Small extracellular vesicles promote stiffness-mediated metastasis
Posted on: 3 August 2023 , updated on: 29 May 2024
Preprint posted on 5 July 2023
Article now published in Cancer Research Communications at http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0431
Small but mighty: Sneider and colleagues demonstrate the impact of tissue stiffness on extracellular vesicle-mediated metastasis in breast cancer.
Selected by Jade Chan, yohalie kalukulaCategories: biophysics, cancer biology, cell biology
Updated 29 May 2024 with a postLight by Jade Chan and Yohalie Kalukula
This highlighted preprint has now been published in Cancer Research Communications, a new journal from the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR). In this study, A. Sneider, Y. Liu, B. Starich and colleagues demonstrate that the function, content, and overall quantity of extracellular vesicles secreted by cancer cells depends on the stiffness of their microenvironment. Importantly, they show that tumour-derived extracellular vesicles can alter the properties of metastatic sites even at great distances from the original tumour.
The preprint article and the published version are largely identical with minor differences in the formatting of the figures, which attests to the scientific rigor of the initial manuscript. Congratulations again to the authors for their contribution to the field!
Introduction
The diverse functions carried out by the different tissues and organs in our bodies are not only influenced by biochemical signalling, but by physical cues like stiffness as well. Different tissues exhibit different average stiffnesses, ranging from 100 Pa in the brain to over 106 Pa in bone (1). Tissue stiffness is largely influenced by the extracellular matrix (ECM), a mesh-like network composed of proteins such as collagens. Changes to the mechanical properties of the ECM during tumorigenesis have been reported in several solid tumour types (2-6). For example, tissue stiffness is correlated with tumour aggression and grade in glioma (7). Tissue stiffness can also influence cells within the tumour microenvironment. For example, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) increase collagen deposition in proximity to tumour cells, which can promote metastatic behaviours (8).
One way in which cancer cells can communicate with their environment is through the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are 30-150 nm wide and contain proteins and nucleic acids (9). Due to their tiny size, tumour-derived EVs can travel long distances from their cells of origin and influence processes such as immune evasion and metastatic niche priming (10-13).
In almost all prior studies on EVs, cancer cells were cultured on plastic, which does not accurately reflect stiffness levels experienced by cancer cells in vivo and may affect the protein cargo carried by EVs. In this study, the authors used a combination of cell culture, mouse models, and zebrafish models of metastasis to determine the impact of physiologically relevant tissue stiffness on EV-mediated metastatic dissemination.
Key Findings
Matrix stiffness impacts EV quantity and protein cargo
The authors measured the stiffness of breast tumour tissues from patients and found a wide range of stiffnesses, from ~3 kPa to over ~80 kPa. Breast cancer is known to commonly metastasize to the lung, which has a stiffness range of 0.5-5 kPa. Using fresh tumour samples for compression analysis, the authors found that stiff tumour regions (>10 kPA) released more extracellular vesicles (EVs) than soft regions (<10 kPA).
The authors also wondered whether stiffness affected the protein cargo within EVs. Thus, they developed “soft” (0.5 kPa) and “stiff” (25 kPa) matrices to model physiologically relevant stiffness levels. When the authors isolated EVs from highly invasive, triple-negative breast cancer cells cultured on soft or stiff matrices, they found striking differences in the protein content between these conditions through mass spectrometry. Proteins enriched in stiff EVs compared to soft EVs were primarily involved in tumorigenesis, cell adhesion, and cell migration, prompting the authors to investigate whether matrix stiffness could affect the ability of EVs to spread to different organs.
Stiff EVs show enhanced biodistribution in vivo
To see whether matrix stiffness affected the ability of EVs to spread, the authors injected immunocompromised mice with fluorescent EVs via the tail vein and tracked them throughout the body. Using near-infrared imaging, they observed that stiff EVs had a greater signal intensity in the lungs, liver, and spleen compared to soft EVs. Importantly, this observation in their mouse model mimics human breast cancer, which mainly metastasizes to the lungs.
But how do stiff EVs distribute more readily than soft EVs? The authors hypothesized that stiff versus soft EVs differed in their ability to bind to ECM proteins. Using an ECM binding assay, they found that stiff EVs attached more strongly to collagen IV than soft EVs. This enhanced binding could potentially be due to the enrichment of adhesion proteins like CD44 in stiff versus soft EVs.
Stiff EVs promote cancer cell dissemination and survival in vivo
Based on the accumulation of stiff EVs within common tumour secondary sites, the authors wondered whether stiff EVs could affect circulating cancer cells during metastasis (14). Indeed, the escape of cancer cells from the primary tumour is often choreographed by chemotaxis, the biased migration of cells under a chemical gradient. Therefore, they tested the chemotactic properties of stiff versus soft EVs using a transwell assay. In this experiment, breast cancer cells were separated from EV concentrated media by a semipermeable membrane. After 16 hours, cell migration towards stiff EVs was threefold higher than towards soft EVs.
