Bromodomain Inhibition Blocks Inflammation-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction and SARS-CoV2 Infection in Pre-Clinical Models
Posted on: 27 November 2020
Preprint posted on 16 October 2020
‘In the eye of the (Cytokine) Storm’: COVID-19 inflammation and heart function in 3D-engineered cardiac tissues
Selected by Alexander Ward, Osvaldo ContrerasBackground
The ongoing novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic has infected over 60 million people worldwide, with more than 1.4 million fatalities1. Aside from the occurrence of well-characterised respiratory symptoms of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), 20-50% affected patients are presenting with cardiac complications, including myocarditis (inflammation of the heart), cardiac cell death, heart failure (acute and chronic types) and arrhythmias2.
The reasons for the increased cardiac complications in COVID-19, as compared with other coronavirus diseases, are as yet unknown. It has been speculated that both direct and indirect consequences of infection contribute to diverse cardiac pathologies. With respect to the direct consequences, SARS-CoV-2 shows a significantly greater affinity for its primary target, the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, than SARS-CoV-1, potently and directly targeting cardiac tissues high in ACE22. Exactly which cells of the heart SARS-CoV-2 affects remains unclear; however, direct infection of cardiomyocytes, the beating muscular, conducting cells, has also been observed3. In addition to direct effects on cardiomyocytes, the secondary inflammatory response and increased clotting risk associated with COVID-19 are thought to damage cardiac tissue indirectly 2. In severe cases, acute systemic inflammation induces a ‘Cytokine Storm’, the effects and composition of which are poorly understood.
Despite the recent news of efficacy of a number of novel COVID-19 vaccines4,5, treatments which can alleviate the secondary symptoms remain behind vaccination efforts. Anti-inflammatory agents, inhibiting diverse inflammatory pathways, have made it to clinical trials; the corticosteroid, Dexamethasone, has been shown to reduce mortality in ventilated patients6.
Given the difficulties of studying the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the human heart and the sheer speed of dissemination of COVID-19 related preprints, there is a necessity to quickly understand the molecular mechanisms of the disease firstly in an in vitro setting. The Hudson laboratory are world leaders in the generation of high-throughput bioengineered heart tissues (human cardiac organoids: hCO), using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiac cells and their patented Heart-Dyno system7. Their system provides them with a unique opportunity to screen vast numbers of exogenous molecules and therapeutics, in mature cardiac-like tissues8, and, due to spontaneous beating, measure functional contractile parameters comparable to those measured in the heart. In the current preprint, Mills et al., use their tissue engineered hCO model to address the effects of the cytokine storm on cardiac function and cardiac cell composition following stimulation.
