Circumvention of common labeling artifacts using secondary nanobodies
Posted on: 3 April 2020
Preprint posted on 25 October 2019
Categories: cell biology, immunology
Background
The most common procedure to reveal the location of specific subcellular elements in biological samples is via immunostaining followed by optical imaging. Standard immunodetection approaches use typically a primary antibody which binds the protein of interest and a secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody and carries a detection element which can be either a fluorophore or a single strand of DNA (used in DNA-PAINT). Although this classical immunostaining procedure is widely used, important limitations are size (leading to displacement errors incompatible with super-resolution microscopy) and the ability of secondary antibodies to bind more than one epitope. An alternative to secondary antibodies that addresses these limitations are monovalent recombinant secondary nanobodies. Moreover, nanobodies are more suitable for staining thick biological samples, greatly reducing the incubation times usually needed when using secondary antibodies. Finally, nanobodies overcome the issues faced when performing classical multiplexed immunostaining, which requires primary antibodies to be raised in different species. Nanobodies can be pre-mixed with primary antibodies prior to staining, circumventing the species limitation. In this preprint, Sograte-Idrissi et al (1) explore the use and advantages of secondary nanobodies over antibodies.
Key findings and developments
General findings
- In their work, the authors explored the use of secondary nanobodies for several microscopy applications.
- They confirmed that usage of secondary nanobodies decreases linkage error in STED microscopy and DNA-PAINT and increases localization accuracy compared to secondary antibodies.
- They showed that pre-mixing of secondary nanobodies with primary antibodies before staining is successful- leading to reduced experimental time, and allowing the use of multiple primary antibodies from the same animal species.
- They demonstrate that secondary nanobodies are better able to penetrate thick tissues by using them in optically cleared samples,
- They show that secondary nanobodies avoid artificial clustering sometimes observed when using secondary antibodies.
Specific findings
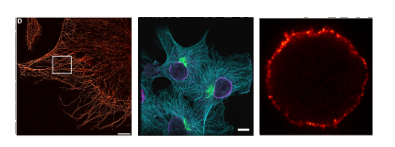
Secondary nanobodies provide higher staining accuracy than secondary antibodies
- Using STED microscopy, the authors imaged COS-7 cells stained with a monoclonal primary anti-tubulin antibody directly conjugated to Abberior Star635P and further recognized by either a polyclonal secondary antibody or a monovalent secondary nanobody carrying AbberiorStar580.
- An autocorrelation analysis was performed on these images to evaluate the staining accuracy of the secondary probes. Analysis of the secondary nanobody showed greater accuracy. This was confirmed upon staining peroxisomes within primary hippocampal neurons.
- The authors then explored secondary nanobody accuracy in the context of DNA-PAINT. The microtubule network of a fibroblast cell line was stained with monoclonal primary antibodies against alpha-tubulin, and detected with a secondary nanobody coupled to a docking strand. Greater accuracy on the apparent diameter of microtubule filaments was achieved.
Bypassing the primary antibody animal species limitations
- Pre-mixing the primary and secondary antibodies prior to incubating them with the sample would save experimental time and costs, however, this is currently not possible due to the polyclonality and the bivalency of secondary antibodies that result in aggregation of the primary-secondary antibody complex and failure to stain the intended target in the sample.
- Bypassing the pre-mixing limitation with monovalent secondary probes would allow using several primary antibodies raised in the same species.
- In their work, the authors used monoclonal antibodies raised in mice against different components (tubulin, Golgi and nuclear pore complex), and pre-mixed each with secondary nanobodies anti-mouse carrying different fluorophores. Upon staining COS7 cells, minimal background and negligible cross-talk was observed between the channels.
- Using Exchange-PAINT they obtained a super-resolved view of a single neuronal synapse in 3D using two primary antibodies from the same species.
Secondary nanobodies enhance sample penetration in shorter incubation time
- The authors pre-mixed primary antibodies with secondary nanobodies for use in a complex thick sample: cochleae extracted from mice. They then compared how long the primary/secondary antibody and the primary antibody/secondary nanobody combinations need, to achieve homogeneous staining of the sample. They then imaged the sample after decalcification and optical clearing.
- They observed faster homogeneous staining upon use of the primary antibody-secondary nanobody mix.