But what would happen in a more complex and challenging microenvironment? To model this scenario, the authors created a zebrafish xenograft model. In this experiment, stiff or soft EVs were injected into the yolk sac of zebrafish embryos 2 days post-fertilization, followed by injection of cancer cells. Cell dissemination and the leakage of cancer cells into perivascular locations (extravasation) were assessed 24h and 72h post injection, respectively. In the absence of EVs, only 4.2% of cancer cells were able to disseminate. Strikingly, 33.8% of embryos injected with stiff EVs showed disseminated cells in contrast to only 10.7% of embryos injected with soft EVs. Similarly, 20% of embryos treated with stiff EVs had extravasated cells, whereas none of the embryos injected with soft EVs exhibited extravasation.
Soft EVs transform fibroblasts into CAF-like cells
The authors investigated whether stiff versus soft EVs from breast cancer cells had different effects on tumour formation at secondary sites by transforming resident fibroblasts. Indeed, the nesting of future sites of metastasis is a process orchestrated by the crosstalk between the microenvironment and transformed resident stromal cells, such as cancer associated fibroblasts (CAF). Since EVs showed greater retention in the lungs in vivo, the authors assessed EV-mediated changes in the phenotype of normal lung fibroblasts.
Lung tissue is relatively soft (0.5-5 kPa), similar to normal breast tissue (15,16). Lung fibroblasts treated with soft EVs upregulated CAF-associated genes such as smooth muscle actin, collagen I, and VEGFA (8,17) compared to fibroblasts treated with stiff EVs. Next, the authors investigated the expression of inflammatory S100 proteins since they were found to be critical for successful pre-metastatic niche formation (18). Lung fibroblasts exposed to soft EVs upregulated the expression of four S100 genes, whereas treatment with stiff EVs resulted in downregulation.
Altogether, the authors found that in contrast to stiff EVs, soft EVs induce a potent CAF-like phenotype in lung fibroblasts, highlighting the different roles played by soft versus stiff EVs during the metastatic cascade.
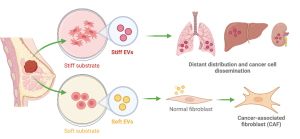
Above: A summary of the different effects of stiff versus soft EVs during metastasis. Tumour tissue stiffens over the course of tumour development, resulting in a change in the protein content of EVs. Stiff EVs upregulate adhesion molecules and distribute more readily into distant sites. Tumour derived EVs with a ‘soft’ gene expression profile promote a CAF identity in neighboring fibroblasts. Schematic created using BioRender.
Why we chose this preprint
Yohalie: This preprint holds particular significance given the growing interest in extracellular vesicles (EV) as new biomarkers in cancer diagnosis. The authors demonstrate how EVs can exhibit distinct roles in the metastatic cascade based on their production conditions. They highlight the crucial role of soft EVs in preparing distant organs during late-stage metastasis, while stiff EVs are crucial for cell dissemination during early-stage metastasis.
Jade: I found this preprint particularly interesting due to the finding that the stiffness of the primary tumour could affect the success of metastatic colonization even at great distances from the original site. Solid tumours exhibit a high degree of intra- and intertumoral heterogeneity in terms of stiffness, and I believe this preprint nicely highlights how different steps in the metastatic process (from escaping the primary tumour to remodelling resident cells of the metastatic niche) are influenced by the mechanical properties of the original tumour.
Questions for the authors
- What upstream signalling events occur in tumour cells that determine the protein cargo of stiff versus soft EVs?
- Are there in vitro assays to assess matrix remodelling by lung derived fibroblasts upon treatment with soft EVs? Would there be differences in fiber alignment, or changes to the architecture of the collagen matrix?
- Can stiff EVs impact fibroblasts at the primary tumour site to help cells escape the tumour?
- In vivo, most matrices are viscoelastic. Do you think the content of EVs could be impacted by matrix viscosity?
- Which molecules contained by stiff versus soft EVs could be responsible for inducing a CAF-like phenotype?
References
- Cox, T. R., & Erler, J. T. (2011). Remodeling and homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: implications for fibrotic diseases and cancer. Dis model mech, 4(2), 165–178.
- Colpaert, C., Vermeulen, P., Van Marck, E., and Dirix, L. (2001). The presence of a fibrotic focus is an independent predictor of early metastasis in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Am J Surg Pathol 25, 1557–1558.
- Hasebe, T., Tsuda, H., Hirohashi, S., Shimosato, Y., Iwai, M., Imoto, S., and Mukai, K. (1996). Fibrotic focus in invasive ductal carcinoma: an indicator of high tumor aggressiveness. Jpn J Cancer Res 87, 385–394.
- Hasebe, T., Tsuda, H., Hirohashi, S., Shimosato, Y., Tsubono, Y., Yamamoto, H., and Mukai, K. (1998). Fibrotic focus in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast: a significant histopathological prognostic parameter for predicting the long-term survival of the patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 49, 195–208.
- Hasebe, T., Sasaki, S., Imoto, S., Mukai, K., Yokose, T., and Ochiai, A. (2002). Prognostic Significance of Fibrotic Focus in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast: A Prospective Observational Study. Mod Pathol 15, 502–516.