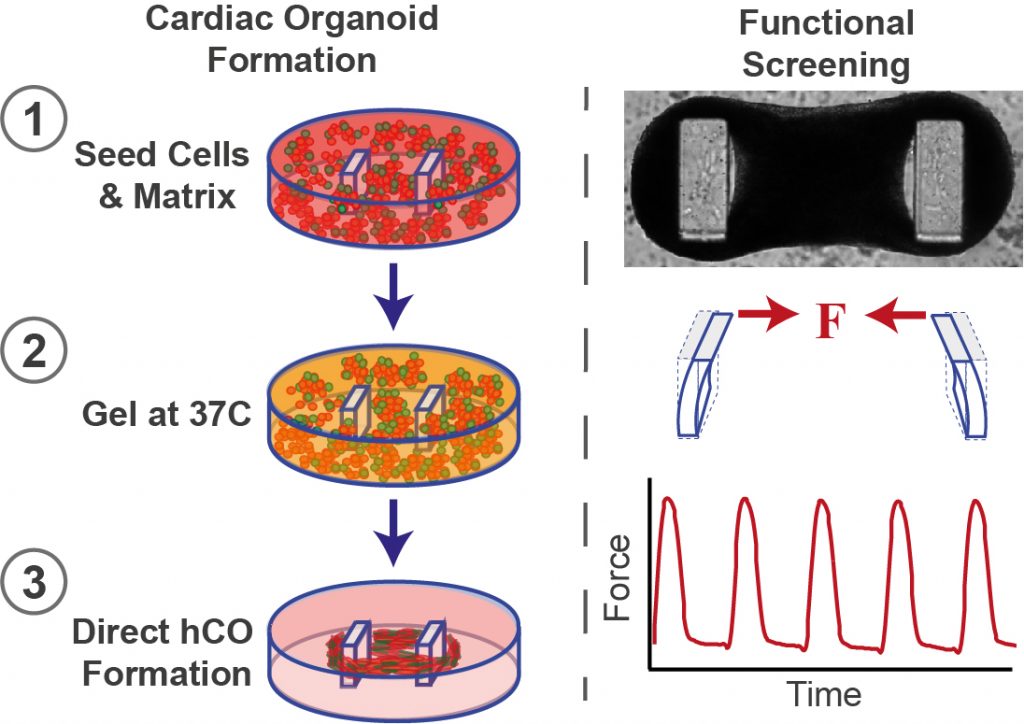
Key findings
Much like the adult human heart, the dynamic, beating hCO tissues include diverse cardiac cell-types, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and pericytes. Using single nuclei RNA-seq (snRNA-seq), Mills et al. showed that the expression levels of several proinflammatory genes linked to the cytokine storm were very similar to those seen in the human heart. Using their high-throughput system, they next screened several pro-inflammatory factors, including cytokines, TNFa, IL-1b, IL-6, IL-8, IL-8, IL-17 and IFN-g, and pathogen associated molecule polyIC and LPS. A number of the components of the cytokine storm resulted in profound alterations to cardiac function in stimulated hCOs. TNFa induced a broad reduction in force (equating to systolic dysfunction), as has been suggested previously9. Whilst IL-1b, IFN-g and polyIC caused an increase in the relaxation time of tissues in between beats, which is clinically representative of diastolic dysfunction in heart failure, where the left ventricle fails to relax normally. This prolonged relaxation time of their cardiac tissues also resulted in an arrhythmic beating, a manifestation which is commonly seen in COVID-19 patients.
Video 1. Spontaneously contracting hCO, beating against the poles of the Heart Dyno. Credit to Richard J Mills.
The profound effects of the cytokine storm on cardiac dysfunction led the authors to investigate the potential downstream effectors of this inflammatory response in heart tissue. Given the critical role of phosphoproteins in transducing inflammatory signals, they interrogated the phosphoproteome using the high-sensitivity EasyPhos technique. The authors identified many differentially phosphorylated effectors, which included transcription factors and chromatin-binding proteins, as well as a handful of other transcription-related machinery, including STAT1 and BRD4. Many of these effectors appeared to be involved in cell proliferation. Upon cytokine storm stimulation, there was a shift in cell populations; fibroblasts became more activated, and cardiomyocyte populations were drastically altered. This activated, proliferative signature hint that the cytokine storm may be inducing cell-fate changes in cardiac tissue, possibly predisposing to heart failure-like cardiac dysfunction.
Next, Mills and colleagues performed a drug screening of potential small molecules that could prevent cardiac dysfunction after TNFa and cytokine storm-driven diastolic dysfunction. The authors provide evidence that suggests a protective role for the CDK8 inhibitors SEL120-34A and BI-1347 in cardiac dysfunction. Having observed induced phosphorylation of the Bromo- and Extra-Terminal domain (BET) family member BRD4 following cytokine storm exposure, they evaluated the potential protective role of BET inhibitors against cytokine storm-derived cardiac dysfunction. Among them, INCB054329 was the most effective in preventing cytokine storm-induced diastolic dysfunction, and remarkably, it also prevented diastolic dysfunction caused by COVID-19 patient serum with high CTNI and BPN, but not with low levels of these cardiac-derived proteins.
