Carly Guiltinan
Generalized Biomolecular Modeling and Design with RoseTTAFold All-Atom
Saanjbati Adhikari
Multi-pass, single-molecule nanopore reading of long protein strands with single-amino acid sensitivity
Benjamin Dominik Maier, Samantha Seah
Also in the cell biology category:
Cell cycle-dependent mRNA localization in P-bodies
Mohammed JALLOH
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
Roberto Amadio
Notch3 is a genetic modifier of NODAL signalling for patterning asymmetry during mouse heart looping
Bhaval Parmar
Also in the immunology category:
Control of Inflammatory Response by Tissue Microenvironment
Roberto Amadio
G6b-B antibody-based cis-acting platelet receptor inhibitors (CAPRIs) as a new family of anti-thrombotic therapeutics
Simon Cleary
Feedback loop regulation between viperin and viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus through competing protein degradation pathways
UofA IMB565 et al.
Also in the molecular biology category:
Cell cycle-dependent mRNA localization in P-bodies
Mohammed JALLOH
Notch3 is a genetic modifier of NODAL signalling for patterning asymmetry during mouse heart looping
Bhaval Parmar
Fetal brain response to maternal inflammation requires microglia
Manuel Lessi
Also in the pathology category:
LINC complex alterations are a hallmark of sporadic and familial ALS/FTD
Megane Rayer et al.
Hypoxia blunts angiogenic signaling and upregulates the antioxidant system in elephant seal endothelial cells
Sarah Young-Veenstra
H2O2 sulfenylates CHE linking local infection to establishment of systemic acquired resistance
Marc Somssich
Also in the plant biology category:
Plasmodesmal closure elicits stress responses
Yueh Cho
Generalized Biomolecular Modeling and Design with RoseTTAFold All-Atom
Saanjbati Adhikari
Plant plasmodesmata bridges form through ER-driven incomplete cytokinesis
AND
Plasmodesmata act as unconventional membrane contact sites regulating inter-cellular molecular exchange in plants
Gwendolyn K. Kirschner
preLists in the bioengineering category:
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Advances in microscopy
This preList highlights exciting unpublished preprint articles describing advances in microscopy with a focus on light-sheet microscopy.
| List by | Stephan Daetwyler |
Also in the cell biology category:
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the immunology category:
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the molecular biology category:
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Also in the pathology category:
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
Also in the plant biology category:
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
SDB 78th Annual Meeting 2019
A curation of the preprints presented at the SDB meeting in Boston, July 26-30 2019. The preList will be updated throughout the duration of the meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)