- Conklin, M.W., Eickhoff, J.C., Riching, K.M., Pehlke, C.A., Eliceiri, K.W., Provenzano, P.P., Friedl, A., and Keely, P.J. (2011). Aligned Collagen Is a Prognostic Signature for Survival in Human Breast Carcinoma. Am J Pathol 178, 1221–1232.
- Miroshnikova, Y. A., Mouw, J. K., Barnes, J. M., Pickup, M. W., Lakins, J. N., Kim, Y., Lobo, K., Persson, A. I., Reis, G. F., McKnight, T. R., Holland, E. C., Phillips, J. J., & Weaver, V. M. (2016). Tissue mechanics promote IDH1-dependent HIF1α-tenascin C feedback to regulate glioblastoma aggression. Nat Cell Biol, 18(12), 1336–1345.
- Kalluri, R., and Zeisberg, M. (2006). Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6, 392–401.
- van Niel, G., D’Angelo, G., and Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19, 213.
- Marar, C., Starich, B., and Wirtz, D. (2021). Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression. Nat Immunol, 1–11.
- Clayton, A., Mitchell, J.P., Court, J., Linnane, S., Mason, M.D., and Tabi, Z. (2008). Human Tumor-Derived Exosomes Down-Modulate NKG2D Expression. J Immunol 180, 7249–7258.
- Hoshino, A., Costa-Silva, B., Shen, T.-L., Rodrigues, G., Hashimoto, A., Tesic Mark, M., Molina, H., Kohsaka, S., Di Giannatale, A., Ceder, S., et al. (2015). Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 527, 329–335.
- Costa-Silva, B., Aiello, N.M., Ocean, A.J., Singh, S., Zhang, H., Thakur, B.K., Becker, A., Hoshino, A., Mark, M.T., Molina, H., et al. (2015). Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 17, 816–826.
- Du, W., Nair, P., Johnston, A., Wu, P.-H., and Wirtz, D. (2022). Cell Trafficking at the Intersection of the Tumor–Immune Compartments. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 24, 275–305.
- Hinz, B. (2012). Mechanical Aspects of Lung Fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 9, 137–147.
- Polio, S. R., Kundu, A. N., Dougan, C. E., Birch, N. P., Aurian-Blajeni, D. E., Schiffman, J. D., Crosby, A. J., & Peyton, S. R. (2018). Cross-platform mechanical characterization of lung tissue. PloS one, 13(10), e0204765.
- Bhowmick, N.A., Neilson, E.G., and Moses, H.L. (2004). Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 432, 332–337.
- Kaplan, R.N., Riba, R.D., Zacharoulis, S., Bramley, A.H., Vincent, L., Costa, C., MacDonald, D.D., Jin, D.K., Shido, K., Kerns, S.A., et al. (2005). VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 438, 820–827.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.35186
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the biophysics category:
'Preprints by preLighters': Cell loss disrupts mechanical homeostasis to drive retinal pigment epithelium ageing-like phenotype in vitro
Reinier Prosee, Teodora Piskova
Active flows drive clustering and sorting of membrane components with differential affinity to dynamic actin cytoskeleton
Teodora Piskova
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Also in the cancer biology category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Taxane-Induced Conformational Changes in the Microtubule Lattice Activate GEF-H1-Dependent RhoA Signaling
Vibha SINGH
ROCK2 inhibition has a dual role in reducing ECM remodelling and cell growth, while impairing migration and invasion
Sharvari Pitke
Also in the cell biology category:
Cell-intrinsic compliance mechanism enables release of tensile stress to prevent tissue rupture
Ruoheng Li
'Preprints by preLighters': Cell loss disrupts mechanical homeostasis to drive retinal pigment epithelium ageing-like phenotype in vitro
Reinier Prosee, Teodora Piskova
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
preLists in the biophysics category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
66th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, 2022
Preprints presented at the 66th BPS Annual Meeting, Feb 19 - 23, 2022 (The below list is not exhaustive and the preprints are listed in no particular order.)
| List by | Soni Mohapatra |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Biophysical Society Meeting 2020
Some preprints presented at the Biophysical Society Meeting 2020 in San Diego, USA.
| List by | Tessa Sinnige |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Biomolecular NMR
Preprints related to the application and development of biomolecular NMR spectroscopy
| List by | Reid Alderson |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
Also in the cancer biology category:
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Anticancer agents: Discovery and clinical use
Preprints that describe the discovery of anticancer agents and their clinical use. Includes both small molecules and macromolecules like biologics.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the cell biology category:
Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology 2026
The Keystone Symposium on Stem Cell Models in Embryology, 2026, was organised by Jun Wu (UT Southwestern), Jianping Fu (University of Michigan) and Miki Ebisuya (TU Dresden) and held at Asilomar Conference Grounds in California (US). The meeting discussed recent advances made in establishing stem-cell-based embryo models, what fundamental insights into developmental processes have been gleaned from them, as well as how they are beginning to be applied more widely. This prelist contains preprints by presenters at the talk and poster sessions at the conference, which our Reviews Editor in attendance spotted. Please do reach out to preLights@biologists.com if you notice any that we’ve missed.
| List by | Ingrid Tsang |
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)