In order to recapitulate the cytokine storm observed in humans following SARS-CoV-2 infection and translate these previous findings into a clinically relevant animal model, the authors utilized a murine model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation. The treatment with INCB054329 BRD inhibitor blocked the LPS-mediated inflammation and also restricted the LPS-induced fibrotic response of fibroblasts. Remarkably, the BRD inhibitor also extended the life of LPS-challenged mice. Overall, these data suggest that INCB054329 represents a potent, robust and promising small molecule BRD inhibitor for improving cardiac function and cytokine storm-mediated mortality.
Using 2D cultured human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes, the authors also indicated that INCB054329 protects cardiac cells against SARS-CoV-2 infection and sarcomere degradation. Owing to the fact that the BRD inhibitor reduced the expression of ACE2, the authors speculated that reduced viral infiltration could be the cause for diminished viral load and infection in response to INCB054329 treatment. These favourable findings suggest that pre-treatment with BRD inhibitors could protect patients’ hearts against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Why we chose this preprint and what we liked about it
Following on from our first prelight (https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.23879), which addressed the role of BRD4 inhibition on the reversion of activated cardiac fibroblasts in ischaemic and hypertrophic mouse injury models, the current preprint used a similar approach to treat the COVID-19-induced cytokine storm. Here, Mills and colleagues demonstrated that BRD4 inhibition prevented fibroblast activation and cardiac dysfunction in response to the cytokine storm, in their hCO model, arriving at similar conclusions to the study from the Haldar and Srivastava laboratories10. The comprehensive efficacy of BRD4 inhibition in treating cardiac dysfunction in these two studies makes the recent preprints highly complementary and extremely exciting for the field.
This preprint utilises state-of-the-art techniques in conjunction with the unique Heart Dyno system developed in the Hudson lab, to address the critical question of how heart function can be affected directly and indirectly by SARS-CoV-2 infection. They have been able to elegantly and quickly identify a combination of cytokines with profound effects on the function of their heart tissues, as well as establish effective potential therapeutics to ameliorate cytokine-induced cardiac dysfunction. The assay-throughput and functional similarity of the hCO system to the adult heart are huge strengths of this study. As such, this preprint represents an important step in furthering our understanding of the mechanisms of COVID-19 in the heart.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/prelights.25933
Read preprintSign up to customise the site to your preferences and to receive alerts
Register hereAlso in the bioengineering category:
A Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) - Strategy to Target EGFRVIII-Mutated Glioblastoma Cells via Macrophages
Dina Kabbara
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages modify development of human kidney organoids
Theodora Stougiannou
Matrix viscoelasticity regulates dendritic cell migration and immune priming
Roberto Amadio
Also in the bioinformatics category:
The lipidomic architecture of the mouse brain
CRM UoE Journal Club et al.
Kosmos: An AI Scientist for Autonomous Discovery
Roberto Amadio et al.
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the clinical trials category:
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
Identifiability-Guided Assessment of Digital Twins in Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Research and Care
My Nguyen
MCL1 may not mediate chemoresistance
Kanishka Parashar
Also in the genomics category:
Microbial Feast or Famine: dietary carbohydrate composition and gut microbiota metabolic function
Jasmine Talevi
A high-coverage genome from a 200,000-year-old Denisovan
AND
A global map for introgressed structural variation and selection in humans
Siddharth Singh
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Also in the molecular biology category:
A drought stress-induced MYB transcription factor regulates pavement cell shape in leaves of European aspen (Populus tremula)
Jeny Jose
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
Junctional Heterogeneity Shapes Epithelial Morphospace
Bhaval Parmar
Also in the pharmacology and toxicology category:
Snake venom metalloproteinases are predominantly responsible for the cytotoxic effects of certain African viper venoms
Daniel Osorno Valencia
Cryo-EM reveals multiple mechanisms of ribosome inhibition by doxycycline
Leonie Brüne
In vitro pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the diarylquinoline TBAJ-587 and its metabolites against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Zhang-He Goh
Also in the physiology category:
Resilience to cardiac aging in Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus
Theodora Stougiannou
Trade-offs between surviving and thriving: A careful balance of physiological limitations and reproductive effort under thermal stress
Tshepiso Majelantle
Imaging cellular activity simultaneously across all organs of a vertebrate reveals body-wide circuits
Muhammed Sinan Malik
Also in the systems biology category:
Human single-cell atlas analysis reveals heterogeneous endothelial signaling
Charis Qi
Longitudinal single cell RNA-sequencing reveals evolution of micro- and macro-states in chronic myeloid leukemia
Charis Qi
Environmental and Maternal Imprints on Infant Gut Metabolic Programming
Siddharth Singh
preLists in the bioengineering category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
3D Gastruloids
A curated list of preprints related to Gastruloids (in vitro models of early development obtained by 3D aggregation of embryonic cells). Updated until July 2021.