Secondary nanobodies reduce probe-induced clusters of target proteins on living cells
- To test if the 2-nanobodies reduce probe-induced clustering of target molecules, the authors analysed the surface distribution of IgM containing B cell receptors (IgM-BCRs) on a human B cell line.
- Cells were stained and chemically fixed with aldehydes to be imaged under stimulation emission depletion (STED) microscopy.
- They found that the use of secondary nanobodies reduces probe-induced clusters, still observed using primary/secondary antibody combinations.
Probe-induced clusters of target proteins in aldehyde-fixed cells
- Conventional fixations times with 4% PFA do not necessarily prevent protein movement. A more efficient fixative such as glutaraldehyde (GLU) could be used, but it generates unwanted autofluorescence and only few affinity molecules find their target epitopes after GLU crosslinking. An alternative is glyoxal, although its implementation is very recent.
- Using primary/secondary antibody mixes, artefactual clustering formation was observed at most times of incubation with 4% PFA, except 30 minute incubation. Conversely, using secondary nanobodies had no significant change between live, 10 or 30 minutes of fixation with 4%PFA.
What I like about this preprint
I like that the authors explored and validated a relatively novel tool. Often, introducing new technologies to research can be a challenge, and thorough validation helps doing this.
Open questions
- You explored in great detail the comparison to secondary antibodies. Are there any limitations the science community should be aware of upon using nanobodies?
- Why in your opinion, is it still not a widely used tool?
- Are there any advantages in using nanobodies beyond fluorescence microscopy? Namely in other assays that also depend on immune complex formation?
- What are the characteristics of nanobodies in the context of photobleaching and blead-through?
References
- Sograte-Idrissi S, et al., Circumvention of common labelling artefacts using secondary nanobodies, 2019, bioRxiv,doi:10.1101/818351.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.18097
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the cell biology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Self-renewal of neuronal mitochondria through asymmetric division
Lorena Olifiers
Also in the immunology category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Loss of MGST1 during fibroblast differentiation enhances vulnerability to oxidative stress in human heart failure
Jeny Jose
Scalable transcription factor mapping uncovers the regulatory dynamics of natural and synthetic transcription factors in human T cell states
Inês Caiado
preLists in the cell biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
July in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell Signalling and Mechanosensing (2) Cell Cycle and Division (3) Cell Migration and Cytoskeleton (4) Cancer Biology (5) Cell Organelles and Organisation
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
December in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cell cycle and division 2) cell migration and cytoskeleton 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
November in preprints – the CellBio edition
This is the first community-driven preList! A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. Categories include: 1) cancer cell biology 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell migration and cytoskeleton 4) cell organelles and organisation 5) cell signalling and mechanosensing 6) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
preLights peer support – preprints of interest
This is a preprint repository to organise the preprints and preLights covered through the 'preLights peer support' initiative.
| List by | preLights peer support |
The Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting
This preList is made up of the preprints discussed during the Society for Developmental Biology 82nd Annual Meeting that took place in Chicago in July 2023.
| List by | Joyce Yu, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
Planar Cell Polarity – PCP
This preList contains preprints about the latest findings on Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) in various model organisms at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels.
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
BioMalPar XVI: Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite
[under construction] Preprints presented at the (fully virtual) EMBL BioMalPar XVI, 17-18 May 2020 #emblmalaria
| List by | Dey Lab, Samantha Seah |
1
Cell Polarity
Recent research from the field of cell polarity is summarized in this list of preprints. It comprises of studies focusing on various forms of cell polarity ranging from epithelial polarity, planar cell polarity to front-to-rear polarity.
| List by | Yamini Ravichandran |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
Preprints presented at the BSCB/BSDB Annual Meeting 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Biophysical Society Annual Meeting 2019
Few of the preprints that were discussed in the recent BPS annual meeting at Baltimore, USA
| List by | Joseph Jose Thottacherry |
ASCB/EMBO Annual Meeting 2018
This list relates to preprints that were discussed at the recent ASCB conference.
| List by | Dey Lab, Amanda Haage |
Also in the immunology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
Journal of Cell Science meeting ‘Imaging Cell Dynamics’
This preList highlights the preprints discussed at the JCS meeting 'Imaging Cell Dynamics'. The meeting was held from 14 - 17 May 2023 in Lisbon, Portugal and was organised by Erika Holzbaur, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Rob Parton and Michael Way.
| List by | Helen Zenner |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)