| List by | Paul Gerald L. Sanchez and Stefano Vianello |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
Advances in microscopy
This preList highlights exciting unpublished preprint articles describing advances in microscopy with a focus on light-sheet microscopy.
| List by | Stephan Daetwyler |
Also in the bioinformatics category:
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the clinical trials category:
Also in the genomics category:
November in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology have nominated a few developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints posted in November they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Concise preprint highlights, prepared by the preLighter community – a quick way to spot upcoming trends, new methods and fresh ideas.
| List by | Aline Grata et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
March in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) cancer biology 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics and genomics 6) other
| List by | Girish Kale et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Early 2025 preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) bioinformatics 2) epigenetics 3) gene regulation 4) genomics 5) transcriptomics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
End-of-year preprints – the genetics & genomics edition
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of genetics and genomics have worked together to create this preprint reading list. Categories include: 1) genomics 2) bioinformatics 3) gene regulation 4) epigenetics
| List by | Chee Kiang Ewe et al. |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Semmelweis Symposium 2022: 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 'Semmelweis Symposium 2022' (7-9 November), organised around the 40th anniversary of international medical education at Semmelweis University covering a wide range of topics.
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
20th “Genetics Workshops in Hungary”, Szeged (25th, September)
In this annual conference, Hungarian geneticists, biochemists and biotechnologists presented their works. Link: http://group.szbk.u-szeged.hu/minikonf/archive/prg2021.pdf
| List by | Nándor Lipták |
EMBL Conference: From functional genomics to systems biology
Preprints presented at the virtual EMBL conference "from functional genomics and systems biology", 16-19 November 2020
| List by | Jesus Victorino |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
Zebrafish immunology
A compilation of cutting-edge research that uses the zebrafish as a model system to elucidate novel immunological mechanisms in health and disease.
| List by | Shikha Nayar |
Also in the molecular biology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
October in preprints – Cell biology edition
Different preLighters, with expertise across cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, most picks fall under (1) Cell organelles and organisation, followed by (2) Mechanosignaling and mechanotransduction, (3) Cell cycle and division and (4) Cell migration
| List by | Matthew Davies et al. |
September in preprints – Cell biology edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading list. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation, (2) Cell signalling and mechanosensing, (3) Cell metabolism, (4) Cell cycle and division, (5) Cell migration
| List by | Sristilekha Nath et al. |
June in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: (1) Cell organelles and organisation (2) Cell signaling and mechanosensation (3) Genetics/gene expression (4) Biochemistry (5) Cytoskeleton
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
May in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) Biochemistry/metabolism 2) Cancer cell Biology 3) Cell adhesion, migration and cytoskeleton 4) Cell organelles and organisation 5) Cell signalling and 6) Genetics
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Keystone Symposium – Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate
This preList contains preprints discussed during the Metabolic and Nutritional Control of Development and Cell Fate Keystone Symposia. This conference was organized by Lydia Finley and Ralph J. DeBerardinis and held in the Wylie Center and Tupper Manor at Endicott College, Beverly, MA, United States from May 7th to 9th 2025. This meeting marked the first in-person gathering of leading researchers exploring how metabolism influences development, including processes like cell fate, tissue patterning, and organ function, through nutrient availability and metabolic regulation. By integrating modern metabolic tools with genetic and epidemiological insights across model organisms, this event highlighted key mechanisms and identified open questions to advance the emerging field of developmental metabolism.
| List by | Virginia Savy, Martin Estermann |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
February in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry and cell metabolism 2) cell organelles and organisation 3) cell signalling, migration and mechanosensing
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
Community-driven preList – Immunology
In this community-driven preList, a group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of immunology have worked together to create this preprint reading list.
| List by | Felipe Del Valle Batalla et al. |
January in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell migration 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) genetics/gene expression
| List by | Barbora Knotkova et al. |
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting
This preList features preprints that were discussed and presented during the BSCB-Biochemical Society 2024 Cell Migration meeting in Birmingham, UK in April 2024. Kindly put together by Sara Morais da Silva, Reviews Editor at Journal of Cell Science.
| List by | Reinier Prosee |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
CSHL 87th Symposium: Stem Cells
Preprints mentioned by speakers at the #CSHLsymp23
| List by | Alex Eve |
9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination
This preList contains preprints discussed during the 9th International Symposium on the Biology of Vertebrate Sex Determination. This conference was held in Kona, Hawaii from April 17th to 21st 2023.
| List by | Martin Estermann |
Alumni picks – preLights 5th Birthday
This preList contains preprints that were picked and highlighted by preLights Alumni - an initiative that was set up to mark preLights 5th birthday. More entries will follow throughout February and March 2023.
| List by | Sergio Menchero et al. |
CellBio 2022 – An ASCB/EMBO Meeting
This preLists features preprints that were discussed and presented during the CellBio 2022 meeting in Washington, DC in December 2022.
| List by | Nadja Hümpfer et al. |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
ECFG15 – Fungal biology
Preprints presented at 15th European Conference on Fungal Genetics 17-20 February 2020 Rome
| List by | Hiral Shah |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
Lung Disease and Regeneration
This preprint list compiles highlights from the field of lung biology.
| List by | Rob Hynds |
MitoList
This list of preprints is focused on work expanding our knowledge on mitochondria in any organism, tissue or cell type, from the normal biology to the pathology.
| List by | Sandra Franco Iborra |
Also in the pharmacology and toxicology category:
SciELO preprints – From 2025 onwards
SciELO has become a cornerstone of open, multilingual scholarly communication across Latin America. Its preprint server, SciELO preprints, is expanding the global reach of preprinted research from the region (for more information, see our interview with Carolina Tanigushi). This preList brings together biological, English language SciELO preprints to help readers discover emerging work from the Global South. By highlighting these preprints in one place, we aim to support visibility, encourage early feedback, and showcase the vibrant research communities contributing to SciELO’s open science ecosystem.
| List by | Carolina Tanigushi |
April in preprints – the CellBio edition
A group of preLighters, with expertise in different areas of cell biology, have worked together to create this preprint reading lists for researchers with an interest in cell biology. This month, categories include: 1) biochemistry/metabolism 2) cell cycle and division 3) cell organelles and organisation 4) cell signalling and mechanosensing 5) (epi)genetics
| List by | Vibha SINGH et al. |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
COVID-19 / SARS-CoV-2 preprints
List of important preprints dealing with the ongoing coronavirus outbreak. See http://covidpreprints.com for additional resources and timeline, and https://connect.biorxiv.org/relate/content/181 for full list of bioRxiv and medRxiv preprints on this topic
| List by | Dey Lab, Zhang-He Goh |
1
Drug use in special populations
Any drugs that are being used in special populations: Patients with liver and kidney failure, in paediatrics, in geriatrics, and in pregnant or lactating patients. Includes the discovery of factors that could potentially affect drug use in these special populations.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Toxicology of toxicants, existing therapeutics, and investigational drugs
Preprints that describe the toxicology of environmental pollutants and existing and upcoming drugs. Includes both toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics, as well as technological improvements that will help in the characterisation of this field.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Antimicrobials: Discovery, clinical use, and development of resistance
Preprints that describe the discovery of new antimicrobials and any improvements made regarding their clinical use. Includes preprints that detail the factors affecting antimicrobial selection and the development of antimicrobial resistance.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Anticancer agents: Discovery and clinical use
Preprints that describe the discovery of anticancer agents and their clinical use. Includes both small molecules and macromolecules like biologics.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Advances in Drug Delivery
Advances in formulation technology or targeted delivery methods that describe or develop the distribution of small molecules or large macromolecules to specific parts of the body.
| List by | Zhang-He Goh |
Also in the physiology category:
October in preprints – DevBio & Stem cell biology
Each month, preLighters with expertise across developmental and stem cell biology nominate a few recent developmental and stem cell biology (and related) preprints they’re excited about and explain in a single paragraph why. Short, snappy picks from working scientists — a quick way to spot fresh ideas, bold methods and papers worth reading in full. These preprints can all be found in the October preprint list published on the Node.
| List by | Deevitha Balasubramanian et al. |
Biologists @ 100 conference preList
This preList aims to capture all preprints being discussed at the Biologists @100 conference in Liverpool, UK, either as part of the poster sessions or the (flash/short/full-length) talks.
| List by | Reinier Prosee, Jonathan Townson |
Fibroblasts
The advances in fibroblast biology preList explores the recent discoveries and preprints of the fibroblast world. Get ready to immerse yourself with this list created for fibroblasts aficionados and lovers, and beyond. Here, my goal is to include preprints of fibroblast biology, heterogeneity, fate, extracellular matrix, behavior, topography, single-cell atlases, spatial transcriptomics, and their matrix!
| List by | Osvaldo Contreras |
FENS 2020
A collection of preprints presented during the virtual meeting of the Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) in 2020
| List by | Ana Dorrego-Rivas |
TAGC 2020
Preprints recently presented at the virtual Allied Genetics Conference, April 22-26, 2020. #TAGC20
| List by | Maiko Kitaoka et al. |
Autophagy
Preprints on autophagy and lysosomal degradation and its role in neurodegeneration and disease. Includes molecular mechanisms, upstream signalling and regulation as well as studies on pharmaceutical interventions to upregulate the process.
| List by | Sandra Malmgren Hill |
Cellular metabolism
A curated list of preprints related to cellular metabolism at Biorxiv by Pablo Ranea Robles from the Prelights community. Special interest on lipid metabolism, peroxisomes and mitochondria.
| List by | Pablo Ranea Robles |
Also in the systems biology category:
2024 Hypothalamus GRC
This 2024 Hypothalamus GRC (Gordon Research Conference) preList offers an overview of cutting-edge research focused on the hypothalamus, a critical brain region involved in regulating homeostasis, behavior, and neuroendocrine functions. The studies included cover a range of topics, including neural circuits, molecular mechanisms, and the role of the hypothalamus in health and disease. This collection highlights some of the latest advances in understanding hypothalamic function, with potential implications for treating disorders such as obesity, stress, and metabolic diseases.
| List by | Nathalie Krauth |
‘In preprints’ from Development 2022-2023
A list of the preprints featured in Development's 'In preprints' articles between 2022-2023
| List by | Alex Eve, Katherine Brown |
EMBL Synthetic Morphogenesis: From Gene Circuits to Tissue Architecture (2021)
A list of preprints mentioned at the #EESmorphoG virtual meeting in 2021.
| List by | Alex Eve |
Single Cell Biology 2020
A list of preprints mentioned at the Wellcome Genome Campus Single Cell Biology 2020 meeting.
| List by | Alex Eve |
ASCB EMBO Annual Meeting 2019
A collection of preprints presented at the 2019 ASCB EMBO Meeting in Washington, DC (December 7-11)
| List by | Madhuja Samaddar et al. |
EMBL Seeing is Believing – Imaging the Molecular Processes of Life
Preprints discussed at the 2019 edition of Seeing is Believing, at EMBL Heidelberg from the 9th-12th October 2019
| List by | Dey Lab |
Pattern formation during development
The aim of this preList is to integrate results about the mechanisms that govern patterning during development, from genes implicated in the processes to theoritical models of pattern formation in nature.
| List by | Alexa Sadier |











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)